Abstract
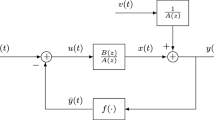
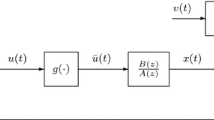
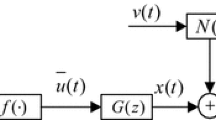
Two identification algorithms, an iterative gradient and a recursive stochastic gradient based, are developed for a Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX model, a linear dynamical block following a memoryless nonlinear block. The basic idea is to use the gradient search principle, to replace unmeasurable noise terms in the information vectors by their estimates, and to compute iteratively or recursively the noise estimates based on the obtained parameter estimates. Convergence analysis of the recursive stochastic gradient algorithm indicates that the parameter estimation error consistently converges to zero under certain conditions. The simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narendra, K. S. and Gallman, P. G., ‘An iterative method for the identification of nonlinear systems using a Hammerstein model’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 11(3), 1966, 546–550.
Stoica, P., ‘On the convergence of an iterative algorithm used for Hammerstein system identification’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 26(4), 1981, 967–969.
Rangan, S., Wolodkin, G., and Poolla, K., ‘Identification methods for Hammerstein systems’, in Proceedings of the 34th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, New Orleans, LA, 1995, pp. 697–702.
Haist, N. D., Chang, F., and Luus, R., ‘Nonlinear identification in the presence of correlated noise using a Hammerstein model’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 18(5), 1973, 553–555.
Cerone, V. and Regruto, D., ‘Parameter bounds for discrete-time Hammerstein models with bounded output errors’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 48(10), 2003, 1855–1860.
Bai, E. W., ‘An optimal two-stage identification algorithm for Hammerstein–Wiener nonlinear systems’, Automatica 34(3), 1998, 333–338.
Bai, E. W., ‘Identification of linear systems with hard input nonlinearities of known structure’, Automatica 38(5), 2002, 853–860.
Bai, E. W., ‘A blind approach to the Hammerstein–Wiener model identification’, Automatica 38(6), 2002, 967–979.
Wigren, T. and Nordsjö, A. E., ‘Compensation of the RLS algorithm for output nonlinearities’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 44(10), 1999, 1913–1918.
Chang, F. and Luus, R., ‘A noniterative method for identification using Hammerstein model’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 16(5), 1971, 464–468.
Nešić, D. and Mareels, I. M. Y., ‘Dead-beat control of simple Hammerstein models’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 43(8), 1998, 1184–1188.
Ding, F. and Chen, T., ‘Identification of Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems’, Automatica 41(9), 2005, 1479–1489.
Bai, E. W., ‘Decoupling the linear and nonlinear parts in Hammerstein model identification’, Automatica 40(4), 2004, 671–676.
Pawlak, M., ‘On the series expansion approach to the identification of Hammerstein system’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 36(6), 1991, 763–767.
Ninness, B. and Gibson, S., ‘Quantifying the accuracy of Hammerstein model estimation’, Automatica 38(12), 2002, 2037–2051.
Vörös, J., ‘Recursive identification of Hammerstein systems with discontinuous nonlinearities containing dead-zones’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 48(12), 2003, 2203–2206.
Gallman, P. G., ‘A comparison of two Hammerstein model identification algorithms’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 21(1), 1976, 124–126.
Ljung, L., System Identification: Theory for the User, 2nd edn., Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1999.
Goodwin, G. C. and Sin, K. S., Adaptive Filtering, Prediction and Control, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1984.
Ding, F. and Chen, T., ‘Combined parameter and output estimation of dual-rate systems using an auxiliary model’, Automatica 40(10), 2004, 1739–1748.
Ding, F. and Chen, T., ‘Hierarchical gradient-based identification of multivariable discrete-time systems’, Automatica 41(2), 2005, 315–325.
Ding, F., Shi, Y., and Chen, T., ‘Performance analysis of estimation algorithms of non-stationary ARMA processes’, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, in press.
Lai, T. L. and Wei, C. Z., ‘Extended least squares and their applications to adaptive control and prediction in linear systems’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 31(10), 1986, 898–906.
Guo, L. and Chen, H. F., ‘The {Å}ström–Wittenmark self-tuning regulator revisited and ELS-based adaptive trackers’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 36(7), 1991, 802–812.
Ren, W. and Kumar, P. K., ‘Stochastic adaptive prediction and model reference control’, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 39(10), 1994, 2047–2060.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11071-006-9159-0.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, F., Shi, Y. & Chen, T. Gradient-Based Identification Methods for Hammerstein Nonlinear ARMAX Models. Nonlinear Dyn 45, 31–43 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-005-1850-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-005-1850-z