Abstract
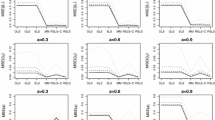
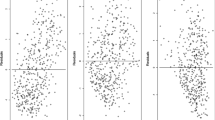
We investigate the model selection problem for nonlinear autoregressive with exogenous variables models estimated using the weighted least squares (WLS) method. Because WLS changes the statistical property of data under study and violates the assumptions imposed on the well-developed model evaluation and selection methods (e.g. Akaike’s information criterion, Schwarz’s Bayesian information criterion, and the error reduction ratio based methods), therefore, new approaches should be investigated. In this research, an information criterion based method and two l 1-norm regularization methods are taken into consideration: (a) in the former method, for models estimated using WLS, we first derive an information criterion in terms of the generalized information criterion (GIC, proposed by Konishi and Kitagawa in Biometrica 83(4):875–890, 1996), which is a theoretical framework for the analysis and extension of information criteria via a statistical functional approach. Then we develop a robust selection procedure by combining the GIC-based forward stepwise method with Subsampling; (b) in the latter two methods, we employ the l 1-norm regularization methods, including Lasso and adaptive Lasso, to select models estimated with WLS. Finally, a numerical example is given to test and compare the performance of the three methods.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rugh, W.: Nonlinear System Theory. John Hopkins Univ. Press, London (1981)
Bai, E.: A blind approach to the Hammerstein–Wiener model identification. Automatica 38(6), 967–979 (2002)
Hagenblad, A., Ljung, L., Wills, A.: Maximum likelihood identification of wiener models. Automatica 44(11), 2697–2705 (2008)
Liu, Y., Bai, E.: Iterative identification of Hammerstein systems. Automatica 43(2), 346–354 (2007)
Paduart, J., Lauwers, L., Swevers, J., Smolders, K., Schoukens, J., Pintelon, R.: Identification of nonlinear systems using polynomial nonlinear state space models. Automatica 46(4), 647–656 (2010)
Chen, S., Billings, S.A., Cowan, C.F.N., Grant, P.M.: Practical identification of NARMAX models using radial basis functions. Int. J. Control 52(6), 1327–1350 (1990)
Chiras, N., Evans, C., Rees, D.: Nonlinear gas turbine modeling using NARMAX structures. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 50(4), 893–898 (2001)
Leontaritis, I.J., Billings, S.A.: Input–output parametric models for non-linear systems—Part I: deterministic non-linear systems. Int. J. Control 41(2), 303–328 (1985)
Chen, S., Wang, X.X., Harris, C.J.: NARX-based nonlinear system identification using orthogonal least squares basis hunting. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 16(1), 78–84 (2008)
De Nicolao, G., Ferrari Trecate, G.: Consistent identification of NARX models via regularization networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 44(11), 2045–2049 (1999)
Kyoung, K.A., Ho, P.H.A.: Inverse double NARX fuzzy modeling for system identification. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 15(1), 136–148 (2010)
Wei, H.L., Billings, S.A.: A unified wavelet-based modelling framework for non-linear system identification: the WANARX. Int. J. Control 77(4), 351–366 (2004)
Wei, H.L., Billings, S.A.: Improved model identification for non-linear systems using a random subsampling and multifold modelling (RSMM) approach. Int. J. Control 82(1), 27–42 (2009)
Wei, H.L., Billings, S.A.: Improved parameter estimates for non-linear dynamical models using a bootstrap method. Int. J. Control 82(11), 1991–2001 (2009)
Billings, S.A., Wei, H.L.: A new class of wavelet networks for nonlinear system identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 16(4), 862–874 (2005)
Billings, S.A., Wei, H.L.: The wavelet-NARMAX representation: a hybrid model structure combining polynomial models with multiresolution wavelet decompositions. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 36(3), 137–152 (2005)
Piroddi, L., Spinelli, W.: An identification algorithm for polynomial NARX models based on simulation error minimization. Int. J. Control 76(17), 1767–1781
Sjöberg, J., Zhang, Q., Ljung, L., Benveniste, A., Deylon, B., Glorennec, P.Y., Hjalmarsson, H., Juditsky, A.: Non-linear black-box modelling in system identification: a unified overview. Automatica 31(12), 1691–1724 (1995)
Akaike, H.: A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19(6), 716–723 (1974)
Schwarz, G.: Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 6(2), 461–464 (1978)
Billings, S.A., Chen, S., Korenberg, M.J.: Identification of MIMO non-linear system using a forward-regression orthogonal estimator. Int. J. Control 49(6), 2157–2189 (1989)
Bai, E.: A random least-trimmed-squares identification algorithm. Automatica 39(9), 1651–1659 (2003)
Ljung, L.: System Identification: Theory for the User, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, New York (1999)
Konishi, S., Kitagawa, G.: Generalised information criteria in model selection. Biometrika 83(4), 875–890 (1996)
Konishi, S., Kitagawa, G.: Information Criteria and Statistical Modeling. Springer, New York (2008)
Taniguchi, M., Hirukawa, J.: Generalized information criterion. J. Time Ser. Anal. 33(2), 286–297 (2012)
Nishii, R.: Asymptotic properties of criteria for selection of variables in multiple regression. Ann. Stat. 12(2), 758–765 (1984)
Qin, N., Nishii, R.: Selection of ARX models estimated by the penalized weighted least squares method. Bull. Inform. Cybern. 42, 35–43 (2010)
Politis, D.N., Romano, J.P.: Large sample confidence regions based on subsamples under minimal assumptions. Ann. Stat. 22(4), 2031–2050 (1994)
Tibshirani, R.: Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
Zou, H.: The adaptive Lasso and its Oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101(476), 1418–1429 (2006)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning—Data Mining Inference, and Prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2009)
Li, K., Peng, J.X., Bai, E.: A two-stage algorithm for identification of nonlinear dynamic systems. Automatica 42(7), 1189–1197 (2006)
Garatti, S., Bitead, R.R.: On resampling and uncertainty estimation in linear system identification. Automatica 46(55), 785–795 (2010)
Efron, B., Hastie, T., Johnstone, I., Tibshirni, R.: Least angle regression. Ann. Stat. 32(2), 407–499 (2004)
Fu, U.: Penalized regressions: the bridge versus the Lasso. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 7(3), 397–416 (1998)
Wang, H., Li, G., Tsai, C.L.: Regression coefficient and autoregressive order shrinkage and selection via LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 69(1), 63–78 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their deepest gratitude to the two reviewers for their constructive comments and kind suggestions. We also thank Professor Wakayama, who is the director of Institute of Mathematics for Industry at Kyushu University, for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, P., Nishii, R. & Yang, ZJ. Selection of NARX models estimated using weighted least squares method via GIC-based method and l 1-norm regularization methods. Nonlinear Dyn 70, 1831–1846 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0576-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0576-y