Abstract
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) is a Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channel that is involved in the development of neuropathic pain. P2X7 receptor (P2X7) belongs to a class of ATP-gated nonselective cation channels that plays an important role in neuropathic pain. Nevertheless, little is known about the interaction between them for neuropathic pain. In this paper, we investigated role of TRPV4-P2X7 pathway in neuropathic pain. We evaluated the effect of TRPV4-P2X7 pathway on neuropathic pain in a chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) (hereafter termed CCD) model. We analyzed the effect of P2X7 on mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia mediated by TRPV4 in CCD. Furthermore, we assessed the effect of TRPV4 on the expression of P2X7 and the release of IL-1β and IL-6 in DRG after CCD. We found that intraperitoneal injection of TRPV4 agonist GSK-1016790A led to a significant increase of mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in CCD, which was partially suppressed by P2X7 blockade with antagonist Brilliant Blue G (BBG). Then, we further noticed that GSK-1016790A injection increased the P2X7 expression of CCD, which was decreased by TRPV4 blockade with antagonist RN-1734 and HC-067047. Furthermore, we also discovered that the expressions of IL-1β and IL-6 were upregulated by GSK-1016790A injection but reduced by RN-1734 and HC-067047. Our results provide evidence that P2X7 contributes to development of neuropathic pain mediated by TRPV4 in the CCD model, which may be the basis for treatment of neuropathic pain relief.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpaa M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, Treede RD (2011) A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 152:2204–2205
Moore C, Gupta R, Jordt SE, Chen Y, Liedtke WB (2018) Regulation of pain and Itch by TRP channels. Neurosci Bull 34:120–142
Everaerts W, Nilius B, Owsianik G (2010) The vanilloid transient receptor potential channel TRPV4: from structure to disease. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 103:2–17
Costa R, Bicca MA, Manjavachi MN, Segat GC, Dias FC, Fernandes ES, Calixto JB (2018) Kinin receptors sensitize TRPV4 channel and induce mechanical hyperalgesia: relevance to paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. Mol Neurobiol 55:2150–2161
Materazzi S, Fusi C, Benemei S, Pedretti P, Patacchini R, Nilius B, Prenen J, Creminon C, Geppetti P, Nassini R (2012) TRPA1 and TRPV4 mediate paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice via a glutathione-sensitive mechanism. Pflugers Arch 463:561–569
Maqboul A, Elsadek B (2018) Expression profiles of TRPV1, TRPV4, TLR4 and ERK1/2 in the dorsal root ganglionic neurons of a cancer-induced neuropathy rat model. PeerJ 6:e4622
Ding XL, Wang YH, Ning LP, Zhang Y, Ge HY, Jiang H, Wang R, Yue SW (2010) Involvement of TRPV4-NO-cGMP-PKG pathways in the development of thermal hyperalgesia following chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion in rats. Behav Brain Res 208:194–201
Ning L, Wang C, Fan X, Ding X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, Yue S (2014) Role of colchicine-induced microtubule depolymerization in hyperalgesia via TRPV4 in rats with chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion. Neurol Res 36:70–78
Rahman M, Sun R, Mukherjee S, Nilius B, Janssen LJ (2018) TRPV4 stimulation releases ATP via pannexin channels in human pulmonary fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 59:87–95
Ohsaki A, Tanuma SI, Tsukimoto M (2018) TRPV4 channel-regulated ATP release contributes to gamma-irradiation-induced production of IL-6 and IL-8 in epidermal keratinocytes. Biol Pharm Bull 41:1620–1626
Bonvini SJ, Birrell MA, Grace MS, Maher SA, Adcock JJ, Wortley MA, Dubuis E, Ching YM, Ford AP, Shala F, Miralpeix M, Tarrason G, Smith JA, Belvisi MG (2016) Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 and airway sensory afferent activation: role of adenosine triphosphate. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138(249–261):e212
Burnstock G, Kennedy C (1985) Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol 16:433–440
Kolachala VL, Bajaj R, Chalasani M, Sitaraman SV (2008) Purinergic receptors in gastrointestinal inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G401-410
Kennedy C, Burnstock G (1985) ATP produces vasodilation via P1 purinoceptors and vasoconstriction via P2 purinoceptors in the isolated rabbit central ear artery. Blood Vessels 22:145–155
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G (1994) Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors? Pharmacol Ther 64:445–475
Burnstock G (2016) Purinergic mechanisms and pain. Adv Pharmacol 75:91–137
Burnstock G (2013) Purinergic mechanisms and pain–an update. Eur J Pharmacol 716:24–40
Zou L, Gong Y, Liu S, Liang S (2019) Natural compounds acting at P2 receptors alleviate peripheral neuropathy. Brain Res Bull 151:125–131
Liu PY, Lee IH, Tan PH, Wang YP, Tsai CF, Lin HC, Lee FY, Lu CL (2015) P2X7 receptor mediates spinal microglia activation of visceral hyperalgesia in a rat model of chronic pancreatitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 1(710–720):e715
Xie J, Liu S, Wu B, Li G, Rao S, Zou L, Yi Z, Zhang C, Jia T, Zhao S, Schmalzing G, Hausmann R, Nie H, Li G, Liang S (2017) The protective effect of resveratrol in the transmission of neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X7 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Neurochem Int 103:24–35
Chu YX, Zhang Y, Zhang YQ, Zhao ZQ (2010) Involvement of microglial P2X7 receptors and downstream signaling pathways in long-term potentiation of spinal nociceptive responses. Brain Behav Immun 24:1176–1189
Thoppil RJ, Adapala RK, Cappelli HC, Kondeti V, Dudley AC, Gary Meszaros J, Paruchuri S, Thodeti CK (2015) TRPV4 channel activation selectively inhibits tumor endothelial cell proliferation. Sci Rep 5:14257
Mueller-Tribbensee SM, Karna M, Khalil M, Neurath MF, Reeh PW, Engel MA (2015) Differential contribution of TRPA1, TRPV4 and TRPM8 to colonic nociception in mice. PLoS ONE 10:e0128242
Everaerts W, Zhen X, Ghosh D, Vriens J, Gevaert T, Gilbert JP, Hayward NJ, McNamara CR, Xue F, Moran MM, Strassmaier T, Uykal E, Owsianik G, Vennekens R, De Ridder D, Nilius B, Fanger CM, Voets T (2010) Inhibition of the cation channel TRPV4 improves bladder function in mice and rats with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19084–19089
Rodriguez-Alvarez N, Jimenez-Mateos EM, Engel T, Quinlan S, Reschke CR, Conroy RM, Bhattacharya A, Boylan GB, Henshall DC (2017) Effects of P2X7 receptor antagonists on hypoxia-induced neonatal seizures in mice. Neuropharmacology 116:351–363
Sakamoto K, Endo K, Suzuki T, Fujimura K, Kurauchi Y, Mori A, Nakahara T, Ishii K (2015) P2X7 receptor antagonists protect against N-methyl-d-aspartic acid-induced neuronal injury in the rat retina. Eur J Pharmacol 756:52–58
Zhang Y, Wang YH, Ge HY, Arendt-Nielsen L, Wang R, Yue SW (2008) A transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 contributes to mechanical allodynia following chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion in rats. Neurosci Lett 432:222–227
Qu YJ, Jia L, Zhang X, Wei H, Yue SW (2016) MAPK pathways are involved in neuropathic pain in rats with chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2016:6153215
Kobayashi K, Yamanaka H, Noguchi K (2013) Expression of ATP receptors in the rat dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord. Anat Sci Int 88:10–16
Chen Y, Li G, Huang LY (2012) P2X7 receptors in satellite glial cells mediate high functional expression of P2X3 receptors in immature dorsal root ganglion neurons. Mol Pain 8:9
Hu SJ, Xing JL (1998) An experimental model for chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion produced by intervertebral foramen stenosis in the rat. Pain 77:15–23
Song XJ, Xu DS, Vizcarra C, Rupert RL (2003) Onset and recovery of hyperalgesia and hyperexcitability of sensory neurons following intervertebral foramen volume reduction and restoration. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 26:426–436
Ma C, Greenquist KW, Lamotte RH (2006) Inflammatory mediators enhance the excitability of chronically compressed dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol 95:2098–2107
Zhou J, Feng D, Zhang X, Xia C, Zhang Z, Kang J, Tan Z, Wu B (2019) Involvement of P2X7 receptors in satellite glial cells of dorsal root ganglia in the BmK I -induced pain model of rats. Gen Physiol Biophys 38:407–416
Chessell IP, Hatcher JP, Bountra C, Michel AD, Hughes JP, Green P, Egerton J, Murfin M, Richardson J, Peck WL, Grahames CB, Casula MA, Yiangou Y, Birch R, Anand P, Buell GN (2005) Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 114:386–396
Ji RR, Chamessian A, Zhang YQ (2016) Pain regulation by non-neuronal cells and inflammation. Science 354:572–577
Halassa MM, Fellin T, Haydon PG (2009) Tripartite synapses: roles for astrocytic purines in the control of synaptic physiology and behavior. Neuropharmacology 57:343–346
Koizumi S, Fujishita K, Inoue K (2005) Regulation of cell-to-cell communication mediated by astrocytic ATP in the CNS. Purinergic Signalling 1:211–217
Jasmin L, Vit JP, Bhargava A, Ohara PT (2010) Can satellite glial cells be therapeutic targets for pain control? Neuron Glia Biol 6:63–71
North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Lecca D, Ceruti S, Fumagalli M, Abbracchio MP (2012) Purinergic trophic signalling in glial cells: functional effects and modulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and death. Purinergic Signalling 8:539–557
Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang C, Huang LY (2007) Neuronal somatic ATP release triggers neuron-satellite glial cell communication in dorsal root ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:9864–9869
Mihara H, Boudaka A, Sugiyama T, Moriyama Y, Tominaga M (2011) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4)-dependent calcium influx and ATP release in mouse oesophageal keratinocytes. J Physiol 589:3471–3482
Turner RD, Birring SS (2019) Chronic cough: ATP, afferent pathways and hypersensitivity. Eur Respir Jl 54:1900889
Clark AK, Staniland AA, Marchand F, Kaan TK, McMahon SB, Malcangio M (2010) P2X7-dependent release of interleukin-1beta and nociception in the spinal cord following lipopolysaccharide. J Neurosci 30:573–582
Li J, Li X, Jiang X, Yang M, Yang R, Burnstock G, Xiang Z, Yuan H (2017) Microvesicles shed from microglia activated by the P2X7-p38 pathway are involved in neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats. Purinergic Signalling 13:13–26
Zhang J, Chu M (2019) Targeting of IL-6-relevant long noncoding RNA profiles in inflammatory and tumorous disease. Inflammation 42:1139–1146
Dubovy P, Brazda V, Klusakova I, Hradilova-Svizenska I (2013) Bilateral elevation of interleukin-6 protein and mRNA in both lumbar and cervical dorsal root ganglia following unilateral chronic compression injury of the sciatic nerve. J Neuroinflammation 10:55
Shieh CH, Heinrich A, Serchov T, van Calker D, Biber K (2014) P2X7-dependent, but differentially regulated release of IL-6, CCL2, and TNF-alpha in cultured mouse microglia. Glia 62:592–607
Di Virgilio F, Dal Ben D, Sarti AC, Giuliani AL, Falzoni S (2017) The P2X7 receptor in infection and inflammation. Immunity 47:15–31
Rabah Y, Rubino B, Moukarzel E, Agulhon C (2020) Characterization of transgenic mouse lines for selectively targeting satellite glial cells and macrophages in dorsal root ganglia. PLoS ONE 15:e0229475
Hu X, Liu Y, Wu J, Liu Y, Liu W, Chen J, Yang F (2020) Inhibition of P2X7R in the amygdala ameliorates symptoms of neuropathic pain after spared nerve injury in rats. Brain Behav Immun 88:507–514
Shi J, Jiang K, Li Z (2018) MiR-145 ameliorates neuropathic pain via inhibiting inflammatory responses and mTOR signaling pathway by targeting Akt3 in a rat model. Neurosci Res 134:10–17
Sluyter R (2017) The P2X7 Receptor. Adv Exp Med Biol 1051:17–53
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81401868, Liping Ning; Grant No. 81502148, Chuanwei Wang), the Shandong Province Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project (Grant No. 2017WS468, Liang Zhou), and the Teaching reform and research project of undergraduate education in Clinical Medicine College of Shandong University (Grant No. LCJY-72, Shaocan Tang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (TIF 4963 kb)
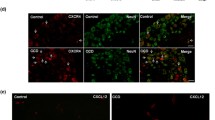
Confocal laser scanning micrographs of SGCs showing immunostaining for P2X7 (green; A) and GFAP (red; B) in CCD rats. C. Merged image showed a partial colocalization between P2X7 and GFAP. Scale bars=25um, n = 3 rats in each group.
Supplementary file2 (TIF 3475 kb)
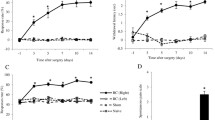
Role of TRPV4 antagonist in hyperalgesia of CCD rats. A: Effect of RN-1734 and HC-067047 on CCD-induced mechanical hyperalgesia. B: Effect of RN-1734 and HC-067047 on CCD-induced thermal hyperalgesia. **P < 0.01 compared with sham group. ##P < 0.01 compared with CCD+NS group. n = 6 rats in each group. CCD: chronic compression of the dorsal root ganglion; PWMT: paw withdrawal mechanical threshold; PWTL: paw withdrawal thermal latency.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Wang, C., Han, J. et al. Role of TRPV4-P2X7 Pathway in Neuropathic Pain in Rats with Chronic Compression of the Dorsal Root Ganglion. Neurochem Res 46, 2143–2153 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03352-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03352-8