Abstract
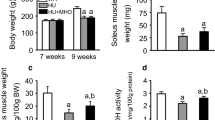
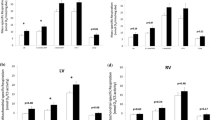
Rats with type 2 diabetes exhibit decreased oxidative capacity, such as reduced oxidative enzyme activity, low-intensity staining for oxidative enzymes in fibers, and no high-oxidative type IIA fibers, in the skeletal muscle, especially in the soleus muscle. In contrast, there are no data available concerning the oxidative capacity of spinal motoneurons innervating skeletal muscle of rats with type 2 diabetes. This study examined the oxidative capacity of motoneurons innervating the soleus muscle of non-obese rats with type 2 diabetes. In addition, this study examined the effects of mild hyperbaric oxygen at 1.25 atmospheres absolute with 36 % oxygen for 10 weeks on the oxidative capacity of motoneurons innervating the soleus muscle because mild hyperbaric oxygen improves the decreased oxidative capacity of the soleus muscle in non-obese rats with type 2 diabetes. Spinal motoneurons innervating the soleus muscle were identified using nuclear yellow, a retrograde fluorescent neuronal tracer. Thereafter, the cell body sizes and succinate dehydrogenase activity of identified motoneurons were analyzed. Decreased succinate dehydrogenase activity of small-sized alpha motoneurons innervating the soleus muscle was observed in rats with type 2 diabetes. The decreased succinate dehydrogenase activity of these motoneurons was improved by mild hyperbaric oxygen. Therefore, we concluded that rats with type 2 diabetes have decreased oxidative capacity in motoneurons innervating the soleus muscle and this decreased oxidative capacity is improved by mild hyperbaric oxygen.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATA:
-
Atmosphere absolute
- CSA:
-
Cross-sectional area
- GK:
-
Goto-Kakizaki
- HbA1c:
-
Glycosylate hemoglobin
- LETO:
-
Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka
- OD:
-
Optical density
- OLETF:
-
Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty
- SDH:
-
Succinate dehydrogenase
- WR:
-
Wistar
References
Yasuda K, Ishihara A, Adachi T, Shihara N, Seino Y, Tsuda K (2001) Growth-related changes in skeletal muscle fiber type and insulin resistance in diabetic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Acta Histochem Cytochem 34:371–382
Yasuda K, Nishikawa W, Iwanaka N, Nakamura E, Seino Y, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2002) Abnormality in fibre type distribution of soleus and plantaris muscles in non-obese diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29:1001–1008
Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, McNeill AM, Heiss G, Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Pankow JS (2008) Metabolic syndrome risk for cardiovascular disease and diabetes in the ARIC study. Int J Obes 32:S21–S24
Kelley DE, Goodpaster BH, Wing RR, Simoneau JA (1999) Skeletal muscle fatty acid metabolism in association with insulin resistance, obesity, and weight loss. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 277:1130–1141
Abdul-Ghani MA, DeFronzo RA (2010) Pathogenesis of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:476279. doi:10.1155/2010/476279
Ishihara A, Taguchi S, Araki H, Nishihira Y (1991) Retrograde neuronal labeling of motoneurons in the rat by fluorescent tracers, and quantitative analysis of oxidative enzyme activity in labeled neurons. Neurosci Lett 124:141–143
Ishihara A, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (1995) Succinate dehydrogenase activity and soma size of motoneurons innervating different portions of the rat tibialis anterior. Neuroscience 68:813–822
Tibbles PM, Edelsberg JS (1996) Hyperbaric-oxygen therapy. N Engl J Med 334:1642–1648
Leach RM, Rees PJ, Wilmshurst P (1998) ABC of oxygen: hyperbaric oxygen therapy. BMJ 317:1140–1143
Ishihara A, Nagatomo F, Fujino H, Kondo H (2014) Exposure to mild hyperbaric oxygen increases blood flow and resting energy expenditure but not oxidative stress. J Sci Res Rep 3:1886–1896
Matsumoto A, Okiura T, Morimatsu F, Ohira Y, Ishihara A (2007) Effects of hyperbaric exposure with high oxygen concentration on the physical activity of developing rats. Dev Neurosci 29:452–459
Nishizaka T, Nagatomo F, Fujino H, Nomura T, Sano T, Higuchi K, Takeda I, Ishihara A (2010) Hyperbaric oxygen exposure reduces age-related decrease in oxidative capacity of the tibialis anterior muscle in mice. Enzyme Res 2010:824763. doi:10.4061/2010/824763
Yasuda K, Aoki N, Adachi T, Tsujimoto G, Gu N, Matsunaga T, Kikuchi N, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2006) Hyperbaric exposure with high oxygen concentration inhibits growth-associated increase in the glucose level of diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Diabetes Obes Metab 8:714–715
Yasuda K, Adachi T, Gu N, Matsumoto A, Matsunaga T, Tsujimoto G, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2007) Effects of hyperbaric exposure with high oxygen concentration on glucose and insulin levels and skeletal muscle-fiber properties in diabetic rats. Muscle Nerve 35:337–343
Matsumoto A, Nagatomo F, Yasuda K, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2007) Hyperbaric exposure with high oxygen concentration improves altered fiber types in the plantaris muscle of diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Physiol Sci 57:133–136
Gu N, Nagatomo F, Fujino F, Takeda I, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2010) Hyperbaric oxygen exposure improves blood glucose level and muscle oxidative capacity in rats with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 12:125–133
Nagatomo F, Roy RR, Takahashi H, Edgerton VR, Ishihara A (2011) Effect of exposure to hyperbaric oxygen on diabetes-induced cataracts in mice. J Diabetes 3:301–308
Nagatomo F, Fujino H, Takeda I, Ishihara A (2010) Effects of hyperbaric oxygenation on blood pressure levels of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Hypertens 32:193–197
Nagatomo F, Gu N, Fujino H, Okiura T, Morimatsu F, Takeda I, Ishihara A (2010) Effects of exposure to hyperbaric oxygen on oxidative stress in rats with type II collagen-induced arthritis. Clin Exp Med 10:7–13
Nishizaka T, Nomura T, Sano T, Higuchi K, Nagatomo F, Ishihara A (2011) Hyperbaric oxygen improves UVB irradiation-induced melanin pigmentation and diminishes senile spot size. Skin Res Technol 17:332–338
Ishihara A, Kawano F, Ishioka N, Oishi H, Higashibata A, Shimazu T, Ohira Y (2003) Growth-related changes in cell body size and succinate dehydrogenase activity of spinal motoneurons innervating the rat soleus muscle. Int J Dev Neurosci 21:461–469
Ishihara A, Kawano F, Ishioka N, Oishi H, Higashibata A, Shimazu T, Ohira Y (2004) Effects of running exercise during recovery from hindlimb unloading on soleus muscle fibers and their spinal motoneurons in rats. Neurosci Res 48:119–127
Nagatomo F, Ishihara A, Ohira Y (2009) Effects of hindlimb unloading at early postnatal growth on cell body size in spinal motoneurons innervating soleus muscle of rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 27:21–26
Ishihara A, Hayashi S, Roy RR, Tamada Y, Yokoyama C, Ohira Y, Edgerton VR, Ibata Y (1997) Mitochondrial density of ventral horn neurons in the rat spinal cord. Acta Anat 160:248–253
Ishihara A, Hori A, Roy RR, Oishi Y, Talmadge RJ, Ohira Y, Kobayashi S, Edgerton VR (1997) Perineal muscles and their innervation: metabolic and functional significance of the motor unit. Acta Anat 159:156–166
Ishihara A, Ohira Y, Tanaka M, Nishikawa W, Ishioka N, Higashibata A, Izumi R, Shimazu T, Ibata Y (2001) Cell body size and succinate dehydrogenase activity of spinal motoneurons innervating the soleus muscle in mice, rats, and cats. Neurochem Res 26:1301–1304
Nagatomo F, Gu N, Fujino H, Takeda I, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2009) Skeletal muscle characteristics of rats with obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. J Atheroscler Thromb 16:576–585
Nagatomo F, Fujino H, Kondo H, Gu N, Takeda I, Ishioka N, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2011) PGC-1α mRNA level and oxidative capacity of the plantaris muscle in rats with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes. Acta Histochem Cytochem 44:73–80
Mårin P, Andersson B, Krotkiewski M, Björntorp P (1994) Muscle fiber composition and capillary density in women and men with NIDDM. Diabetes Care 17:382–386
Hickey MS, Carey JO, Azevedo JL, Houmard JA, Pories WJ, Israel RG, Dohm GL (1995) Skeletal muscle fiber composition is related to adiposity and in vitro glucose transport rate in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 268:453–457
Nyholm B, Qu Z, Kaal A, Pedersen SB, Gravholt CH, Andersen JL, Saltin B, Schmitz O (1997) Evidence of an increased number of type IIb muscle fibers in insulin-resistant first-degree relatives of patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 46:1822–1828
Gaster M, Staehr P, Beck-Nielsen H, Schrøder HD, Handberg A (2001) GLUT4 is reduced in slow muscle fibers of type 2 diabetic patients: is insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes a slow, type 1 fiber disease? Diabetes 50:1324–1329
Hennig R, Lømo T (1985) Firing patterns of motor units in normal rats. Nature 314:164–166
Nakatani T, Nakashima T, Kita T, Hirofuji C, Itoh K, Itoh M, Ishihara A (1999) Succinate dehydrogenase activities of fibers in the rat extensor digitorum longus, soleus, and cardiac muscles. Arch Histol Cytol 62:393–399
Nakatani T, Nakashima T, Kita T, Ishihara A (2003) Cell size and oxidative enzyme activity of type-identified fibers in rat hindlimb muscles: a review. Acta Histochem Cytochem 36:105–114
Yasuda K, Adachi T, Kikuchi N, Tsujimoto G, Aoki N, Tsuda K, Ishihara A (2006) Effects of running exercise on fibre-type distribution of soleus and plantaris muscles in diabetic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Diabetes Obes Metab 8:311–321
Ishihara A, Nagatomo F, Fujino H, Kondo H, Nojima K (2012) A threshold dose of heavy ion radiation that decreases the oxidative enzyme activity of spinal motoneurons in rats. Neurochem Res 37:387–393
Ishihara A, Ohira Y, Roy RR, Nagaoka S, Sekiguchi C, Hinds WE, Edgerton VR (1996) Influence of spaceflight on succinate dehydrogenase activity and soma size of rat ventral horn neurons. Acta Anat 157:303–308
Ishihara A, Ohira Y, Roy RR, Nagaoka S, Sekiguchi C, Hinds WE, Edgerton VR (2002) Succinate dehydrogenase activity in rat dorsolateral ventral horn motoneurons at L6 after spaceflight and recovery. J Gravit Physiol 9:39–48
Ishihara A, Nagatomo F, Fujino H, Kondo H, Ohira Y (2013) Decreased succinate dehydrogenase activity of gamma and alpha motoneurons in mouse spinal cords following 13 weeks of exposure to microgravity. Neurochem Res 38:2160–2167
Ishihara A, Ohira Y, Roy RR, Nagaoka S, Sekiguchi C, Hinds WE, Edgerton VR (2000) Comparison of the response of motoneurons innervating perineal and hind limb muscles to spaceflight and recovery. Muscle Nerve 23:753–762
Ishihara A, Yamashiro J, Matsumoto A, Higashibata A, Ishioka N, Shimazu T, Ohira Y (2006) Comparison of cell body size and oxidative enzyme activity in motoneurons between the cervical and lumbar segments in the rat spinal cord after spaceflight and recovery. Neurochem Res 31:411–415
Edgerton VR, Roy RR (1996) Neuromuscular adaptations to actual and simulated spaceflight. In: Fregly MJ, Blatteis CM (eds) Handbook of physiology. Section 4. Environmental physiology. III. The gravitational environment. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 721–763
Ishihara A, Fujino H, Nagatomo F, Takeda I, Ohira Y (2008) Gene expression levels of heat shock proteins in the soleus and plantaris muscles of rats after hindlimb suspension or spaceflight. J Physiol Sci 58:413–417
Ishihara A, Kawano F, Okiura T, Morimatsu F, Ohira Y (2005) Hyperbaric exposure with high oxygen concentration enhances oxidative capacity of neuromuscular units. Neurosci Res 52:146–152
Burke RE, Strick PL, Kanda K, Kim CC, Walmsley B (1977) Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 40:667–680
Burke RE, Dum RP, Fleshman JW, Glenn LL, Lev-Tov A, O’Donovan MJ, Pinter MJ (1982) An HRP study of the relation between cell size and motor unit type in cat ankle extensor motoneurons. J Comp Neurol 209:17–28
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grand-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takemura, A., Ishihara, A. Mild Hyperbaric Oxygen Improves Decreased Oxidative Capacity of Spinal Motoneurons Innervating the Soleus Muscle of Rats with Type 2 Diabetes. Neurochem Res 41, 2336–2344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1947-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1947-4