Abstract
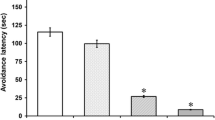
Substance P (SP) is a neuropeptide that plays an important role in inflammation, respiration, pain, aggression, anxiety, and learning and memory mainly through its high affinity neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R). The marginal division (MrD) is a pan-shaped subdivision in the caudomedial margin of the neostriatum in the mammalian brain and is known to be involved in learning and memory. We studied the expression of SP, NK1R and NK1R mRNA in the rat striatum by immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and in situ hybridization, and found that the levels of SP, NK1R protein and NK1R mRNA were high in the cell bodies, fibers and terminals of neurons in the neostriatum, especially in the MrD. Knocking down NK1R activity in the MrD by using an antisense oligonucleotide against NK1R mRNA inhibited learning and memory in a Y-maze behavioral test. Our results show that NK1R mediates the role of SP in the MrD in learning and memory.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Severini C, Improta G, Falconieri-Erspamer G et al (2002) The tachykinin peptide family. Pharmacol Rev 54:285–322
Carvalho MC, Masson S, Brandao ML et al (2008) Anxiolytic like effects of substance P administration into the dorsal, but not ventral, hippocampus and its influence on serotonin. Peptides 29:1191–1200
Hasenöhrl RU, De Souza-Silva MA, Nikolaus S (2000) Substance P and its role in neural mechanisms governing learning, anxiety and functional recovery. Neuropeptides 34:272–280
Langosch JM, Kupferschmid S, Heinen M et al (2005) Effects of substance P and its antagonist L-733060 on long term potentiation in guinea pig hippocampal slices. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 29:315–319
Mengual E, Chan J, Lane D et al (2008) Neurokinin-1 receptors in cholinergic neurons of the rat ventral pallidum have a predominantly dendritic distribution that is affected by apomorphine when combined with startle-evoking auditory stimulation. Neuroscience 151:711–724
Singerwald N, Chicchi G, Thurner C et al (2008) Modulation of basal and stress-induced amygdaleoid substance P release by the potent and selective NK1 receptor antagonist L-822429. J Neurochem 106:2476–2488
Graybiel AM, Ragsdale CW (1978) Histochemically distinct compartments in the striatum of human, monkeys, and cat demonstrated by acetylthiocholinesterase staining. PNAS 75:5723–5726
Gerfen CR, Sawchenko PE (1984) An anterograde neuroanatomical tracing method that shows the detailed morphology of neurons, their axons and terminals: immunohistochemical localization of an axonally transported plant lectin, Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L). Brain Res 290:219–238
Gerfen CR (1989) The neostriatal mosaic: striatal patch-matrix organization is related to cortical lamination. Science 246:385–388
Shu SY, Penny GR, Peterson GM (1988) The ‘marginal division’: a new subdivision in the neostriatum of the rat. J Chem Neuroanat 1:147–163
Shu SY, Bao XM, Zhang C et al (2000) A new subdivision, marginal division, in the neostriatum of the monkey brain. Neurochem Res 25:231–237
Zeng JX, Shu SY, Bao XM et al (1999) Properties of acetylcholine receptor ion channels in the acutely dissociated neurons of the marginal division in the rat striatum. Neurochem Res 24:1573–1576
Shu SY (2003) Marginal division of neostriatum: a subcortical memory center. J Biomed Sci 10:14–29
Shu SY, Bao XM, Ning Q et al (2003) New component of the limbic system: marginal division of the neostriatum that links the limbic system to the basal nucleus of Meynert. J Neurosci Res 71:751–757
Heimer L, Alheid GF (1991) Piecing together the puzzle of basal forebrain anatomy. In: Napier TC, Kalivas PW, Hanin I (eds) The basal forebrain. Plenum press, New York, pp 1–42
Heimer L, Zahm DS, Alheid GF (1995) Basal ganglia. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, New York, pp 579–628
Rosin DL, Talley EM, Lee A (1996) Distribution of α2C-adrenergic receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 372:135–165
Schoen SW, Graybiel AM (1993) Species-specific patterns of glycoprotein expression in the developing rodent caudoputamen: association of 5′-nucleotidase activity with dopamine islands and striosomes in rat, but with extrastriosomal matrix in mouse. J Comp Neurol 333:578–596
Chudler EH, Sugiyama K, Dong WK (1993) Nociceptive responses in the neostriatum and globus pallidus of the anesthetized rat. J Neurophysiol 69:1890–1903
Shu SY, Ju G, Fan LZ (1988) The glucose oxidase-DAB-nickel method in peroxidase histochemistry of the nervous system. Neurosci Lett 85:169–171
Shu SY, Bao XM (1991) The stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. People’s Medical Publishing House, Bei Jing
Fletcher PJ (1989) Tryptamine impairs the acquisition of a one-way active avoidance task. Pharmacol Biochem Be 32:317–321
Dang MT, Yokoi F, Yin HH (2006) Disrupted motor learning and long-term synaptic plasticity in mice lacking NMDAR1 in the striatum. PNAS 103:15254–15259
Dahlin E, Neely AS, Larsson A (2008) Transfer of learning after updating training mediated by the striatum. Science 320:1510–1512
Shu SY, Bao XM, Zhang X (1991) Ultrastructural characteristics of substance P-immunoreactive terminals in marginal division of rat striatum. Chin Med J (Engl) 104:887–896
Huston JP, Oitzl MS (1989) The relationship between reinforcement and memory: parallels in the rewarding and mnemonic effects of the neuropeptide substance P. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 13:171–180
Kertesa E, Lászlób K, Bertab B et al (2009) Effects of substance P microinjections into the globus pallidus and central nucleus of amygdala on passive avoidance learning in rats. Behav Brain Res 198:397–403
Kertesa E, Lászlób K, Bertab B et al (2010) Positive reinforcing effects of substance P in the rat globus pallidus revealed by conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 215:152–155
Huston JP, Hasenöhrl RU (1995) The role of neuropeptides in learning: focus on the neurokinin substance P. Behav Brain Res 66:117–127
Taufiq AM, Fujii S, Yamazaki Y et al (2005) Involvement of IP3 receptors in LTP and LTD induction in guinea pig hippocampal CA1 neurons. Learn Mem 12:594–600
Myöhänen TT, Venäläinen JI, Garcia-Horsman JA et al (2008) Spatial association of prolyl oligopeptidase, inositol 1, 4, 5-triphosphate type 1 receptor, substance P and its neurokinin-1 receptor in the rat brain: an immunohistochemical colocalization study. Neuroscience 153:1177–1189
Acknowledgments
This project was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30600797 and No. 30873238).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Xm., Shu, S.Y., Zeng, Cc. et al. The Role of Substance P in the Marginal Division of the Neostriatum in Learning and Memory is Mediated Through the Neurokinin 1 Receptor in Rats. Neurochem Res 36, 1896–1902 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0511-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0511-5