Abstract
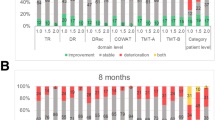
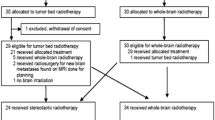
Intraoperative permanent Cesium-131 (Cs-131) brachytherapy can provide a viable alternative to WBRT with excellent response rates and minimal toxicity. This study reports the results of the prospective trial of the impact of intraoperative Cs-131 on neurocognitive function and quality of life (QoL) in patients with resected brain metastases. Between 2010 and 2012, 24 patients with newly diagnosed metastasis to the brain were accrued on a prospective protocol and treated with Cs-131 brachytherapy seeds after surgical resection. Physicians administered the mini-mental status examination (MMSE) and functional assessment of cancer therapy-brain (FACT-Br) questionnaire to all patients before treatment and again every 2 months for the duration of 6 months with additional follow-up again at 12 months. Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to analyze statistically significant changes in MMSE over time and paired t test was used to analyze changes in FACT-BR. There was a statistical improvement in overall FACT-BR score at 4 and 6 months of follow-up when compared to baseline (162 vs. 143, P = 0.004; 164 vs. 143, P = 0.005 respectively) with a non-significant trend toward improvement at 2 and 12 months (154 vs. 143, P = 0.067; 159 vs. 149, P = 0.4). MMSE score was statistically improved at 4 and up to 12 months compared to pre-treatment MMSE (30 vs. 29, P = 0.017; 30 vs. 29, P = 0.001 respectively). Patients with brain metastasis who received intra-operative permanent Cs-131 brachytherapy implants saw an improvement of their neurocognitive status and self-assessment of QoL. In addition to the excellent local control of metastasis, this approach may contribute to the improvements in cognitive function and QOL.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WBRT:
-
Whole brain radiotherapy
- Cs-131:
-
Cesium-131
- SRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- NCF:
-
Neurocognitive function
- MMSE:
-
Mini mental status exam
- Qol:
-
Quality of life
- FFP:
-
Freedom from progression
- FACT-Br:
-
Functional assessment of cancer therapy brain
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- I-125:
-
Iodine-125
- HSRT:
-
Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy
References
Wefel JS, Kayl AE, Meyers CA (2004) Neuropsychological dysfunction associated with cancer and cancer therapies: a conceptual review of an emerging target. Br J Cancer 90(9):1691–1696. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601772
Li J, Bentzen SM, Li J, Renschler M, Mehta MP (2008) Relationship Between neurocognitive function and quality of life after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol 71(1):64–70. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360301607045798. Accessed January 21, 2014
Tsao MN, Rades D, Wirth A et al (2011) Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis(es): An American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol 2(3):210–225. doi:10.1016/j.prro.2011.12.004
Tsao MN, Lloyd N, Wong RKS et al (2012) Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple brain metastases. Cochrane database Syst Rev 4:CD003869. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003869.pub3
Kalkanis SN, Kondziolka D, Gaspar LE et al (2010) The role of surgical resection in the management of newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 96(1):33–43. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-0061-8
Suh JH, Videtic GMM, Aref AM et al (2010) ACR appropriateness criteria: single brain metastasis. Curr Probl Cancer 34(3):162–174. doi:10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2010.04.003
Videtic GMM, Gaspar LE, Aref AM et al (2009) American College of Radiology appropriateness criteria on multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75(4):961–965. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1720
Zhong X, Huang B, Feng J, Yang W, Liu H (2015) Delayed leukoencephalopathy of non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases underwent whole brain radiation therapy. J Neurooncol. doi:10.1007/s11060-015-1888-9
Duffey P, Chari G, Cartlidge NE, Shaw PJ (1996) Progressive deterioration of intellect and motor function occurring several decades after cranial irradiation. A new facet in the clinical spectrum of radiation encephalopathy. Arch Neurol 53(8):814–8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8759989. Accessed May 12, 2014
Monaco EA, Faraji AH, Berkowitz O et al (2013) Leukoencephalopathy after whole-brain radiation therapy plus radiosurgery versus radiosurgery alone for metastatic lung cancer. Cancer 119(1):226–232. doi:10.1002/cncr.27504
Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA (1994) Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol 12(3):627–42. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8120563. Accessed May 12, 2014
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(11):1037–1044. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3
Schultheiss TE, Kun LE, Ang KK, Stephens LC (1995) Radiation response of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31(5):1093–1112. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(94)00655-5
Do L, Pezner R, Radany E, Liu A, Staud C, Badie B (2009) Resection followed by stereotactic radiosurgery to resection cavity for intracranial metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73(2):486–491. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.04.070
Robbins JR, Ryu S, Kalkanis S et al (2012) Radiosurgery to the surgical cavity as adjuvant therapy for resected brain metastasis. Neurosurgery 71(5):937–943. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e31826909f2
Quigley MR, Fuhrer R, Karlovits S, Karlovits B, Johnson M (2008) Single session stereotactic radiosurgery boost to the post-operative site in lieu of whole brain radiation in metastatic brain disease. J Neurooncol 87(3):327–332. doi:10.1007/s11060-007-9515-z
Soltys SG, Adler JR, Lipani JD et al (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgery of the postoperative resection cavity for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(1):187–193. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.06.068
Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC et al (2008) Tumor bed radiosurgery after resection of cerebral metastases. Neurosurgery 62(4):817–823. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000316899.55501.8b discussion 823–4
Huang K, Sneed PK, Kunwar S et al (2009) Surgical resection and permanent iodine-125 brachytherapy for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 91(1):83–93. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9686-2
Dagnew E, Kanski J, McDermott MW, et al. (2007) Management of newly diagnosed single brain metastasis using resection and permanent iodine-125 seeds without initial whole-brain radiotherapy: a two institution experience. Neurosurg Focus 22(3):E3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17608356. Accessed September 4, 2015
Rogers LR, Rock JP, Sills AK et al (2006) Results of a phase II trial of the GliaSite radiation therapy system for the treatment of newly diagnosed, resected single brain metastases. J Neurosurg 105(3):375–384. doi:10.3171/jns.2006.105.3.375
Petr MJ, McPherson CM, Breneman JC, Warnick RE (2009) Management of newly diagnosed single brain metastasis with surgical resection and permanent I-125 seeds without upfront whole brain radiotherapy. J Neurooncol 92(3):393–400. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9868-6
Wernicke AG, Yondorf MZ, Peng L et al (2014) Phase I/II study of resection and intraoperative cesium-131 radioisotope brachytherapy in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases. J Neurosurg. doi:10.3171/2014.3.JNS131140
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12(3):189–98. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1202204. Accessed April 29, 2014
Weitzner MA, Meyers CA, Gelke CK, Byrne KS, Cella DF, Levin VA (1995) The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) scale. Development of a brain subscale and revalidation of the general version (FACT-G) in patients with primary brain tumors. Cancer 75(5):1151–61. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7850714. Accessed June 8, 2015
Brown PD, Buckner JC, O’Fallon JR et al (2004) Importance of baseline mini-mental state examination as a prognostic factor for patients with low-grade glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59(1):117–125. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.10.040
Li J, Bentzen SM, Renschler M, Mehta MP (2007) Regression after whole-brain radiation therapy for brain metastases correlates with survival and improved neurocognitive function. J Clin Oncol 25(10):1260–1266. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2536
Regine WF, Schmitt FA, Scott CB et al (2004) Feasibility of neurocognitive outcome evaluations in patients with brain metastases in a multi-institutional cooperative group setting: results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group trial BR-0018. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58(5):1346–1352. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.023
Murray KJ, Scott C, Zachariah B, et al. (2000) Importance of the mini-mental status examination in the treatment of patients with brain metastases: a report from the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group protocol 91-04. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48(1):59–64. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10924972. Accessed January 20, 2014
Meyers CA, Wefel JS (2003) The use of the mini-mental state examination to assess cognitive functioning in cancer trials: no ifs, ands, buts, or sensitivity. J Clin Oncol 21(19):3557–3558. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.07.080
Wolfson AH, Bae K, Komaki R et al (2011) Primary Analysis of a Phase II Randomized Trial Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 0212: impact of different total doses and schedules of prophylactic cranial irradiation on chronic neurotoxicity and quality of life for patients with limited-disease. Int J Radiat Oncol. 81(1):77–84. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.013
Corn BW, Moughan J, Knisely JPS et al (2008) Prospective evaluation of quality of life and neurocognitive effects in patients with multiple brain metastases receiving whole-brain radiotherapy with or without thalidomide on Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) trial 0118. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71(1):71–78. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.09.015
Meyers CA, Smith JA, Bezjak A et al (2004) Neurocognitive function and progression in patients with brain metastases treated with whole-brain radiation and motexafin gadolinium: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 22(1):157–165. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.05.128
Meyers CA, Rock EP, Fine HA (2012) Refining endpoints in brain tumor clinical trials. J Neurooncol 108(2):227–230. doi:10.1007/s11060-012-0813-8
Sun A, Bae K, Gore EM et al (2011) Phase III trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation compared with observation in patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: neurocognitive and quality-of-life analysis. J Clin Oncol 29(3):279–286. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.29.6053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, A., Yondorf, M.Z., Parashar, B. et al. Neurocognitive function and quality of life in patients with newly diagnosed brain metastasis after treatment with intra-operative cesium-131 brachytherapy: a prospective trial. J Neurooncol 127, 63–71 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2009-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2009-5