Abstract
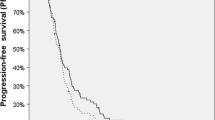
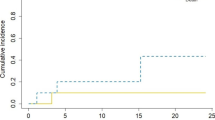
Purpose To evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of surgical resection and permanent iodine-125 brachytherapy without adjuvant whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for brain metastases. Methods and materials Forty patients were treated with permanent iodine-125 brachytherapy at the time of resection of brain metastases from 1997 to 2003. Actuarial freedom from progression (FFP) and survival were measured from the date of surgery and estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method, with censoring at last imaging for FFP endpoints. Results The median survival was 11.3 months overall, 12.0 months in 19 patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases and 7.3 months in 21 patients with recurrent brain metastases. Twenty-two patients (55%) remained free of progression of brain metastases, three failed at the resection cavity (including one with leptomeningeal dissemination), two failed with leptomeningeal spread only, and 13 failed elsewhere in the brain including two who also had leptomeningeal disease. The 1-year resection cavity FFP probabilities were 92%, 86% and 88%; and brain FFP probabilities were 29%, 43% and 37% for the newly diagnosed, recurrent and all patients, respectively. Symptomatic necrosis developed 7.4–40.0 months (median, 19.5 months) after brachytherapy in 9 patients (23%), confirmed by resection in 6 patients. Conclusions Excellent local control was achieved using permanent iodine-125 brachytherapy for brain metastasis resection cavities, although there is a high risk of radiation necrosis over time. These data support consideration of permanent brachytherapy without adjuvant WBRT as a treatment option in patients with symptomatic or large newly diagnosed or recurrent brain metastases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hojo S, Hirano A (1982) Pathology of metastases affecting the central nervous system. In: Takakura K, Sano K, Hojo S (eds) Metastatic tumors of the central nervous system. Igaku-Shoin, Tokyo, pp 5–35
Posner JB, Chernik NL (1978) Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol 19:579–592
Chevalier T, Smith FP, Caille P et al (1985) Sites of primary malignancies in patients presenting with cerebral metastases. A review of 120 cases. Cancer 56:880–882. doi :10.1002/1097-0142(19850815)56:4<880::AID-CNCR2820560430>3.0.CO;2-I
Sheline GE, Brady LW (1987) Radiation therapy for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 4:219–225. doi:10.1007/BF00150613
Patel JK, Didolkar MS, Pickren JW et al (1978) Metastatic pattern of malignant melanoma. A study of 216 autopsy cases. Am J Surg 135:807–810. doi:10.1016/0002-9610(78)90171-X
Borgelt B, Gelber R, Kramer S et al (1980) The palliation of brain metastases: final results of the first two studies by the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 6:1–8
Coia LR (1992) The role of radiation therapy in the treatment of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:229–238
Kondziolka D, Patel A, Lunsford LD et al (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:427–434. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00198-4
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW et al (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363(9422):1665–1672. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8
Noordijk EM, Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H et al (1994) The choice of treatment of single brain metastasis should be based on extracranial tumor activity and age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 29:711–717
Phillips TL, Scott CB, Leibel SA et al (1995) Results of a randomized comparison of radiotherapy and bromodeoxyuridine with radiotherapy alone for brain metastases: report of RTOG trial 89-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 33:339–348. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(95)00168-X
Asai A, Matsutani M, Kohno T et al (1989) Subacute brain atrophy after radiation therapy for malignant brain tumor. Cancer 63:1962–1974. doi :10.1002/1097-0142(19890515)63:10<1962::AID-CNCR2820631016>3.0.CO;2-V
DeAngelis LM, Delattre JY, Posner JB (1989) Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 39:789–796
Swennen MH, Bromberg JE, Witkamp TD et al (2004) Delayed radiation toxicity after focal or whole brain radiotherapy for low-grade glioma. J Neurooncol 66(3):333–339. doi:10.1023/B:NEON.0000014518.16481.7e
Nieder C, Leicht A, Motaref B et al (1999) Late radiation toxicity after whole brain radiotherapy: the influence of antiepileptic drugs. Am J Clin Oncol 22(6):573–579. doi:10.1097/00000421-199912000-00007
Sneed PK, Lamborn KR, Forstner JM et al (1999) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: is whole brain radiotherapy necessary? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43:549–558. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00447-7
Sartorius CJ, Berger MS (1998) Rapid termination of intraoperative stimulation-evoked seizures with application of cold Ringer’s lactate to the cortex. Technical note. J Neurosurg 88:349–351
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (1996) Intraoperative navigation during resection of brain metastases. Neurosurg Clin N Am 7:267–277
Nath R, Anderson LL, Luxton G et al (1995) Dosimetry of interstitial brachytherapy sources: recommendations of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 43. American Association of Physicists in Medicine. Med Phys 22:209–234. doi:10.1118/1.597458
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(96)00619-0
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280:1485–1489. doi:10.1001/jama.280.17.1485
Bernstein M, Cabantog A, Laperriere N et al (1995) Brachytherapy for recurrent single brain metastasis. Can J Neurol Sci 22:13–16
Bogart JA, Ungureanu C, Shihadeh E et al (1999) Resection and permanent I-125 brachytherapy without whole brain irradiation for solitary brain metastasis from non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Neurooncol 44:53–57. doi:10.1023/A:1006285304892
McDermott MW, Cosgrove GR, Larson DA et al (1996) Interstitial brachytherapy for intracranial metastases. Neurosurg Clin N Am 7:485–495
Ostertag CB, Kreth FW (1995) Interstitial iodine-125 radiosurgery for cerebral metastases. Br J Neurosurg 9:593–603. doi:10.1080/02688699550040873
Schulder M, Black PM, Shrieve DC et al (1997) Permanent low-activity iodine-125 implants for cerebral metastases. J Neurooncol 33:213–221. doi:10.1023/A:1005798027813
Zamorano L, Yakar D, Dujovny M et al (1992) Permanent iodine-125 implant and external beam radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant brain tumors. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 59:183–192. doi:10.1159/000098940
Rogers LR, Rock JP, Sills AK et al (2006) Results of a phase II trial of the GliaSite radiation therapy system for the treatment of newly diagnosed, resected single brain metastases. J Neurosurg 105(3):375–384. doi:10.3171/jns.2006.105.3.375
Dagnew E, Kanski J, McDermott MW et al (2007) Management of newly diagnosed single brain metastasis using resection and permanent iodine-125 seeds without initial whole-brain radiotherapy: a two institution experience. Neurosurg Focus 22(3):E3. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.22.3.4
van der Ree TC, Dippel DW, Avezaat CJ et al (1999) Leptomeningeal metastasis after surgical resection of brain metastases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1966:225–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, K., Sneed, P.K., Kunwar, S. et al. Surgical resection and permanent iodine-125 brachytherapy for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 91, 83–93 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9686-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9686-2