Abstract
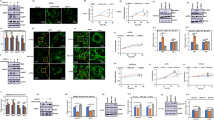
The correlation of c-Myc expression with resveratrol-induced turnover of medulloblastoma cells was investigated in this study by checking (1) c-Myc expression in medulloblastoma tissues and cell lines (UW228-2 and UW228-3), (2) the in vitro effect of resveratrol on c-Myc expression and (3) the influences of c-Myc inhibition in cell growth and survival. Immunohistochemical staining of human medulloblastomas and noncancerous cerebellar tissues revealed that 8 out of 11 tumor tissues (72.7%) expressed c-Myc, in which 4 cases (50%) showed intensified nuclear labeling. RT-PCR, Western blotting, immunocytochemical and immunofluorescence stainings revealed c-Myc downregulation accompanied with growth suppression and apoptosis. Flow cytometry analysis showed S phase arrest in resveratrol-treated cell populations. Transfection of c-Myc directed antisense oligonucleotides to the cultured medulloblastoma cells could reduce c-Myc expression, inhibit cell growth and arrest the cell cycle at S phase. Our results thus for the first time demonstrate that c-Myc downregulation is a critical molecular event of resveratrol-mediated anti-medulloblastoma activity, which is closely associated with growth suppression, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of medulloblastoma cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Boughton B (2002) Childhood cancer treatment causes complications later in life. Lancet Oncol 3:390
Ehrlich PF, Lamkin T (2003) Unusual delayed complication of central venous access. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 23:472–473
Liu J, Guo L, Li JW, Liu N, Li H (2000) All-trans retinoic acid modulates fas expression and enhances chemosensitivity of human medulloblastoma cells. Int J Mol Med 5:145–149
Liu J, Guo L, Lou Y, Li JW, Li H (2000) All-trans retinoic acid suppresses in vitro growth and down-regulates LIF gene expression as well as telomerase activity of human medulloblastoma cells. Anticancer Res 20:2659–2664
Soleas GJ, Diamandis EP, Goldberg DM (1997) Resveratrol: a molecule whose time has come? And gone? Clin Biochem 30:91–113
Sanders TH, Mcmichael RW, Hendrix KW (2000) Occurrence of resveratrol in edible peanuts. J Agric Food Chem 48:1243–1246
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV (1997) Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 275:218–220
Kundu JK, Surh YJ (2004) Molecular basis of chemoprevention by resveratrol: NF-kappaB and AP-1 as potential targets. Mutat Res 555:65–80
Wang Q, Li H, Wang XW, Wu DC, Chen XY, Liu J (2003) Resveratrol promotes differentiation and induces Fas-independent apoptosis of medulloblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 351:83–86
McManus ME, Burgess WM, Veronese ME, Huggett A, Quattrochi LC, Turkey RH (1990) Metabolism of 2-acetylaminofluorene and benzo(α)pyrene and activation of food-derived heterocyclic amine mutagens by human cytochromes P450. Cancer Res 50:3367–3376
Shimada T, Oda Y, Gillam EMJ, Guengerich P, Inoue K (2001) Metabolic activiation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other procarcinogens by cytochromes P450 1A1 and P450 1B1 allelic variant and other human cytochromes P450 in Salmonella typhimurium. Drug Metab Dispos 29:1176–1182
Liu J, Wang Q, Wu DC, Wang XW, Sun Y, Chen XY, Zhang KL, Li H (2004) Differential regulation of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 expression in resveratrol-treated human medulloblastoma cells. Neurosci Lett 363:257–261
Wu ML, Li H, Wu DC, Wang XW, Wang XY, Chen XY, Kong QY, Ma JX, Gao Y, Li H (2005) CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 expressions in medulloblastoma cells are AhR-independed and have no direct link with resveratrol-induced differentiation and apoptosis. Neurosci Lett 284:33–37
Alvaro JO, Maria KM, John MS (1999) Mysterious liaison: the relationship between c-Myc and the cell cycle. Oncogene 18:2934–2941
Adachi S, Obaya AJ, Han ZY, Desimone NR, Wyche JH, Sedivy JM (2001) c-Myc is necessary for DNA damage-induced apoptosis in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol 21:4929–4937
Smith AG, Popov N, Imreh M, Axelson H, Henriksson M (2004) Expression and DNA-binding activity of MYCN/Max and Mnt/Max during induced differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Biochem 92:1282–1295
Miyazaki T, Liu ZJ, Kawahara A, Minami Y, Yamada K (1995) Three distinct IL-2 signaling pathways mediated by bcl-2, c-myc, and lck cooperate in hematopoietic cell proliferation. Cell 81:223–231
Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan G (2002) C-Myc: more than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer 2:764–776
Hoffman B, Amanullah A, Shafarenko M, Liebermann DA (2002) The proto-oncogene c-myc in hematopoietic development and leukemogenesis. Oncogene 21:3414–3421
Scheurlen WG, Schwabe GC, Joos S, Mollenhauer J, Sorensen N, Kuhl J (1998) Molecular analysis of childhood primitive neuroectodermal tumors defines markers associated with poor outcome. J Clin Oncol 16:2478–2485
Grotzer MA, Hogarty MD, Janss AJ, Liu X, Zhao H, Eggert A (2001) C-myc expression predicts survival outcome in childhood primitive neuroectodermal tumor/medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 7:2425–2433
Richert CH (2004) Prognosis-related molecular markers in pediatric central nervous system tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:1211–1224
Keles GE, Berger MS, Srinivasan J, Kolstoe DD, Bobola MS, Silber JR (1995) Establishment and characterization of four human medulloblastoma-derived cell lines. Oncol Res 7:493–503
Watson PH, Pon RT, Shiu RPC (1991) Inhibition of c-myc expression by phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotide identifies a critical role for c-myc in the growth of human breast cancer. Cancer Res 51:3996–4000
Whelan HT, Krouwer HG, Schmidt MH, Reichert KW, Kovnar EH (1998) Current therapy and new perspectives in the treatment of medulloblastoma. Pediatr Neurol 18:103–115
Mulhern K., Merchant TE, Gajjar A, Reddick WE, Kun LE (2004) Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. Lancet Oncol 5:399–408
Packer RJ, Goldwein J, Nicholson HS (1999) Treatment of children with medulloblastomas with reduced-dose craniospinal radiation therapy and adjuwant chemotherapy: a Children’s Cancer Group Study. J Clin Oncol 17:2127–2136
Palmer SL, Goloubeva O, Reddick WE (2001) Patterns of intellectual development among survivors of pediatric medulloblastoma: a longitudinal analysis. J Clin Oncol 19:2302–2308
MacDonald TJ, Rood BR, Santi MR, Vezina G, Bingaman K, Cogen PH, Packer RJ (2003) Advances in the Diagnosis, molecular genetic, and treatment of pediatric embryonal CNS tumors. Oncologist 8:174–186
Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Huard C, Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov JP, Coller H, Loh ML (1999) Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 286:531–537
Gilbertson R, Wickramasinghe C, Hernan R (2001) Clinical and molecular stratification of disease risk in medulloblastoma. Br J Cancer 85:705–712
Michiels EMC, Oussoren E, Van Groenigen M, Pauws E, Bossuyt PMM, Voute PA, Baas F (1999) Genes differentially expressed in medulloblastoma and fetal brain. Physiol Genomics 1:83–91
Korenberg MJ (2003) Gene expression monitoring accurately predicts medulloblastoma positive and negative clinical outcome. FEBS Lett 533:110–114
Chopra A, Brown KM, Rood BR, Packer RJ, MacDonald TJ (2003) The use of gene expression analysis to gain insights into signaling mechanisms of metastatic medulloblastoma. Pediatric Neurosurg 39:68–74
Korshunov A, Savostikova M, Ozerov S (2002) Immunohistochemical markers for prognosis of average-risk pediatric medulloblastomas: the effect of apoptotic index, TrkC, and c-myc expression. J Neurooncol 58:271–279
Ramachandran C, Khativ Z, Escalon E, Fonseca HB, Jhabvala P, Medina LS (2002) Molecular studies in pediatric medulloblastomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 19:15–22
Fruhwald MC, O’Dorisio MS, Rush LJ, Reiter JL (2000) Gene amplification in PNETs/medulloblastomas: mapping of a novel amplified gene within the MYCN amplicon. J Med Genet 37:501–509
Herms J, Neidt I, Luscher B, Sommer A, Schurmann P, Schroder T (2000) C-MYC expression in medulloblastoma and its prognostic value. Int J Cancer 89:395–402
Siu IM, Lal A, Blankenship JR, Aldosari N, Riggins GJ (2003) c-Myc promoter activation in medulloblastoma. Cancer Res 63:4773–4776
Eberhart CG, Kratz J, Wang Y, Summers K, Stearns D, Cohen K (2004) Histopathological and molecular prognostic markers in medulloblastoma: c-myc, N-myc, TrkC, and anaplasia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:441–449
Chi SN, Gardner SL, Levy AS, Knopp EA, Miller DC, Wisoff JH, Weiner HL, Finlay JL (2004) Feasibility and response to induction chemotherapy intensified with high-dose methotrexate for young children with newly diagnosed high-risk disseminated medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22:4881–4887
Tabori U, Sung L, Hukin J, Laperriere N, Crooks B, Carret AS (2005) Medulloblastoma in the second decade of life: a specific group with respect to toxicity and management: a Canadian Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study. Cancer 103:1874–1880
Bhat KP, Pezzuto JM (2002) Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol. Ann NY Acad Sci 957:210–229
Wolter F, Turchanowa L, Stein J (2003) Resveratrol-induced modification of polyamine metabolism is accompanied by induction of c-Fos. Carcinogenesis 24:469–474
Yin X, Landay MF, Han W, Levitan ES, Watkins SC, Levenson RM, Farkas DL, Prochownik EV (2001) Dynamic in vivo interactions among Myc network members. Oncogene 20:4650–4664
Mariadason JM, Nicholas C, L’Italien KE, Zhuang M, Smartt HJ, Heerdt BG (2005) Gene expression profiling of intestinal epithelial cell maturation along the crypt-villus axis. Gastroenterology 128:1081–1088
Acknowledgement
This work is supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30370448 and 30527002), the National Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2000-J-P-26) and the Dalian Bureau for Science and Technology, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Li, H., Wu, ML. et al. c-Myc downregulation: a critical molecular event in resveratrol-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human medulloblastoma cells. J Neurooncol 80, 123–131 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9172-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9172-7