Abstract
Because of the ubiquitous production and use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), silver ions (Ag+) released from AgNPs can not only singly pose significant toxicity to aquatic ecosystems but can also mix with other coexisting metal oxide nanoparticles (MONPs), such as ZnO NPs and TiO2 NPs to provoke combined toxicity. However, information regarding the combined impact of MONPs on aquatic organisms is limited. In this study, the impact of exposure to mixtures composed of Ag+ and two different MONPs (i.e., ZnO NPs and TiO2 NPs) on Daphnia magna was examined. The toxicity of the mixtures containing Ag+ concentrations exceeding 0.5–1.5 μg/L and two different MONPs (Ag+-two different MONP mixture) was higher than that of the intrinsic toxicity of each component, indicating a synergistic effect. However, the concentrations of the two different MONPs did not have a strong relationship with the occurrence of the synergistic or antagonistic effect between components in the mixtures. Moreover, the combined risk of the Ag+-two different MONP mixture estimated based on a whole-value risk for the mixture (VaR:192–198) was up to eight times higher than that estimated using a component-based value risk (VaR:736–1623) considering the predicted environmental concentration of Ag+ (20 μg/L). These results imply that the component-based approach could not determine the synergistic effect between the components in the Ag+-two different MONP mixtures. Additionally, when mixed with two different MONPs, Ag+ as a major toxicant induced synergistic effects among the components in the mixture. Therefore, to evaluate the interactive effects and for environmental risk assessment of mixtures, a whole-mixture approach is recommended rather than a component-based approach.

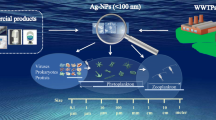
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AgNPs:
-
silver nanoparticles
- Ag+ :
-
silver ion
- ECx :
-
effective concentration values
- ECx mix :
-
total effective concentration estimated from binary mixtures
- HQs:
-
hazard quotients
- MONPs:
-
metal oxide nanoparticles
- OECD:
-
Organization for Econocmic Co-operation and Development
- PEC:
-
predicted environmental concentration
- PNEC:
-
predicted no effect concentration
- STU:
-
the sum of toxic unit
References
Asghari S, Johari SA, Lee JH, Kim YS, Jeon YB, Choi HJ, Moon MC, Yu IJ (2012) Toxicity of various silver nanoparticles compared to silver ions in Daphnia magna. J Nanobiotechnol 10(1):14
Atha DH, Wang H, Petersen EJ, Cleveland D, Holbrook RD, Jaruga P, Dizdaroglu M, Xing B, Nelson BC (2012) Copper oxide nanoparticle mediated DNA damage in terrestrial plant models. Environ Sci Technol 46(3):1819–1827
Aznar R, Barahona F, Geiss O, Ponti J, José Luis T, Barrero-Moreno J (2017) Quantification and size characterization of silver nanoparticles in environmental aqueous samples and consumer products by single particle-ICPMS. Talanta 175:200–208
Beer C, Foldbjerg R, Hayashi Y, Sutherland DS, Autrup H (2012) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles—nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol Lett 208(3):286–292
Boenigk J, Beisser D, Zimmermann S, Bock C, Jakobi J, Grabner D, Großmann L, Rahmann S, Barcikowski S, Sures B (2014) Effects of silver nitrate and silver nanoparticles on a planktonic community: general trends after short-term exposure. PLoS One 9(4):e95340
Bondarenko O, Juganson K, Ivask A, Kasemets K, Mortimer M, Kahru A (2013) Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: a critical review. Arch Toxicol 87(7):1181–1200
Bondarenko O, Heinlaan M, Sihtmäe M, lvask A, Kurvet I, Joonas E, Jemec A, Mannerström M, Heinonen T, Rekulapelly R, Singh S, Zou J, Pyykkö I, Drobne D, Kahru A (2016) Multilaboratory evaluation of 15 bioassays for (eco)toxicity screening and hazard ranking of engineered nanomaterials: FP7 project NANOVALID. Nanotoxicol. 10:1229–1242
Bundschuh M, Filser J, Lüderwald S, McKee MS, Metreveli G, Schaumann GE, Schulz R, Wagner S (2018) Nanoparticles in the environment: where do we come from, where do we go to? Environ Sci Eur 30:6
Bunke D, Groß R, Kalberlah F, Oltmanns J, Schwarz M, Reihlen A, Reineke N (2014) Mixtures in the environment – development of assessment strategies for the regulation of chemicals under REACH. The Federal Environment Agency, Dessau-Roßlau
Das P, Xenopoulos MA, Williams CJ, Hoque ME, Metcalfe CD (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles on bacterial activity in natural waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(1):122–130
European Commission (EC) (1996) Technical guidance document (TGD) in support of commission directive 93/67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances and commission regulation (EC) no 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances. Part II: environmental risk assessment. European Commission, Luxembourg
Federici G, Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2007) Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat Toxicol 84(4):415–430
Fleischauer PD, Alan Kan HK, Shepherd JR (1972) Quantum yields of sliver ion reduction on titanium dioxide and zinc oxide single crystals. J Am Chem Soc 94(1):283–285
Franklin NM, Rogers NJ, Apte SC, Batley GE, Gadd GE, Casey PS (2007) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 41:8484–8490
Hachicho N, Hoffmann P, Ahlert K, Heipieper HJ (2014) Effect of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on growth and adaptive response mechanisms of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. FEMS Microbiol Lett 355(1):71–77
Hartmann NB, Baun A (2010) The nano cocktail: ecotoxicological effects of engineered nanoparticles in chemical mixtures. Integr Environ Aseess Manag 6:311–314
Hartmann NB, Legros S, Von der Krammer F, Hofmann T, Baun A (2012) The potential of TiO2 nanoparticles as carriers for cadmium uptake in Lumbriculus variegatus and Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol 118-119(1–8):1–8
Heinlaan M, Ivask A, Blinova I, Dubourguier H-C, Kahru A (2008) Toxicity of nanosized and vulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere. 71(7):1308–1316
Heys KA, Shore RF, Pereira MG, Jones KC, Martin FL (2016) Risk assessment of environmental mixture effects. RSC Adv 6(53):47844–47857
Jonczyk E, Gilron G (2005) Acute and chronic toxicity testing with Daphnia sp. In: Blaise C, Férard J-F (eds) Small-scale freshwater toxicity investigations volume 1 - toxicity test methods. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 337–393
Jung Y, Metreveli G, Park C-B, Baik S, Schaumann GE (2018) Implications of pony lake fulvic acid for the aggregation and dissolution of oppositely charged surface-coated silver nanoparticles and their ecotoxicological effects on Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 52:436–445
Khan FR, Keller W, Yan ND, Welsh PG, Wood CM, McGeer JC (2012) Application of biotic ligand and toxic unit modeling approaches to predict improvements in zooplankton species richness in smelter-damaged lakes near Sudbury, Ontario. Environ Sci Technol 46(3):1641–1649
Kienzler A, Berggren E, Bessems J, Bopp S, Linden S, Worth A (2014) Joint Research Centre (JRC) science and policy reports: assessment of mixtures – review of regulatory requirements and guidance. European Commission, European Union, Luxembourg
Lecoanet HF, Bottero JY, Wiesner MR (2004) Laboratory assessment of the mobility of nanomaterials in porous media. Environ Sci Technol 38(19):5164–5169
Liu Y, Baas J, Peijnenburg WJGM, Vijver MG (2016) Evaluating the combined toxicity of Cu and ZnO nanoparticles: utility of the concept of additivity and a nested experimental design. Environ Sci Technol 50(10):5328–5337
Lopes S, Pinheiro C, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2016) Joint toxicity prediction of nanoparticles and ionic counterparts: simulating toxicity under a fate scenario. J Hazard Mater 320(Supplement C):1–9
Luo M, Huang Y, Zhu M, Tang Y-N, Ren T, Ren J, Wang H, Li F (2018) Properties of different natural organic matter influence the adsorption and aggregation behavior of TiO2 nanoparticles. J Saudi Chem Soc 22(2):146–154
Mark U, Solbé J (1998) Analysis of the ecetoc aquatic toxicity (EAT) database V — the relevance of Daphnia magna as a representative test species. Chemosphere. 36(1):155–166
Maurer-Jones MA, Gunsolus IL, Murphy CJ, Haynes CL (2013a) Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal Chem 85(6):3036–3049
Maurer-Jones MA, Mousavi MPS, Chen LD, Buhlmann P, Haynes CL (2013b) Characterization of silver ion dissolution from silver nanoparticles using fluorous-phase ion-selective electrodes and assessment of resultant toxicity to Shewanella oneidensis. Chem Sci 4(6):2564–2572
Molins-Delgado D, Gago-Ferrero P, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2016) Single and joint ecotoxicity data estimation of organic UV filters and nanomaterials toward selected aquatic organisms. Urban groundwater risk assessment. Environ Res 145:126–134
Naasz S, Altenburger R, Kühnel D (2018) Environmental mixtures of nanomaterials and chemicals: the Trojan-horse phenomenon and its relevance for ecotoxicity. Sci Total Environ 635:1170–1181
Newton KM, Puppala HL, Kitchens C, Colvin VL, Klaine SJ (2013) Silver nanoparticle toxicity to Daphnia mgana is a function of dissolved silver concentration. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(10):2356–2364
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), 2004. OECD guideline for testing of chemicals. Guideline 202: Daphnia sp., Acute Immobilisation Test, adopted 13 April 2004
Park C-B, Jang J, Kim S, Kim YJ (2017) Single- and mixture toxicity of three organic UV-filters, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene, and avobenzone on Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:57–63
Schmidt J, Vogelsberger W (2006) Dissolution kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: the observation of an unusual kinetic size effect. J Phys Chem B 110(9):3955–3963
Sun TY, Gottschalk F, Hungerbuhler K, Nowack B (2014) Comprehensive probabilistic modelling of environmental emissions of engineered nanomaterials. Environ Pollut 185:69–76
Teklu BM, Hailu A, Wiegant DA, Scholten BS, Van den Brink PJ (2016) Impacts of nutrients and pesticides from small- and large-scale agriculture on the water quality of Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):13207–13216
Wang Z, Chen J, Li X, Shao J, Peijnenburg WJ (2012) Aquatic toxicity of nanosilver colloids to different trophic organisms: contributions of particles and free silver ion. Environ Toxicol Chem 31(10):2408–2413
Warne MJ, van Dam R (2008) NOEC and LOEC data should no longer be generated or used. Australasian J Ecotoxicol 14:1–5
Yang W-W, Miao A-J, Yang L-J (2012) Cd2+toxicity to a green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as influenced by its adsorption on TiO2 engineered nanoparticles. PLoS One 7(3):e32300
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Xu T, Zheng K, Zhang R, Peng Z, Zhang H (2018) Toxic effects of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles in environmental concentration on the nitrogen removal, microbial activity and comminity of Anammox process. Chem Eng J 332:42–48
Zhu X, Zhu L, Chen Y, Tian S (2009) Acute toxicities of six manufactured nanomaterial suspensions to Daphnia magna. J Nanopart Res 11:67–75
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST) grant by the South Korean government (MSIP) (No. CAP-17-01-KIST Europe) and Project 11911.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this study. The final version of the manuscript has been approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 879 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, CB., Jung, JW., Baek, M. et al. Mixture toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles and silver ions on Daphnia magna. J Nanopart Res 21, 166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4606-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4606-2