Abstract
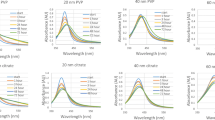
Silver, gold, and silver–gold-alloy nanoparticles were prepared by citrate reduction modified by the addition of tannin during the synthesis, leading to a reduction in particle size by a factor of three. Nanoparticles can be prepared by this easy water-based synthesis and subsequently functionalized by the addition of either tris(3-sulfonatophenyl)phosphine or poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone). The resulting nanoparticles of silver (diameter 15–25 nm), gold (5–6 nm), and silver–gold (50:50; 10–12 nm) were easily dispersable in water and also in cell culture media (RPMI + 10 % fetal calf serum), as shown by nanoparticle tracking analysis and differential centrifugal sedimentation. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy showed a polycrystalline nature of all nanoparticles. EDX on single silver–gold nanoparticles indicated that the concentration of gold is higher inside a nanoparticle. The biologic action of the nanoparticles toward human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) was different: Silver nanoparticles showed a significant concentration-dependent influence on the viability of hMSC. Gold nanoparticles showed only a small effect on the viability of hMSC after 7 days. Surprisingly, silver–gold nanoparticles had no significant influence on the viability of hMSC despite the silver content. Silver nanoparticles and silver–gold nanoparticles in the concentration range of 5–20 μg mL−1 induced the activation of hMSC as indicated by the release of IL-8. In contrast, gold nanoparticles led to a reduction of the release of IL-6 and IL-8.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed M, Karns M, Goodson M, Rowe J, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Hong Y (2008) DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 233:404–410
Barcikowski S, Mafune F (2011) Trends and current topics in the field of laser ablation and nanoparticle generation in liquids. J Phys Chem C 115:4985
Berry CC, de la Fuente JM, Mullin M, Chu SWL, Curtis ASG (2007) Nuclear localization of HIV-1 Tat functionalized gold nanoparticles. NanoBiosci IEEE Trans 6:262–269
Chen HM, Liu RS, Jang LY, Lee JF, Hu SF (2006) Characterization of core-shell type and alloy Ag/Au bimetallic clusters by using extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lett 421:118–123
Devarajan S, Bera P, Sampath S (2005) Bimetallic nanoparticles: a single step synthesis, stabilization, and characterization of Au-Ag, Au-Pd, and Au-Pt in sol-gel derived silicates. J Coll Interface Sci 290:117–129
Fröhlich E, Samberger C, Kueznik T, Absenger M, Roblegg E, Zimmer A, Pieber TR (2009) Cytotoxicity of nanoparticles independent from oxidative stress. J Toxicol Sci 34:363–375
Giljohann DA, Seferos DS, Daniel WL, Massich MD, Patel PC, Mirkin CA (2010) Gold nanoparticles for biology and medicine. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:3280–3294
Goesmann H, Feldmann C (2010) Nanoparticulate functional materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:1362–1395
Gonzalez CM, Liu Y, Scaiano JC (2009) Photochemical strategies for the facile synthesis of gold-silver alloy and core-shell bimetallic nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 113:11861–11867
Greulich C, Kittler S, Epple M, Muhr G, Köller M (2009) Studies on the biocompatibility and the interaction of silver nanoparticles with human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). Langenbecks Arch Surg 394:495–502
Greulich C, Diendorf J, Simon T, Eggeler G, Epple M, Köller M (2011) Uptake and intracellular distribution of silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater 7:347–354
Greulich C, Braun D, Peetsch A, Diendorf J, Siebers B, Epple M, Koller M (2012) The toxic effect of silver ions and silver nanoparticles towards bacteria and human cells occurs in the same concentration range. RSC Adv (in press)
Hahn A, Fuhlrott J, Loos A, Barcikowski S (2012) Cytotoxicity and ion release of alloy nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 14:686
He ST, Xie SS, Yao JN, Gao HJ, Pang SJ (2002) Self-assembled two-dimensional superlattice of Au-Ag alloy nanocrystals. Appl Phys Lett 81(1):150–152
Ho CM, Yau SKW, Lok CN, So MH, Che CM (2010) Oxidative dissolution of silver nanoparticles by biologically relevant oxidants: a kinetic and mechanistic study. Chem Asian J 5:285–293
Homberger M, Simon U (2010) On the application potential of gold nanoparticles in nanoelectronics and biomedicine. Phil Trans R Soc A 368:1405–1453
Hsin YH, Chen CF, Huang S, Shih TS, Lai PS, Chueh PJ (2008) The apoptotic effect of silver nanoparticles is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 179:130–139
Huang X, Neretina S, El-Sayed MA (2009) Gold nanorods: from synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv Mater 21:4880–4910
Huang X, Wu H, Liao X, Shi B (2010) One-step, size-controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles at room temperature using plant tannin. Green Chem 12:395–399
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc Chem Res 41:1578–1586
Johnston HJ, Hutchison G, Christensen FM, Peters S, Hankin S, Stone V (2011) A review of the in vivo and in vitro toxicity of silver and gold particulates: particle attributes and biological mechanisms responsible for the observed toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 40:328–346
Kittler S, Greulich C, Diendorf J, Köller M, Epple M (2010a) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem Mater 22:4548–4554
Kittler S, Greulich C, Gebauer JS, Diendorf J, Treuel L, Ruiz L, Gonzalez-Calbet JM, Vallet-Regi M, Zellner R, Köller M, Epple M (2010b) The influence of proteins on the dispersability and cell-biological activity of silver nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 20:512–518
Li T, Albee B, Alemayehu M, Diaz R, Ingham L, Kamal S, Rodriguez M, Whaley Bishnoi S (2010) Comparative toxicity study of Ag, Au, and Ag-Au bimetallic nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:689–700
Liang AH, Zhang NN, Jiang ZL, Lin RJ (2008) Nanosilver resonance scattering spectral method for determination of hydroxyl radical and its application. Sci China Ser B Chem 51:226–232
Liochev S (1999) The mechanism of “Fenton-like” reactions and their importance for biological systems: a biologist’s view. Met Ions Biol Syst 36:1–39
Liu L, Hurt RH (2010) Ion release kinetics and particle persistence in aqueous nano-silver colloids. Environ Sci Technol 44:2169–2175
Liu J, Sonshine DA, Shervani S, Hurt RH (2010) Controlled release of biologically active silver from nanosilver surfaces. ACS Nano 4:6903–6913
Luther EM, Koehler Y, Diendorf J, Epple M, Dringen R (2011) Accumulation of silver nanoparticles by cultured primary brain astrocytes. Nanotechnology 22:375101
Mahl D, Greulich C, Meyer-Zaika W, Köller M, Epple M (2010) Gold nanoparticles: dispersability in biological media and cell-biological effect. J Mater Chem 20:6176–6181
Mahl D, Diendorf J, Meyer-Zaika W, Epple M (2011) Possibilities and limitations of different analytical methods for the size determination of a bimodal dispersion of metallic nanoparticles. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 377:386–392
Mallin MP, Murphy CJ (2002) Solution-phase synthesis of sub-10 nm Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles. Nano Lett 2:1235–1237
Mohapatra S, Kumar RK, Maji TK (2011) Green synthesis of catalytic and ferromagnetic gold nanoparticles. Chem Phys Lett 508:76–79
Monopoli MP, Bombelli FB, Dawson KA (2011a) Nanoparticle coronas take shape. Nat Nanotechnol 6:11–12
Monopoli MP, Walczyk D, Campbell A, Elia G, Lynch I, Bombelli FB, Dawson KA (2011b) Physical-chemical aspects of protein corona: relevance to in vitro and in vivo biological impacts of nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 133:2525–2534
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramirez JT, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16:2346–2353
Mukherjee B, Weaver JW (2010) Aggregation and charge behavior of metallic and nonmetallic nanoparticles in the presence of competing similarly-charged inorganic ions. Environ Sci Technol 44:3332–3338
Orts-Gil G, Natte K, Drescher D, Bresch H, Mantion A, Kneipp J, Österle W (2011) Characterisation of silica nanoparticles prior to in vitro studies: from primary particles to agglomerates. J Nanopart Res 13(4):1593–1604
Pal A, Shah S, Kulkarni V, Murthy RSR, Devi S (2009) Template free synthesis of silver-gold alloy nanoparticles and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles in Chinese Hamster Ovary cell. Mater Chem Phys 113:276–282
Pan Y, Leifert A, Ruau D, Neuss S, Bornemann J, Schmid G, Brandau W, Simon U, Jahnen-Dechent W (2009) Gold nanoparticles of diameter 1.4 nm trigger necrosis by oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Small 5:2067–2076
Rostek A, Mahl D, Epple M (2011) Chemical composition of surface-functionalized gold nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:4809–4814
Ruparelia JP, Chatterjee AK, Duttagupta SP, Mukherji S (2008) Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater 4:707–716
Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P, Murray RW (2009) Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir 25:13840–13851
Schmid G (ed) (2004) Nanoparticles. From theory to application. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Slawnson RM, Lee H, Trevors JT (1990) Bacterial interactions with silver. Biol Metals 3:151–154
Sotiriou GA, Pratsinis SE (2011) Engineering nanosilver as an antibacterial, biosensor and bioimaging material. Curr Opinion Chem Eng 1:3–10
Sperling RA, Rivera P, Zhang F, Zanella M, Parak WJ (2008) Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 37:1896–1908
Tsoli M, Kuhn H, Brandau W, Esche H, Schmid G (2005) Cellular uptake and toxicity of Au(55) clusters. Small 1:841–844
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hilliery J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55
Vaidyanathan R, Kalishwaralal K, Gopalram S, Gurunathan S (2009) Nanosilver—the burgeoning therapeutic molecule and its green synthesis. Biotechnol Adv 27:924–937
Wang C, Peng S, Chan R, Sun S (2009) Synthesis of AuAg alloy nanoparticles from core/shell-structured Ag/Au. Small 5:567–570
Wijnhoven SWP, Peijnenburg WJGM, Herberts CA, Hagens WI, Oomen AG, Heugens EHW, Roszek B, Bisschops J, Gosens I, van De Meent D, Dekkers S, De Jong WH, van Zijverden M, Sips AJAM, Geertsma RE (2009) Nano-silver—a review of available data and knowledge gaps in human and environmental risk assessment. Nanotoxicology 3:109–138
Wu DJ, Liu XJ (2010) Optimization of the bimetallic gold and silver alloy nanoshell for biomedical applications in vivo. Appl Phys Lett 97(061904):1–4
Wyrwa DW (2006) PhD Thesis, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen
Yen HJ, Hsu SH, Tsai CL (2009) Cytotoxicity and immunological response of gold and silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Small 5:1553–1561
Acknowledgments
Matthias Epple and Manfred Koeller thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft for funding within the priority program 1313 BioNanoResponses. Michael Farle and Zi-An Li acknowledge support from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the collaborative research center SFB 445. We thank K. Brauner, V. Hiltenkamp, B. Sures, and N. Zimmermann for AAS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahl, D., Diendorf, J., Ristig, S. et al. Silver, gold, and alloyed silver–gold nanoparticles: characterization and comparative cell-biologic action. J Nanopart Res 14, 1153 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1153-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1153-5