Abstract
Purpose
Silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) are widely used in different areas, e.g., in the food, electronic, or clothing industry due to well-known slow-release antiseptic activities. Despite the widespread use of nanosilver, there is a serious lack of information concerning the biological activities of nanosilver on human tissue cells.
Materials and methods
In this study, the influence of spherical Ag-NPs (diameter about 100 nm) on the biological functions (proliferation, cytokine release, and chemotaxis) of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) was analyzed.
Results
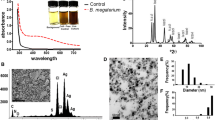
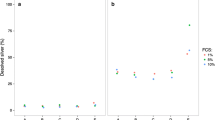
The results showed a concentration-dependent activation of hMSCs at nanosilver levels of 2.5 μg mL−1, and cytotoxic cell reactions occurred at Ag-NPs concentrations above 5 μg mL−1. Cell proliferation and the chemotaxis of hMSC both decreased with increasing Ag-NPs concentrations. Different effects on the cytokine release from hMSCs were observed in the presence of Ag-NPs and Ag+ ions. The release of IL-8 was significantly increased at high but noncytotoxic concentrations of Ag-NPs (2.5 μg mL−1). In contrast, the levels of IL-6 and VEGF were concomitantly decreased compared to the control group. The synthesis of IL-11 was not affected at different Ag-NP concentrations. The agglomeration tendency of Ag-NPs in different biological media increased with a high electrolyte content, e.g., in RPMI. However, complexation with fetal calf serum in the cell culture media stabilized the Ag-NPs against agglomeration.
Conclusion
In summary, the results showed that Ag-NPs exert cytotoxic effects on hMSCs at high concentrations but also induce cell activation (as analyzed by the release of IL-8) at high but nontoxic concentrations of nanosilver.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lok C, Ho C, Chen R, He Q, Yu W, Sun H, Tam P, Chiu J, Che C (2007) Silver nanoparticles:partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J Biol Inorg Chem 12:527–534
Ahmed M, Karns M, Goodson M, Rowe J, Hussain S, Schlager J, Hong Y (2008) DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 233:404–410
Cho K, Park J, Osaka T, Park S (2005) The study of antimicrobial activity and preservative effects of nanosilver ingredient. Electrochim Acta 51:956–960
Jung W, Koo H, Kim K, Shin S, Kim S, Park Y (2008) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2171–2178
Kim J, Kuk E, Yu K, Kim J, Park S, Lee H, Kim S, Park Y, Park YH, Hwang C, Kim Y, Lee Y, Jeong D, Cho M (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3:95–101
Chen X, Schluesener HJ (2008) Nanosilver: A nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol Lett 176:1–12
Matsumura Y, Yoshikata K, Kunisaki S, Tsuchido T (2003) Mode of bactericidal action of silver zeolite and its comparison with that of silver nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4278–4281
Roe D, Karandikar B, Bonn-Savage N, Gibbins B, Roullet JB (2008) Antimicrobial surface functionalization of plastic catheters by silver nanoparticles. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:869–876
Gupta A, Matsui K, Lo JF, Silver S (1999) Molecular basis for resistance to silver cations in Salmonella. Nat Med 5:183–188
Morones J, Elechiguerra J, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri J, Ramirez J, Yacaman M (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver naoparticles.. Nanotechnology 16:2346–2353
Feng Q, Wu J, Chen G, Cui F, Kim T, Kim J (2000) A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Biomed Mater Res 52:662–668
Alt V, Bechert T, Steinrücke P, Wagener M, Seidel P, Dingeldein E, Domann E, Schnettler R (2004) An in vitro assessment of the antibacterial properties and cytotoxicity of nanoparticulate silver bone cement. Biomaterials 25:4383–4391
Kim K, Sung W, Moon S, Choi J, Kim J, Lee D (2008) Antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on dermatophytes. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1482–1484
Elechiguerra J, Burt J, Morones J, Camacho-Bragado A, Gao X, Lara HH, Yacaman J (2005) Interaction of silver nanoparticles with HIV-1. J Nanobiotechnology 3:6–15
Modak S, Sampath L, Fox C (1988) Combined topical use of silver sulfadiazine and antibiotics as a possible solution to bacterial resistance in burn wounds. J Burn Care Rehabil 9:359–363
Silver S (2003) Bacterial silver resistance: molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:341–353
Li X, Nikaido H, Williams K (1997) Silver-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli display active efflux of Ag+ and are deficient in porins. J Bacteriol 179:6127–6132
Pittenger M, Mackay A, Beck S, Jaiswal R, Douglas R, Mosca J, Moorman M, Simonetti D, Craig S, Marshak D (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Baksh D, Song L, Tuan RS (2004) Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med 8:301–316
Im S, Lee Y, Wiley B, Xia Y (2005) Large-scale synthesis of silver nanocubes: the role of HCl in promoting cube perfection and monodispersity. Angew Chem 44:2154–2157
Schildhauer T, Chapman J, Muhr G, Köller M (2006) Cytokine release of mononuclear leukocytes (PBMC) after contact to a carbonated calcium phosphate bone cement. J Biomed Mater Res 78:104–109
Murdock R, Braydich-Stolle L, Schrand A, Schlager J, Hussain S (2008) Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to in vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicol Sci 101:239–253
Mishima Y, Lotz M (2008) Chemotaxis of human articular chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res 26:1407–1412
Kim D, Yoo K, Choi K, Choi J, Choi S, Yang S, Yang Y, Im H, Kim K, Jung H, Sung K, Koo H (2005) Gene expression profile of cytokine and growth factor during differentiation of bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine 31:119–126
Griffitt R, Luo J, Gao J, Bonzongo J, Barber D (2008) Effects of particle composition ans species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1972–1978
Cohen M, Stern J, Vanni A, Kelley R, Baumgart E, Field D, Libertino J, Summerhayes I (2007) In vitro analysis of a nanocrystalline silver-coated surgical mesh. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 8:397–403
Tautenhahn J, Meyer F, Buerger T, Schmidt U, Lippert H, Koenig W, Koenig B (2008) Interaction of neutrophils with silver-coated vascular polyester grafts, Langenbecks Arch. Surg., in print
Roe D, Karandikar B, Bonn-Savage N, Gibbins B, Roullet J (2008) Antimicrobial surface functionalization ofplastic catheters by silver nanoparticles. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:869–876
Trop M, Novak M, Rodl S, Hellborn B, Kroell W, Goessler W (2003) Silver-coated dressing acticoat caused raised liver enzymes and argyria-like symptoms in burn patient. J Trauma 60:648–652
Navarro E, Piccapitra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42:8959–8964
Hsin Y, Chen C, Huang S, Shih T, Lai P, Chueh P (2008) The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 179:130–139
Carlson C, Hussain S, Schrand A, Braydich-Stollen K, Hess K, Jones R, Schlager J (2008) Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B 112:13608–13619
Braydich-Stollen L, Hussain S, Schlager J, Hofman M (2005) In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci 88:412–419
Panacek A, Kvitek L, Prucek R, Kolar M, Vecerova R, Pizurova N, Sharma V, Nevecna T, Zboril R (2006) Silver colloid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity. J Phys Chem B 110:16248–16253
T. Habijan, O. Bremm, S. Esenwein, G. Muhr, M. Köller (2007), Influence of nickel ions on human multipotent mesenchymal stem cells, Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech., 38
Fritz E, Glant T, Vermes C, Jacobs J, Roebuck K (2002) Titanium particles induce the immediate early stress responsive chemokines IL-8 and MCP-1 in osteoblasts. J Orthop Res 20:490–498
Blain T, Rosier R, Puzas J, Looney R, Reynolds P, Reynolds S, O’Keefe R (1996) Increased levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 protein and messenger RNA in human peripheral blood monocytes due to titantium particels. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78:1181–1192
Schmalz G, Schweikl H, Hiller K (2000) Release of prostaglandine E2, IL-6 and IL-8 from human oral epithelial culture models after exposure to compounds of dental materials. Eur J Oral Sci 108:442–448
Wataha J, Lockwood P, Schedle A, Noda M, Bouillaguet S (2002) Ag, Cu, Hg and Ni ions alter the metabolism of human monocytes during extended low-dose exposure. J Oral Rehabil 29:133–139
Wataha J, Lockwood P, Schedle A (2000) Effect of silver, copper, mercury, and nickel ions on cellular proliferation during extended, low-dose exposure. J Biomed Mater Res 52:360–364
Wagner M, Klein C, van Kooten T, Kirkpatrick C (1998) Mechanisms of cell activation by heavy metal ions. J Biomed Mater Res 42:443–452
Doty C, Tshikhudo R, Brust M, Fernig D (2005) Extremely stable water-soluble Ag nanoparticles. Chem Mater 17:4630–4635
Moskovits M, Vlckova B (2005) Adsorbate-induced silver nanoparticle aggregation kinetics. J Phys Chem B 109:14755–14758
Peters T (1996) All About Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics, and Medical Applications. ISBN:0-12-552110-3
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for financial support in the framework of the priority program NanoBioResponses (SPP 1313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
“Best of Abstracts – Chirurgisches Forum 2009, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Chirurgie”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greulich, C., Kittler, S., Epple, M. et al. Studies on the biocompatibility and the interaction of silver nanoparticles with human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). Langenbecks Arch Surg 394, 495–502 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-009-0472-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-009-0472-1