Abstract
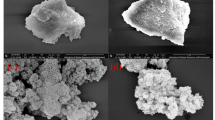
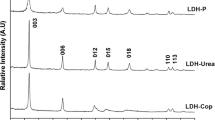
This article investigated sorption of toxic and carcinogenic arsenate (AsO4 3−) ions on positively charged surface of amorphous and nano crystalline MgFe-layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Based on Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), average size, and specific surface area of nano crystalline MgFe-LDHs, which was about range of about 50–200 nm and 90.2 m2/g, was lower and higher when compared to them of amorphous MgFe-LDHs, respectively. In addition, X-ray diffraction (XRD) peak and point of zero charge (PZC) of crystalline MgFe-LDHs was higher intensity and same, respectively, when compared to that of nano crystalline FeMg-LDHs. Adsorption rate of arsenate on amorphous MgFe-LDHs was a little faster when compared to that of nano crystalline MgFe-LDHs. In addition, as pH decreased, adsorption amount of arsenate on amorphous MgFe-LDHs increased significantly when compared to that of nano crystalline MgFe-LDHs. These results indicate that mechanism of arsenate in two materials was significantly different. We investigate sorption characteristic at pH 5, based on XRD and Fourier-transformed infrared (FTIR). In amorphous MgFe-LDHs, ferric arsenate precipitate was formed on surface of amorphous MgFe-LDHs and constituted the predominant surface arsenate. However, in nano crystalline MgFe-LDHs, arsenate was dominantly sorbed as a “non-surface-complexed” As–O bond on surface and anion exchange in interlayer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acro MD, Martin GC, Rives V (2001) FTIR study of isopropanol reactivity on calcined layered double hydroxides. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2001:119–126
Ay AN, Zümreoglu-Karan B, Temel A (2007) Boron removal by hydrotalcite-like, carbonate-free Mg–Al–NO3 −LDH and a rationale on the mechanism. Micropor Mesopor Mater 98(1–3):1–5
Bish DL (1980) Anion-exchange in takovite: applications to other hydroxide minerals. Bone Miner 103:170–175
Bujdoso T, Patzko A, Galbac Z, Dekany I (2009) Structural characterization of arsenate ion exchanged MgAl-layered double hydroxide. Appl Clay Sci 44:75–82
Carja G, Nakamura R, Niiyama H (2005) Tailoring the porous properties of iron containing mixed oxides for As(V) removal from aqueous solutions. Micropor Mesopor Mater 83:94–100
Carja G, Ratoi S, Ciobanu G, Balasanian I (2008) Uptake of As(V) from aqueous solution by anionic clays type FeLDHs. Desalination 223:243–248
Cavani F, Trifirb F, Vaccari A (1991) Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: preparation, properties and applications. Catal Today 11(2):173–301
Cummings DE, Caccavo JF, Fendorf S, Rosenzweig RF (1999) Arsenic mobilization by the dissimilatory Fe(III)-reducing bacterium Shewanella aiga BrY. Environ Sci Technol 33:723–729
Das HK, Mitra AK, Sengupta PK, Hossain A, Islam F, Rabbani GH (2004) Arsenic concentrations in rice, vegetables and fish in Bangladesh: a preliminary study. Environ Int 30:383–387
Ding Y, Gui Z, Zhu J, Hu Y, Wang Z (2008) Exfoliated poly(methyl methacrylate)/MgFe-layered double hydroxide nanocomposites with small inorganic loading and enhanced properties. Mater Res Bull 43:3212–3220
Evans DG, Duan X (2006) Preparation of layered double hydroxides and their applications as additives in polymers, as precursors to magnetic materials and in biology and medicine. Chem Commun 5:485–496
Gaboriaud F, Ehrhardt JJ (2003) Effects of different crystal faces on the surface charge of colloidal goethite (α-FeOOH) particles: an experimental and modeling study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67(5):967–983
Gasser MS, Mohsen HT, Aly HF (2008) Humic acid adsorption onto Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide. Colloids Surf A 331:195–201
Goh KH, Lim TT, Dong Z (2009) Enhanced arsenic removal by hydrothermally treated nanocrystalline Mg/Al layered double hydroxide with nitrate intercalation. Environ Sci Technol 43(7):2537–2543
Goldberg S, Johnston CT (2001) Mechanism of arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 234(1):204–216
Jia YF, Xu L, Fang Z, Demopoulos GP (2006) Observation of surface precipitation of arsenate on ferrihydrite. Environ Sci Technol 40(10):3248–3253
Kaltreider RC, Davis A, Lariviere JP, Hamilton JW (2001) Arsenic alters the function of the glucocorticoid receptor as a transcription factor. Environ Health Perspect 109:245–251
Lazarridis NK, Hourzemanoglou A, Matis KA (2002) Flotation of metal-loaded clay anion exchangers. Part II: The case of arsenates. Chemosphere 47(3):319–324
Li F, Duan X (2005) Application of layered double hydroxides. Struct Bond 119(1):193–223
Liang X, Hou W, Xu J (2009) Sorption of Pb(II) on Mg-Fe layered double hydroxide. Chin J Chem 27(10):1981–1988
Lloyd JR, Ormland RS (2006) Microbial transformations of arsenic in the environment: from soda lakes to aquifers. Elements 2:85–90
Myneni SCB, Traina SJ, Waychunas GA, Logan TJ (1998) Experimental and theoretical vibrational spectroscopic evaluation of arsenate coordination in aqueous solutions, solids and at mineral-water interfaces. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62(19–20):3285–3300
Prasanna SV, Vishnu KP (2009) Synthesis and characterization of arsenate-intercalated layered double hydroxides (LDHs): prospects for arsenic mineralization. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:439–445
Sherman DM, Randall S (2003) Surface complexation of arsenic(V) to iron(III) (hydro)oxides: structural mechanism from molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67(22):4223–4230
Singh S, Greene RM, Pisano MM (2009) Arsenate-induced apoptosis in murine embryonic maxillary mesenchymal cells via mitochondrial-mediated oxidative injury. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 88(1):25–34
Toraishi T, Nagasaki S, Tanaka S (2002) Adsorption behavior of IO3 − by CO3 2− and NO3 − hydrotalcite. Appl Clay Sci 22(1–2):17–23
Vacari A (1998) Preparation and catalytic properties of cationic and anionic clays. Catal Today 41(1–3):53–71
Wang SL, Hseu RJ, Chang RR, Chiang PN, Chen JH, Tzou YM (2006) Adsorption and thermal desorption of Cr(VI) on Li/Al layered double oxide. Colloids Surf A 277(1–3):8–14
Xu ZP, Braterman PS (2003) High affinity of dodecylbenzene sulfonate for layered double hydroxide and resulting morphologically changes. J Mater Chem 13:268–273
Xu ZP, Stevenson GS, Lu CQ, Lu GQ, Bartlett PF, Gray PP (2006) Stable suspension of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc 128(1):36–37
Yang L, Shahrivari Z, Liu PKT, Sahimi M, Tsotsis TT (2005) Removal of trace levels of arsenic and selenium from aqueous solutions by calcined and uncalcined layered double hydroxides (LDH). Ind Eng Chem Res 44(17):6804–6815
Yang L, Dadwhal M, Shahrivari Z, Ostwal M, Paul KT, Sahimi M, Tsotsis TT (2006) Adsorption of arsenic on layered double hydroxides: effect of particle size. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(13):4742–4751
Yong R, Warkentin BP (1990) Buffer capacity and lead retention in some clay materials. Water Air Pollut 53(1–2):53–67
You YW, Zhao HT, Vance GF (2001) Removal of arsenite from aqueous solutions by anionic clays. Environ Technol 22(12):1447–1457
Zhang M, Reardon EJ (2003) Removal of B, Cr, Mo, and Se from wastewater by incorporation into hydrocalumite and ettringite. Environ Sci Technol 37(13):2947–2952
Zhao H, Stanforth R (2001) Competitive adsorption of phosphate and arsenate on goethite. Environ Sci Technol 35(24):4753–4757
Zobrist J, Dowdle PR, Davis JA, Oremland RS (2000) Mobilization or arsenite by dissimilatory reduction of adsorbed arsenate. Environ Sci Technol 34:4747–4753
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JY., Kim, JH. Characterization of adsorbed arsenate on amorphous and nano crystalline MgFe-layered double hydroxides. J Nanopart Res 13, 887–894 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9936-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9936-z