Abstract
Background
The present study aimed to investigate the mechanisms through which long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) maternally expressed 3 (MEG3) affected the endothelial differentiation of mouse derived adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs).
Materials and methods
ADSCs were isolated and identified by specific surface marker detection. The effects of lncRNA MEG3 on endothelial differentiation of ADSCs were also detected via quantitative PCR, western blotting, immunofluorescence and Matrigel angiogenesis assays. In addition, using target gene prediction tools and luciferase reporter assays, the downstream target gene was demonstrated.
Results
LncRNA MEG3 targeted and reduced the expression levels of microRNA-145-5p (miR-145-5p), which upregulated the expression levels of Krüppel like factor 4 (KLF4), promoting endothelial differentiation of ADSCs.
Conclusion
LncRNA MEG3 induced endothelial differentiation of ADSCs by targeting miR-145-5p/KLF4, which may provide novel insights to illustrate the mechanism of endothelial differentiation of ADSCs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
An Y, Lin S, Tan X, Zhu S, Nie F, Zhen Y, Gu L, Zhang C, Wang B, Wei W, Li D, Wu J (2021) Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells and application to skin wound healing. Cell Prolif 54:e12993
Brassard JA, Lutolf MP (2019) Engineering stem cell self-organization to build better organoids. Cell Stem Cell 24:860–876
Fraser JK, Wulur I, Alfonso Z, Hedrick MH (2006) Fat tissue: an underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 24:150–154
Bukowska J, Szostek-Mioduchowska AZ, Kopcewicz M, Walendzik K, Machcinska S, Gawronska-Kozak B (2021) Adipose-derived stromal/stem cells from large animal models: from basic to applied science. Stem Cell Rev Rep 17:719–738
Zou ML, Liu SY, Sun ZL, Wu JJ, Yuan ZD, Teng YY, Feng Y, Yuan FL (2021) Insights into the role of adipose-derived stem cells: wound healing and clinical regenerative potential. J Cell Physiol 236:2290–2297
Mazini L, Rochette L, Amine M, Malka G (2019) Regenerative capacity of adipose derived stem cells (ADSCs), comparison with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Int J Mol Sci 20:2523
Han Y, Ren J, Bai Y, Pei X, Han Y (2019) Exosomes from hypoxia-treated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenesis through VEGF/VEGF-R. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 109:59–68
He T, Yang J, Liu P, Xu L, Lu Q, Tan Q (2021) Research progress of adipose-derived stem cells in skin scar prevention and treatment. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 35:234–240
Aich M, Chakraborty D (2020) Role of lncRNAs in stem cell maintenance and differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol 138:73–112
Mishra S, Verma SS, Rai V, Awasthee N, Chava S, Hui KM, Kumar AP, Challagundla KB, Sethi G, Gupta SC (2019) Long non-coding RNAs are emerging targets of phytochemicals for cancer and other chronic diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:1947–1966
Al-Rugeebah A, Alanazi M, Parine NR (2019) MEG3: an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Pathol Oncol Res 25:859–874
Hsieh PF, Yu CC, Chu PM, Hsieh PL (2021) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 in cellular stemness. Int J Mol Sci 22:5348
Sun H, Peng G, Wu H, Liu M, Mao G, Ning X, Yang H, Deng J (2020) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 is involved in osteogenic differentiation and bone diseases (Review). Biomed Rep 13:15–21
Ghafouri-Fard S, Moghadam MHB, Shoorei H, Bahroudi Z, Taheri M, Taheriazam A (2021) The impact of non-coding RNAs on normal stem cells. Biomed Pharmacother 142:112050
You D, Yang C, Huang J, Gong H, Yan M, Ni J (2019) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits chondrogenic differentiation of synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells by epigenetically inhibiting TRIB2 via methyltransferase EZH2. Cell Signal 63:109379
Li Z, Jin C, Chen S, Zheng Y, Huang Y, Jia L, Ge W, Zhou Y (2017) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via miR-140-5p. Mol Cell Biochem 433:51–60
Munoz M, Munoz MF, Ayala A (2017) Immunolocalization of substance P and NK-1 receptor in ADIPOSE stem cells. J Cell Biochem 118:4686–4696
Tseng YC, Roan JN, Ho YC, Lin CC, Yeh ML (2017) An in vivo study on endothelialized vascular grafts produced by autologous biotubes and adipose stem cells (ADSCs). J Mater Sci Mater Med 28:166
Yang Y, Cai Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Xu Z (2018) Exosomes secreted by adipose-derived stem cells contribute to angiogenesis of brain microvascular endothelial cells following oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro through microRNA-181b/TRPM7 axis. J Mol Neurosci 65:74–83
Bento LW, Zhang Z, Imai A, Nor F, Dong Z, Shi S, Araujo FB, Nor JE (2013) Endothelial differentiation of SHED requires MEK1/ERK signaling. J Dent Res 92:51–57
Sommerkamp P, Renders S, Ladel L, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Schonberger K, Zeisberger P, Przybylla A, Sohn M, Zhou Y, Klibanski A, Cabezas-Wallscheid N, Trumpp A (2019) The long non-coding RNA Meg3 is dispensable for hematopoietic stem cells. Sci Rep 9:2110
Huang X, Fu C, Liu W, Liang Y, Li P, Liu Z, Sheng Q, Liu P (2019) Chemerin-induced angiogenesis and adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes is mediated by lncRNA Meg3 through regulating Dickkopf-3 by sponging miR-217. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 385:114815
Chin DD, Poon C, Wang J, Joo J, Ong V, Jiang Z, Cheng K, Plotkin A, Magee GA, Chung EJ (2021) miR-145 micelles mitigate atherosclerosis by modulating vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. Biomaterials 273:120810
Zhu L, Zhang YJ, Wang B, Yang L, Zheng YQ, Sun LD, Tian L, Chen T, Wang JD (2021) PCDHB17P/miR-145-3p/MELK/NF-kappaB feedback loop promotes metastasis and angiogenesis of breast cancer. Front Oncol 11:660307
Wang J, Lin Y, Jiang DH, Yang X, He XG (2021) CircRNA ZNF609 promotes angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating miR-145/STMN1 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 37:686–698
Farina FM, Hall IF, Serio S, Zani S, Climent M, Salvarani N, Carullo P, Civilini E, Condorelli G, Elia L, Quintavalle M (2020) miR-128-3p is a novel regulator of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch and vascular diseases. Circ Res 126:e120–e135
Pan Y, Hui X, Hoo RLC, Ye D, Chan CYC, Feng T, Wang Y, Lam KSL, Xu A (2019) Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J Clin Invest 129:834–849
Jiang F, Chen Q, Wang W, Ling Y, Yan Y, Xia P (2020) Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis via microRNA-1. J Hepatol 72:156–166
Cantoni S, Bianchi F, Galletti M, Olivi E, Alviano F, Galie N, Ventura C (2015) Occurring of in vitro functional vasculogenic pericytes from human circulating early endothelial precursor cell culture. Stem Cells Int 2015:943671
Windmolders S, De Boeck A, Koninckx R, Daniels A, De Wever O, Bracke M, Hendrikx M, Hensen K, Rummens JL (2014) Mesenchymal stem cell secreted platelet derived growth factor exerts a pro-migratory effect on resident Cardiac Atrial appendage Stem Cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 66:177–188
Dong H, Jiang G, Zhang J, Kang Y (2021) MiR-506-3p promotes the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via targeting KLF4. Pathobiology 88:277–288
Qiu ZH, He J, Chai TC, Zhang YL, Zhou H, Zheng H, Chen XS, Zhang L, Li YM, Chen LW (2021) miR-145 attenuates phenotypic transformation of aortic vascular smooth muscle cells to prevent aortic dissection. J Clin Lab Anal 35:e23773
Gunasekharan V, Laimins LA (2013) Human papillomaviruses modulate microRNA 145 expression to directly control genome amplification. J Virol 87:6037–6043
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Nanjing Berke Biology Co., Ltd. provided technical support of adipose-derived stem cell separation technology.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Project of Heilongjiang (Grant Nos. ZHY2020-041 and ZHY19-062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ conceived and designed the analysis. GL, BW and LY performed the experiments. XM and XY analyzed and interpreted the data. XY drafted the manuscript. HZ confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All operations were approved by the Ethics Research Committee of the Heilongjiang Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (permit no. SY3R-2019004; Harbin, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2022_7671_MOESM1_ESM.tif
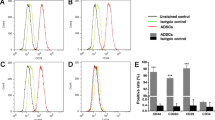
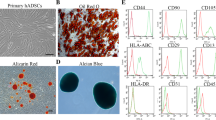
S1. Characterization of ADSCs. ADSCs were isolated from the adipose tissues. At the third passage, the expression levels of ADSCs markers (A) CD44 and CD90, and (B) CD31 and HLA-DR were analyzed via flow cytometry. ADSCs, adipose-derived stem cells; HLA-DR, major histocompatibility complex, class II antigen-associated. Supplementary file1 (TIF 4791 kb)
11033_2022_7671_MOESM2_ESM.tif
S2. Transfection efficiency in ADSCs. ADSCs were transfected with (A) sh-MEG3, (B) miR-145-5p mimic, (C) miR-145-5p inhibitor, (D) sh-KLF4 and (E) pc-MEG3 and qRT-PCR were conducted to measure the transfection efficiency 36 h post-transfection. Supplementary file2 (TIF 2081 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Liu, G., Mao, X. et al. LncRNA MEG3 induces endothelial differentiation of mouse derived adipose-derived stem cells by targeting MiR-145-5p/KLF4. Mol Biol Rep 49, 8495–8505 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07671-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07671-z