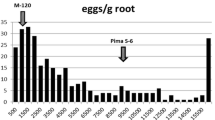
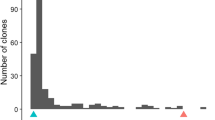
Abstract
Resistance to root-knot nematodes [Meloidogyne arenaria (Neal) Chitwood] is needed for cultivation of peanut in major peanut-growing areas, but significant resistance is lacking in the cultivated species (Arachis hypogaea L.). Markers to two closely-linked genes introgressed from wild relatives of peanut have been identified previously, but phenotypic evidence for the presence of additional genes in wild species and introgression lines has eluded quantitative trait locus (QTL) identification. Here, to improve sensitivity to small-effect QTLs, an advanced backcross population from a cross between a Florunner component line and the synthetic amphidiploid TxAG-6 [Arachis batizocoi × (A. cardenasii × A. diogoi)]4× was screened for response to root-knot nematode infection. Composite interval mapping results suggested a total of seven QTLs plus three putative QTLs. These included the known major resistance gene plus a second QTL on LG1, and a potentially homeologous B-genome QTL on LG11. Additional potential homeologs were identified on linkage group (LG) 8 and LG18, plus a QTL on LG9.2 and putative QTLs on LG9.1 and 19. A QTL on LG15 had no inferred resistance-associated homeolog. Contrary to expectation, two introgressed QTLs were associated with susceptibility, and QTLs at some homeologous loci were found to confer opposite phenotypic responses. Long-term functional conservation accompanied by rapid generation of functionally divergent alleles may be a singular feature of NBS-LRR resistance gene clusters, contributing to the richness of resistance alleles available in wild relatives of crops. The significance for peanut evolution and breeding is discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beavis WD (1998) QTL analyses: power, precision, and accuracy. In: Paterson AH (ed) Molecular dissection of complex traits. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 145–162
Bendezu IF, Starr JL (2003) Mechanism of resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in the peanut cultivar COAN. J Nematol 35:115–118
Bertioli DJ, Leal-Bertioli SCM, Lion MB, Santos VL, Pappas G Jr, Cannon SB, Guimarães PM (2003) A large scale analysis of resistance gene homologues in Arachis. Mol Genet Genomics 270:34–45
Bertioli D, Moretzsohn M, Madsen L, Sandal L, Leal-Bertioli S, Guimaraes P, Hougaard B, Fredslund J, Schauser L, Nielsen A, Sato S, Tabata S, Cannon S, Stougaard J (2009) An analysis of synteny of Arachis with Lotus and Medicago sheds new light on the structure, stability and evolution of legume genomes. BMC Genom 10:45
Burow MD, Simpson CE, Paterson AH, Starr JL (1996) Identification of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) RAPD markers diagnostic of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne arenaria (Neal) Chitwood) resistance. Mol Breed 2:307–319
Burow MD, Simpson CE, Starr JL, Paterson AH (2001) Transmission genetics of chromatin from a synthetic amphidiploids to cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.): broadening the gene pool of a monophyletic polyploid species. Genetics 159:823–837
Caillaud MC, Dubreuil G, Quentin M, Perfus-Barbeoch L, Lecomte P, Almeida Engler J, Abad P, Rosso MN, Favery B (2008) Root-knot nematodes manipulate plant cell functions during a compatible interaction. J Plant Physiol 165:104–113
Cason JM, Simpson CE, Starr JL, Burow MD (2010) Marker-assisted selection in the transfer of root-knot nematode resistance in the commercial peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Tex J Sci 62:49–58
Chittenden LM, Schertz KF, Lin YR, Wing RA, Paterson AH (1994) RFLP mapping of a cross between Sorghum bicolor and S. propinquum, suitable for high-density mapping, suggests ancestral duplication of sorghum chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 87:925–933
Choi K, Burow MD, Church G, Burow G, Paterson AH, Simpson CE, Starr J (1999) Genetics and mechanism of resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in peanut germplasm. J Nematol 31:283–290
Chu Y, Holbrook CC, Timper P, Ozias-Akins P (2007) Development of a PCR-based molecular marker to select for nematode resistance in peanut. Crop Sci 47:841–847
Chu Y, Wu CL, Holbrook CC, Tillman BL, Person G, Ozias-Akins P (2011) Marker-assisted selection to pyramid nematode resistance and the high oleic trait in peanut. Plant Genome 4:110–117
Church GT, Simpson CE, Burow MD, Paterson AH, Starr JL (2000) RFLP markers for identification of resistance genotype in peanut. Nematology 2:575–580
Church GT, Starr JL, Simpson CE (2005) A recessive gene for resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in interspecific Arachis spp. hybrids. J Nematol 37:178–184
Cook DE, Lee TG, Guo X, Melito S, Wang K, Bayless AM, Wang J, Hughes TJ, Willis DK, Clemente TE, Diers BW, Jiang J, Hudson ME, Bent AF (2012) Copy number variation of multiple genes at Rhg1 mediates nematode resistance in soybean. Science 338:1206–1209
Dickson DW (1998) Peanut. In: Barker KR, Pederson GA, Windham GL (eds) Plant and nematode interactions. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 523–566
Garcia GM, Stalker HT, Shroeder E, Kochert G (1996) Identification of RAPD, SCAR, and RFLP markers tightly linked to nematode resistance genes introgressed from Arachis cardenasii into Arachis hypogaea. Genome 39:836–845
Guimarães PM, Garsmeur O, Proite K, Leal-Bertioli SCM, Seijo G, Chaine C, Bertioli DJ, D’Hont A (2008) BAC libraries construction from the ancestral diploid genomes of the allotetraploid cultivated peanut. BMC Plant Biol 8:14
Guimarães PM, Brasileiro ACM, Proite K, Araujo ACG, Leal-Bertioli SCM, Pic-Taylor A, Silva FR, Morgante CV, Ribeiro SG, Bertioli DJ (2010) A study of gene expression in the nematode resistant wild peanut relative, Arachis stenosperma, in response to challenge with Meloidogyne arenaria. Trop Plant Biol 3:183–192
Holbrook CC, Noe JP (1992) Resistance to the peanut root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne arenaria) in Arachis hypogaea. Peanut Sci 19:35–37
Holbrook CC, Timper P, Culbreath AK, Kvien CK (2008) Registration of ‘Tifguard’ peanut. J. Plant Regist 2:92–94
Lambert KN, Ferrie BJ, Nombela G, Brenner ED, Williamson VM (1999) Identification of genes whose transcripts accumulate rapidly in tomato after root-knot nematode infection. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 55:341–348
Larson SR, Mayland HF (2007) Comparative mapping of fiber, protein, and mineral content QTLs in two interspecific Leymus wild rye full-sib families. Mol Breed 20:331–347
Leal-Bertioli SCM, José ACVF, Alves-Freitas DMT, Moretzsohn MC, Guimarães PM, Nielen S, Vidigal BS, Pereira RW, Pike J, Fávero AP, Parniske M, Varshney RK, Bertioli DJ (2009) Identification of candidate genome regions controlling disease resistance in Arachis. BMC Plant Biol 9:112
Leal-Bertioli SCM, Farias MP, Silva PT, Guimarães PM, Brasileiro ACM, Bertioli DJ, Araujo ACG (2010) Ultrastructure of the initial interaction of Puccinia arachidis and Cercosporidium personatum with leaves of Arachis hypogaea and Arachis stenosperma. J Phytopathol 158:792–796
Liu B-H (1998) QTL mapping: interval mapping, chapter 14. In: Statistical genomics: linkage, mapping, and QTL analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Liu S, Kandoth PK, Warren SD, Yeckel G, Heinz R, Alden J, Yang C, Jamai A, El-Mellouki T, Juvale PS, Hill J, Baum TJ, Cianzio S, Whitham SA, Korkin D, Mitchum MG, Meksem K (2012) A soybean cyst nematode resistance gene points to a new mechanism of plant resistance to pathogens. Nature 492:256–260
Milligan SB, Bodeau J, Yaghoobi J, Kaloshian I, Zabel P, Williamson VM (1998) The root knot nematode resistance gene Mi from tomato is a member of the leucine zipper, nucleotide binding, leucine-rich repeat family of plant genes. Plant Cell 10:1307–1320
Morgante CV, Brasileiro ACM, Roberts PA, Leal-Bertioli SCM, Bertioli DJ, Guimarães PM (2011) Transcriptome analysis of Arachis stenosperma for identification of resistance genes to Meloidogyne arenaria. Adv Arachis Through Genomics Biotechnol 5:37
Nagy ED, Chu Y, Guo Y, Khanal S, Tang S, Li Y, Dong WB, Timper P, Taylor C, Ozias-Akins P, Holbrook CC, Beilinson V, Nielsen NC, Stalker HT, Knapp SJ (2010) Recombination is suppressed in an alien introgression in peanut harboring Rma, a dominant root-knot nematode resistance gene. Mol Breed 26:357–370
Nelson SC, Simpson CE, Starr JL (1989) Resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in Arachis spp. germplasm. J Nematol 21:654–660
Nelson SC, Starr JL, Simpson CE (1990) Expression of resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in Arachis batizocoi and A. cardenasii. J Nematol 22:242–244
Norden AJ, Lipscomb RW, Carver WA (1969) Registration of ‘Florunner’ peanuts. Crop Sci 9:850
Potenza C, Thomas SH, Sengupta-Gopalan C (2001) Genes induced during early response to Meloidogyne incognita in roots of resistant and susceptible alfalfa cultivars. Plant Sci 161:289–299
Proite K, Carneiro R, Falcão R, Gomes A, Leal-Bertioli S, Guimarães P, Bertioli D (2008) Post-infection development and histopathology of Meloidogyne arenaria race 1 on Arachis spp. Plant Pathol 57:974–980
Ratnaparkhe MB, Wang X, Li J, Compton RO, Rainville LK, Lemke C, Kim C, Tang H, Paterson AH (2011) Comparative analysis of peanut NBS-LRR gene clusters suggests evolutionary innovation among duplicated domains and erosion of gene microsynteny. New Phytol 192:164–178
Santos SP, Dantas K, Leal-Bertioli SCM, Nielen S, Moretzsohn MC, Guimarães PM, Micas G, Bertioli DJ (2011) New synthetic tetraploids for the introgression of wild alleles into cultivated peanut. Adv Arachis Through Genomics Biotechnol 5:33
Simpson CE (1991) Pathways for introgression of pest resistance into Arachis hypogaea L. Peanut Sci 18:22–26
Simpson CE, Starr JL (2001) Registration of ‘COAN’ peanut. Crop Sci 41:918
Simpson CE, Nelson SC, Starr J, Woodward KE, Smith OD (1993) Registration of TxAG-6 and TxAG-7 peanut germplasm lines. Crop Sci 33:1418
Simpson CE, Starr JL, Church GT, Burow MD, Paterson AH (2003) Registration of ‘NemaTAM’ peanut. Crop Sci 43:1561
Simpson CE, Starr JL, Baring MR, Burow MD, Cason JM, Wilson JN (2013) Registration of ‘Webb’ peanut. J. Plant Regist 7:265–268
Stalker HT, Moss JP (1987) Speciation, cytogenetics and utilization of Arachis species. Adv Agron 41:1–39
Starr JL, Simpson CE (1991) Segregation of resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in progeny of interspecific hybrids. Proc Am Peanut Res Educ Soc 23:23 (abstr)
Starr JL, Schuster GL, Simpson CE (1990) Characterization of the resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in an interspecific Arachis spp. hybrid. Peanut Sci 17:106–108
Vinod K (2006) Mapping of quantitative trait loci. In: Proceedings of the training programme “Innovative quantitative traits – approaches and applications in plant breeding”. Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India, pp 224–242
Wang G, Paterson AH (1994) Prospects for using DNA pooling strategies to tag QTLs with DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 88:355–361
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2007) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC
Yuan M, Gong L, Meng R, Li S, Dang P, Gao B, He G (2009) Development of trinucleotide (GGC)n SSR markers in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Electron J Biotechnol 13(6):5–6
Yüksel B, Paterson AH (2005) Construction and characterization of a peanut HindIII BAC library. Theor Appl Genet 111:630–639
Yüksel B, Estill JC, Schulze SR, Paterson AH (2005) Organization and evolution of resistance gene analogs in peanut. Mol Genet Genomics 274:248–263
Acknowledgments
Aspects of this work were supported funds from the Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Enhancement Project, Granted to J.L.S., C.E.S., and A.H.P.; by United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)—National Research Initiative Competitive Grants Program (NRICGP) Grants 95-37302-2150 to J.L.S., M.D.B., A.H.P., and C.E.S.; by USDA-NRICGP grant 97-35300-4584 to C.E.S., A.H.P., and J.L.S.; by USDA-NRICGP Grant 98-35302-6879 to J.L.S., C.E.S., A.H.P., and M.D.B.; by the Texas Advanced Technology Program Grant 999902-094 to C.E.S., J.L.S., A.H.P., and M.D.B., and by GoldKist, Inc. to A.H.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2014_42_MOESM3_ESM.ppt
Supplementary Figure 1. Galling and damage to roots (A) and pods (B) of peanut, caused by Meloidogyne arenaria. (PPT 172 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burow, M.D., Starr, J.L., Park, CH. et al. Introgression of homeologous quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to the root-knot nematode [Meloidogyne arenaria (Neal) Chitwood] in an advanced backcross-QTL population of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Mol Breeding 34, 393–406 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0042-2