Abstract
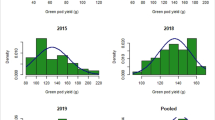
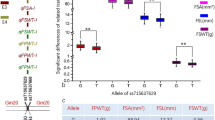
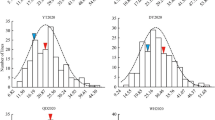
Common bean is an important vegetable legume in many regions of the world. Size and color of fresh pods are the key factors for deciding the commercial acceptance of bean as a fresh vegetable. The genetic basis of important horticultural traits of common bean is still poorly understood, which hinders DNA marker-assisted breeding in this crop. Here we report the identification of single-locus and epistatic quantitative trait loci (QTLs), as well as their environment interaction effects for six pod traits, namely width, thickness, length, size index, beak length and color, using an Andean intra-gene pool recombinant inbred line population from a cross between a cultivated common bean and an exotic nuña bean. The QTL analyses performed detected a total of 23 QTLs (single-locus QTLs and epistatic QTLs): five with only individual additive effects and six with only epistatic effects, while the remaining twelve showed both effects. These QTLs were distributed across linkage groups (LGs) 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11; particularly noteworthy are the QTLs for pod size co-located on LGs 1 and 4, indicative of tight linkage or genes with pleiotropic effects governing these traits. Overall, the results obtained showed that additive and epistatic effects are the major genetic basis of pod size and color traits. The mapping of QTLs including epistatic loci for the six pod traits evaluated provides support for implementing marker-assisted selection toward genetic improvement of common bean.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andargie M, Pasquet RS, Gowda BS, Muluvi GM, Timko MP (2011) Construction of a SSR-based genetic map and identification of QTL for domestication traits using recombinant inbred lines from a cross between wild and cultivated cowpea (V. unguiculata (L.) Walp.). Mol Breed 28:413–420. doi:10.1007/s11032-011-9598-2
Bassett MJ (1996) List of genes—Phaseolus vulgaris L. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 39:1–19
Bassett MJ (2005) A new gene (Prpi-2) for intensified anthocyanin expression (IAE) syndrome in common bean and a reconciliation of gene symbols used by early investigators of gene symbols for purple pod and IAE syndrome. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 130:550–554
Beattie AD, Larsen J, Michaels TE, Pauls KP (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for a common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) ideotype. Genome 46:411–422. doi:10.1139/g03-015
Blair MW, Iriarte G, Beebe S (2006) QTL analysis of yield traits in an advanced backcross population derived from a cultivated Andean wild common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cross. Theor Appl Genet 112:1149–1163. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0217-2
Davis JW, Kean D, Yorgey B, Fourie D, Miklas PN, Myers JR (2006) A molecular marker linkage map of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 49:73–74
De Ron AM, Casquero PA, González AM, Santalla M (2004) Environmental and genotypic effects on pod characteristics related to common bean quality. J Agron Crop Sci 190:248–255
Drijfhout E (1978) Inheritance of temperature-dependent string formation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Neth J Agric Sci 26:99–105
Erdmann PM, Lee RK, Bassett MJ, McClean PE (2002) A molecular marker tightly linked to P, a gene required for flower and seed coat color in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), contains the Ty3-gypsy retrotransposon Tpv3g. Genome 45:728–736. doi:10.1139/g02-037
Galeano CH, Fernandez AC, Franco-Herrera N, Cichy KA, McClean PE (2011) Saturation of an intra-gene pool linkage map: towards a unified consensus linkage map for fine mapping and synteny analysis in common bean. PLoS One 6:12. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028135
Gepts P (1988) A Middle American and an Andean common bean gene pool. Curr Plant Sci Biotechnol Agric 6:375–390
Gepts P (2004) Crop domestication as a long time selection experiment. Plant Breed Rev 24:1–44. doi:10.1002/9780470650288.ch1
Gepts P, Debouck D (1991) Origin, domestication, and evolution of the common bean. In: Voysest O, Van Schoonhoven A (eds) Common beans: research for crop improvement. CAB, Oxon, pp 7–53
Govindaraj P, Vinod KK, Arumugachamy S, Maheswaran M (2009) Analysing genetic control of cooked grain traits and gelatinization temperature in a double haploid population of rice by quantitative trait loci mapping. Euphytica 166:165–176. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9808-0
Guzman-Maldonado SH, Martínez O, Acosta-Gallegos JA, Guevara-Lara F, Paredes-López O (2003) Putative quantitative trait loci for physical and chemical components of common bean. Crop Sci 43:1029–1035. doi:10.2135/cropsci 2003.1029
Holland JB (2001) Epistasis and plant breeding. Plant Breed Rev 21:27–82. doi:10.1002/9780470650196.ch2
Holland JB (2007) Genetic architecture of complex traits in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:156–161. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2007.01.003
Isemura T, Kaga A, Konishi S, Ando T, Tomooka N, Han OK, Vaughan DA (2007) Genome dissection of traits related to domestication in azuki bean (Vigna angularis) and their comparison with other warm season legumes. Ann Bot 100:1053–1071. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm155
Isemura T, Kaga A, Tomooka N, Shimizu T, Vaughan DA (2010) Construction of a genetic linkage map and genetic analysis of the domestication related traits in rice bean (Vigna umbellata). Ann Bot 106:927–944. doi:10.1093/aob/mcq188
Johnson WC, Gepts P (2002) The role of epistasis in controlling seed yield and other agronomic traits in an Andean × Mesoamerican cross of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Euphytica 125:69–79
Kaga A, Isemura T, Tomooka N, Vaughan DA (2008) The genetics of domestication of azuki bean (Vigna angularis). Genetics 178:1013–1036. doi:10.1534/genetics.107.078451
Kang ST, Kwak M, Kim HK, Choung MG, Han WY, Baek IY, Kim MY, Van K, Lee SH (2009) Population-specific QTLs and their different epistatic interactions for pod dehiscence in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Euphytica 166:15–24. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9810-6
Kelly JD, Vallejo VA (2004) A comprehensive review of the major genes conditioning resistance to anthracnose in common bean. HortScience 39:1196–1207
Kelly JD, Gepts P, Miklas PN, Coyne DP (2003) Tagging and mapping of genes and QTL and molecular-marker assisted selection for traits of economic importance in bean and cowpea. Field Crop Res 82:135–154. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00034-0
Koinange EMK, Singh SP, Gepts P (1996) Genetic control of the domestication syndrome in common bean. Crop Sci 36:1037–1045
Kongjaimun A, Kaga A, Tomooka N, Somta P, Shimizu T, Shu Y, Isemura T, Vaughan DA, Srinives P (2012a) An SSR-based linkage map of yardlong bean (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. subsp. unguiculata Sesquipedalis Group) and QTL analysis of pod length. Genome 55:81–92. doi:10.1139/g11-078
Kongjaimun A, Kaga A, Tomooka N, Somta P, Vaughan DA, Srinives P (2012b) The genetics of domestication of yardlong bean, Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. ssp. unguiculata cv.-gr. sesquipedalis. Ann Bot 109:1185–1200. doi:10.1093/aob/mcs048
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Leakey CLA (1988) Genotypic and phenotypic markers in common bean. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic resources of Phaseolus beans. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 245–347
Liu B, Fujita T, Yan ZH, Sakamoto S, Xu D, Abe J (2007) QTL mapping of domestication-related traits in soybean (Glycine max). Ann Bot 100:1027–1038. doi:10.1093/aob/mcm149
McClean PE, Lee RK, Otto C, Gepts P, Bassett MJ (2002) Molecular and phenotypic mapping of genes controlling seed coat pattern and color in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 93:148–152. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.2.148
McClean PE, Cannon S, Gepts P, Hudson M, Jackson S, Rokhsar D, Schmutz J, Vance C (2009) Towards a whole genome sequence of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): background, approaches, applications. http://www.csrees.usda.gov/business/reporting/stakeholder/pdfs/pl_common_bean.pdf. Accessed 26 Dec 2013
Miklas PN, Porch T (2010) Guidelines for common bean QTL nomenclature. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 53:202–204
Myers JR, Bagget JR (1999) Improvement of snap beans. In: Singh SP (ed) Common bean improvement in the twenty-first century. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 289–329
Myers JR, Davis J, Yorgey B, Kean D (2004) Mapping quantitative trait loci for green bean traits of horticultural importance. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 47:75–76
Okonkwo CA, Clayberg CD (1984) Genetics of flower and pod color in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Hered 75:440–444
Park SO, Coyne DP, Jung G, Skroch PW, Arnaud-Santana E, Steadman JR, Ariyarathne HM, Nienhuis J (2000) Mapping of QTL for seed size and shape traits in common bean. J Am Soc Hort Sci 125:466–475
Parvez AS, Rather AG, Warsi MZK (2007) Implications of epistasis in maize breeding. Int J Plant Breed Genet 1:1–11. doi:10.3923/ijpbg.2007.1.11
Pedrosa-Harand A, Porch T, Gepts T (2008) Standard nomenclature for common bean chromosomes and linkage groups. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 51:106–107
Pérez-Vega E, Pañeda A, Rodríguez-Suárez C, Campa A, Giraldez R, Ferreira JJ (2010) Mapping of QTLs for morpho-agronomic and seed quality traits in a RIL population of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 120:1367–1380. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1261-5
Phillips PC (2008) Epistasis—the essential role of gene interactions in the structure and evolution of genetic systems. Nat Rev Genet 9:855–867. doi:10.1038/nrg2452
Prakken R (1934) Inheritance of colours and pod characters in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetica 16:177–294
Silbernagel MJ (1986) Snap bean breeding. In: Bassett M (ed) Breeding vegetable crops. AVI, Westport, CT, pp 243–282
Singh SP (1989) Patterns of variation in cultivated common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae). Econ Bot 43:39–57
Smartt J (1976) Tropical pulses. Longman, London, p 348
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066. doi:10.1126/science.277 5329.1063
Tar’an B, Michaels TE, Pauls KP (2002) Genetic mapping of agronomic traits in common bean. Crop Sci 42:544–556. doi:10.2135/cropsci 2002.5440
Tsai SM, Nodari RO, Moon DH, Camargo LEA, Vencovsky R, Geps P (1998) QTL mapping for nodule number and common bacterial blight in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Soil 204:135–145
Vallejos CE, Sakiyama NS, Chase CD (1992) A molecular-marker-based linkage map of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetics 131:733–740
van Ooijen JH (2006) JoinMap®4, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
VandenLangenberg KM, Bethke PC, Nienhuis J (2012) Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with fructose, glucose, and sucrose concentration in snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) pods. Crop Sci 52:1593–1599. doi:10.2135/cropsci2011.07.0396
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wang CS, Rutledge JJ, Gianola D (1994) Bayesian analysis of mixed linear models via Gibbs sampling with an application to litter size in Iberian pigs. Genet Sel Evol 26:91–115. doi:10.1186/1297-9686-26-2-91
Xu P, Wu X, Wang B, Hu T, Lu Z, Liu Y, Qin D, Wang S, Li G (2013) QTL mapping and epistatic interaction analysis in asparagus bean for several characterized and novel horticulturally important traits. BMC Genet 14:4. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-14-4
Yang J, Hu CC, Hu H, Yu RD, Xia Z, Ye XZ, Zhu J (2008) QTLNetwork: mapping and visualizing genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 24:721–723. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm494
Yuste-Lisbona FJ, Santalla M, Capel C, García-Alcázar M, De La Fuente M, Capel J, De Ron AM, Lozano R (2012) Marker-based linkage map of Andean common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and mapping of QTLs underlying popping ability traits. BMC Plant Biol 12:136. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-136
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and UE-FEDER Program (AGL2011-25562). We thank Junta de Andalucía (Grant Number P10-AGR-06931) and Campus de Excelencia Internacional Agroalimentario-CeiA3 for partially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fernando J. Yuste-Lisbona and Ana M. González have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuste-Lisbona, F.J., González, A.M., Capel, C. et al. Genetic variation underlying pod size and color traits of common bean depends on quantitative trait loci with epistatic effects. Mol Breeding 33, 939–952 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-0008-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-0008-9