Abstract
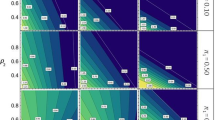
Selective genotyping of individuals from the two tails of the phenotypic distribution of a population provides a cost efficient alternative to analysis of the entire population for genetic mapping. Past applications of this approach have been confounded by the small size of entire and tail populations, and insufficient marker density, which result in a high probability of false positives in the detection of quantitative trait loci (QTL). We studied the effect of these factors on the power of QTL detection by simulation of mapping experiments using population sizes of up to 3,000 individuals and tail population sizes of various proportions, and marker densities up to one marker per centiMorgan using complex genetic models including QTL linkage and epistasis. The results indicate that QTL mapping based on selective genotyping is more powerful than simple interval mapping but less powerful than inclusive composite interval mapping. Selective genotyping can be used, along with pooled DNA analysis, to replace genotyping the entire population, for mapping QTL with relatively small effects, as well as linked and interacting QTL. Using diverse germplasm including all available genetics and breeding materials, it is theoretically possible to develop an “all-in-one plate” approach where one 384-well plate could be designed to map almost all agronomic traits of importance in a crop species. Selective genotyping can also be used for genomewide association mapping where it can be integrated with selective phenotyping approaches. We also propose a breeding-to-genetics approach, which starts with identification of extreme phenotypes from segregating populations generated from multiple parental lines and is followed by rapid discovery of individual genes and combinations of gene effects together with simultaneous manipulation in breeding programs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barua UM, Chalmers KJ, Hackett CA, Thomas WT, Powell W, Waugh R (1993) Identification of RAPD markers linked to a Rhynchosporium secalis resistance locus in barley using near-isogenic lines and bulked segregant analysis. Heredity 71:177–184
Brohede J, Dunne R, Mckay JD, Hannan GN (2005) PPC: an algorithm for accurate estimation of SNP allele frequencies in small equimolar pools of DNA using data from high density microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e142
Buckler SE, Holland JB, McMullen MM, Kresovich S, Acharya C, Bradbury P, Brown P, Browne C, Eller M, Ersoz E, Flint-Garcia S, Garcia A, Glaubitz J, Goodman M, Harjes C, Hutchins K, Kroon D, Larsson S, Lepak N, Li H, Mitchell S, Pressoir G, Peiffer J, Rosas MO, Rocheford T, Romay C, Romero S, Salvo S, Sanchez Villeda H, Sun Q, Tian F, Upadyayula N, Ware D, Yates H, Yu J, Zhang Z (2009) The genetic architecture of maize flowering time. Science 325:714–718
Charcosset A, Gallais A (1996) Estimation of the contribution of quantitative trait loci (QTL) to the variance of quantitative trait by means of genetic markers. Theor Appl Genet 93:1193–1201
Coque M, Gallais A (2006) Genomic regions involved in response to grain yield selection at high and low nitrogen fertilization in maize. Theor Appl Genet 112:1205–1220
Darvasi A, Soller M (1992) Selective genotyping for determination of linkage between a marker locus and a quantitative trait locus. Theor Appl Genet 85:353–359
Darvasi A, Soller M (1994) Selective DNA pooling for determination of linkage between a molecular marker and a quantitative trait. Genetics 138:1365–1373
Darvasi A, Weinreb A, Minke V, Wellert JI, Soller M (1993) Detecting marker-QTL linkage and estimating QTL gene effect and map location using a saturated genetic map. Genetics 134:943–951
Docherty SJ, Butcher LM, Schalkwyk LC, Plomin R (2007) Applicability of DNA pools on 500K SNP microarrays for cost-effective initial screens in genome wide association studies. BMC Genomics 8:214
Dudley JW (2004) 100 generations of selection for oil and protein in corn. Plant Breed Rev 24(Part 1):79–110
Dunninnton EA, Haberefeld A, Stallard LG, Siegel PB, Hillel J (1992) Deoxyribonucleic-acid fingerprint bands linked to loci coding for quantitative traits in chicken. Poult Sci 71:1251–1258
Edwards MD, Stuber CW, Wendel JF (1987) Molecular-marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. I. Numbers, genomic distribution and types of gene action. Genetics 116:113–125
Foolad MR, Jones RA (1993) Mapping salt-tolerance genes in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) using trait-based marker analysis. Theor Appl Genet 87:184–192
Gallais A, Moreau L, Charcosset A (2007) Detection of marker–QTL associations by studying change in marker frequencies with selection. Theor Appl Genet 114:669–681
Gao S, Martinez C, Skinner DJ, Krivanek AF, Crouch JH, Xu Y (2008) Development of a seed DNA-based genotyping system for marker-assisted selection in maize. Mol Breed 22:477–494
Giovannoni JJ, Wing RA, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD (1991) Isolation of molecular markers from specific chromosomal interval using DNA pools from existing mapping populations. Nucleic Acid Res 19:6553–6558
Hillel J, Avner R, Baxter-Jones C, Dunnington EA, Cahaner A, Siegel PB (1990) DNA fingerprints from blood mixes in chickens and turkeys. Anim Biotech 2:201–204
Hormaza JI, Dollo L, Polito VS (1994) Identification of a RAPD marker linked to sex determination in Pistacia vera using bulked segregant analysis. Theor Appl Genet 89:9–13
Jannink JL (2005) Selective phenotyping to accurately mapping quantitative trait loci. Crop Sci 45:901–908
Jin C, Lan H, Attie AD, Churchill GA, Bulutuglo D, Yandell BY (2004) Selective phenotyping for increased efficiency in genetic mapping study. Genetics 168:2285–2293
Knight J, Sham P (2006) Design and analysis of association studies using pooled DNA from large twin samples. Behav Genet 36:665–677
Korol A, Frenkel Z, Cohen L, Lipkin E, Soller M (2007) Fractioned DNA pooling: a new cost-effective strategy for fine mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 176:2611–2623
Kruglyak L (2008) The road to genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 9:314–318
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lebowitz RL, Soller M, Beckmann JS (1987) Trait-based analysis for the detection of linkage between marker loci and quantitative trait loci in cross between inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 73:556–562
Li H, Ye G, Wang J (2007) A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175:361–374
Li H, Ribaut JM, Li Z, Wang J (2008) Inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) for digenic epistasis of quantitative traits in biparental populations. Theor Appl Genet 116:243–260
Macgregor S, Zhao ZZ, Henders A, Nicholas MG, Montgomery GW, Visscher PM (2008) Highly cost-efficient genome-wide association studies using DNA pools and dense SNP arrays. Nucleic Acids Res 36(6):e35
McCarthy MI, Abecasis GR, Cardon LR, Goldstein DB, Little J, Ioannidis JPA, Hirschhorn JN (2008) Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: consensus, uncertainty and challenges. Nat Rev Genet 9:356–369
Meaburn E, Butcher LM, Schalkwyk LC, Plomin R (2006) Genotyping pooled DNA using 100 K SNP microarrays: a step towards genomoewide association scans. Nucleic Acids Res 34(4):e28
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance gene by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Moreau L, Charcosset A, Gallais A (2004) Experimental evaluation of several cycles of marker-assisted selection in maize. Euphytica 137:111–118
Navabi A, Mather DE, Bernier J, Spaner DM, Atlin AN (2009) QTL detection with bidirectional and unidirectional selective genotyping: marker-based and trait-based analyses. Theor Appl Genet 118:347–358
Plotsky Y, Cahaner A, Haberfeld A, Lavi U, Lamont SJ, Hillel J (1993) DNA fingerprint bands applied to linkage analysis with quantitative trait loci in chickens. Anim Genet 24:105–110
Quarrie SA, Lazić-Jančić V, Kovačević D, Steed A, Pekić S (1999) Bulk segregant analysis with molecular markers and its use for improving drought resistance in maize. J Exp Bot 50:1299–1306
Sham P, Bader JS, Craig I, O’Donovan M, Owen M (2002) DNA pooling: a tool for large-scale association studies. Nat Rev Genet 3:862–871
Shifman S, Johannesson M, Bronstein M, Chen SX, Collier DA, Craddock NJ, Kendler KS, Li T, O’Donovan M, O’Neill FA, Owen MJ, Walsh D, Weinberger DR, Sun C, Flint J, Darvasi A (2008) Genome-wide association identifies a common variant in the reelin gene that increases the risk of schizophrenia only in women. PLoS Genet 4(2):e28
Soller M, Beckmann JS (1990) Marker-based mapping of quantitative trait loci using replicated progenies. Theor Appl Genet 80:205–208
Stuber CW, Moll RH, Goodman MM, Schaffer HE, Weir BS (1980) Allozyme frequency changes associated with selection for increased grain yield in maize (Zea mays). Genetics 95:225–336
Stuber CW, Goodman MM, Moll RH (1982) Improvement of yield and ear number resulting from selection at allozyme loci in a maize population. Crop Sci 22:737–740
Tinker NA, Mather DE, Rossnagel BG, Kasha KJ, Kleinhofs A, Hayes PM, Falk DE, Ferguson T, Shugar LP, Legge WG, Irvine RB, Choo TM, Briggs KG, Ullrich SE, Franckowiak JD, Blake TK, Graf RJ, Dofing SM, Saghai Maroof MA, Scoles GJ, Hoffman D, Dahleen LS, Kilian A, Chen F, Biyashev RM, Kudrna DA, Steffenson BJ (1996) Regions of the genome that affect agronomic performance in two-row barley. Crop Sci 36:1053–1062
van Treuren R (2001) Efficiency of reduced primer selectivity and bulked DNA analysis for the rapid detection of AFLP polymorphisms in a range of crop species. Euphytica 117:27–37
Villar M, Lefevre F, Bradshaw HD Jr, du-Cros ET (1996) Molecular genetics of rust resistance in Poplars (Melampsora larici-populina Kleb/Populus sp.) by bulked segregant analysis in a 2 × 2 factorial mating design. Genetics 143:531–536
Wang J (2009) Inclusive composite interval mapping of quantitative trait genes. Acta Agronomica Sinica 35(2):239–245
Wilkening S, Chen B, Wirtenberger M, Burwinkel B, Försti A, Hemminki K, Canzian F (2007) Allelotyping of pooled DNA with 250 K SNP microarrays. BMC Genomics 8:77
Wingbermuehle WJ, Gustus C, Smith KP (2004) Exploiting selective genotyping to study genetic diversity of resistance to Fusarium head blight in barley. Theor Appl Genet 109:1160–1168
Xu Y, Crouch JH (2008) Marker-assisted selection in plant breeding: from publications to practice. Crop Sci 48:391–407
Xu Y, McCouch SR, Shen Z (1998) Transgressive segregation of tiller angle in rice caused by complementary action of genes. Crop Sci 38:12–19
Xu Y, Babu R, Hao Z, Lu Y, Gao S, Yan J, Zhang S, Li J, Vivek BS, Magorokosho C, Mugo S, Makumbi D, Taba S, Palacios N, Pixley K, Guimarães CT, Araus J, Crouch JH (2009) SNP-chip based genomewide scan for germplasm evaluation and marker-trait association analysis and development of a molecular breeding platform. In: Proceedings of 14th Australasian Plant Breeding & 11th Society for the Advancement in Breeding Research in Asia & Oceania Conference, 10–14 August 2009, Cairns, Tropical North Queensland, Australia
Yang HC, Liang YJ, Huang MC, Li LH, Lin CH, Wu JY, Chen YT, Fann CSJ (2006) A genome-wide study of preferential amplification/hybridization in microarray-based pooled DNA experiments. Nucleic Acids Res 34(15):e106
Zhang J, Xu Y, Wu X, Zhu L (2002) A bentazon and sulfonylurea sensitive mutant: breeding, genetics and potential application in seed production of hybrid rice. Theor Appl Genet 105:16–22
Zhang LP, Lin GY, Niño-Liu D, Foolad MR (2003) Mapping QTLs conferring early blight (Alternaria solani) resistance in a Lycopersicon esculentum × L. hirsutum cross by selective genotyping. Mol Breed 12:3–19
Zhang L, Li H, Li Z, Wang J (2008) Interactions between markers can be caused by the dominance effect of QTL. Genetics 180:1177–1190
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National 863 Program of China (No. 2006AA10Z1B1). Genomics and molecular breeding research at CIMMYT has been supported by the Rockefeller Foundation, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, European Community, Generation Challenge Program and HarvestPlus Challenge Program, and through other attributed or unrestricted funds provided by the members of the CGIAR and national governments of USA, Japan and UK. ICIM was implemented by the QTL mapping software package called QTL IciMapping, available from http://www.isbreeding.net.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Wang, J., Crouch, J.H. et al. Efficiency of selective genotyping for genetic analysis of complex traits and potential applications in crop improvement. Mol Breeding 26, 493–511 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9390-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9390-8