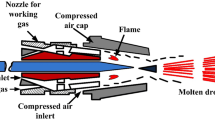
Abstract
Thermal spraying is a widely applied coating technique. The optimisation of the thermal spraying process with respect to temperature or temperature induced residual stress states requires a numerical framework for the simulation of the coating itself as well as of the quenching procedure after the application of additional material. This work presents a finite element framework for the simulation of mass deposition due to coating by means of thermal spraying combined with the simulation of nonlinear heat transfer of a rigid heat conductor. The approach of handling the dynamic problem size is highlighted with focus on the thermodynamical consistency of the derived model. With the framework implemented, numerical examples are employed and material parameters are fitted to experimental data of steel as well as of tungsten-carbide–cobalt-coating.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann CE, Oden JT (1999) A discontinuous hp finite element method for convection—diffusion problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 175(3–4):311–341. doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(98)00359-4
Berthelsen R, Wiederkehr T, Denzer R, Menzel A, Müller H (2014) Efficient simulation of nonlinear heat transfer during thermal spraying of complex workpieces. World J Mech 04(09):289–301. doi:10.4236/wjm.2014.49029
Bonet J, Wood RD (2008) Nonlinear continuum mechanics for finite element analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Clyne TW, Gill SC (1996) Residual stresses in thermal spray coatings and their effect on interfacial adhesion: a review of recent work. J Therm Spray Technol 5(4):401–418. doi:10.1007/BF02645271
Coleman BD, Noll W (1963) The thermodynamics of elastic materials with heat conduction and viscosity. Arch Ration Mech Anal 13(1):167–178. doi:10.1007/BF01262690
Delfosse D, Cherradi N, Ilschner B (1997) Numerical and experimental determination of residual stresses in graded materials. Compos B: Eng 28(1–2):127–141. doi:10.1016/S1359-8368(96)00037-6
Engel G, Garikipati K, Hughes T, Larson M, Mazzei L, Taylor R (2002) Continuous/discontinuous finite element approximations of fourth-order elliptic problems in structural and continuum mechanics with applications to thin beams and plates, and strain gradient elasticity. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191(34):3669–3750. doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(02)00286-4
Fagerstrom M, Larsson R (2008) A thermo-mechanical cohesive zone formulation for ductile fracture. J Mech Phys Solids 56(10):3037–3058. doi:10.1016/j.jmps.2008.06.002
Fleischhauer R, Behnke R, Kaliske M (2013) A thermomechanical interface element formulation for finite deformations. Comput Mech 52(5):1039–1058. doi:10.1007/s00466-013-0862-7
Gérard B (2006) Application of thermal spraying in the automobile industry. Surf Coatings Technol 201(5):2028–2031. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.04.050
Gross M, Betsch P (2011) Galerkin-based energy momentum consistent time-stepping algorithms for classical nonlinear thermo-elastodynamics. Math Comput Simul 82(4):718–770. doi:10.1016/j.matcom.2011.10.009
Hanson T, Hackett C, Settles G (2002) Independent control of HVOF particle velocity and temperature. J Therm Spray Technol 11(1):75–85. doi:10.1361/105996302770349005
Hu C, Lepsky O, Shu CW (2000) The effect of the least square procedure for discontinuous Galerkin methods for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. In: Griebel M, Keyes DE, Nieminen RM, Roose D, Schlick T, Cockburn B, Karniadakis GE, Shu CW (eds) Discontinuous Galerkin methods, vol 11. Springer, Berlin, pp 343–348
Hussainova I, Kubarsepp J, Pirso J (2001) Mechanical properties and features of erosion of cermets. Wear 250(1–12):818–825. doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00737-2
Hutter K (2004) Continuum methods of physical modeling: continuum mechanics, dimensional analysis, turbulence. Springer, Berlin
Klusemann B, Denzer R, Svendsen B (2012) Microstructure-based modeling of residual stresses in WC-12co-sprayed coatings. J Therm Spray Technol 21(1):96–107. doi:10.1007/s11666-011-9690-5
Kuroda S, Clyne T (1991) The quenching stress in thermally sprayed coatings. Thin Solid Films 200(1):49–66. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(91)90029-W
Lewis RW, Nithiarasu P, Seetharamu K (2004) Fundamentals of the finite element method for heat and fluid flow. Wiley, New Jersey
Liu IS (2002) Continuum mechanics. Springer, Berlin
Müller I (1973) Thermodynamik: die Grundlagen d. Materialtheorie. Bertelsmann-Universitätsverlag, Düsseldorf
Nomura T, Moriguchi H, Tsuda K, Isobe K, Ikegaya A, Moriyama K (1999) Material design method for the functionally graded cemented carbide tool. Int J Refract Metals Hard Mater 17(6):397–404. doi:10.1016/S0263-4368(99)00029-3
Sahraoui T, Fenineche NE, Montavon G, Coddet C (2003) Structure and wear behaviour of HVOF sprayed Cr3c2-NiCr and WC-Co coatings. Mater Design 24(5):309–313. doi:10.1016/S0261-3069(03)00059-1
Steinmann P, Häsner O (2005) On material interfaces in thermomechanical solids. Arch Appl Mech 75(1):31–41. doi:10.1007/s00419-005-0383-8
Thorpe ML, Richter HJ (1992) A pragmatic analysis and comparison of HVOF processes. J Therm Spray Technol 1(2):161–170. doi:10.1007/BF02659017
Toparli M, Sen F, Culha O, Celik E (2007) Thermal stress analysis of HVOF sprayed WC-Co/NiAl multilayer coatings on stainless steel substrate using finite element methods. J Mater Process Technol 190(1–3):26–32. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.03.115
Utzinger J, Bos M, Floeck M, Menzel A, Kuhl E, Renz R, Friedrich K, Schlarb AK, Steinmann P (2008) Computational modelling of thermal impact welded PEEK/steel single lap tensile specimens. Comput Mater Sci 41(3):287–296. doi:10.1016/j.commatsci.2007.04.015
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the collaborative research center 708 “3D-Surface Engineering of Tools for Sheet Metal Forming—Manufacturing, Modeling, Machining” within the project B6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berthelsen, R., Tomath, D., Denzer, R. et al. Finite element simulation of coating-induced heat transfer: application to thermal spraying processes. Meccanica 51, 291–307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0236-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0236-7