Abstract
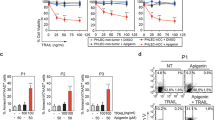
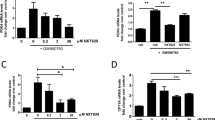
There exists a general recognition of the fact that LXR-α, being a member of the nuclear receptor family, plays a crucial role in the biological process that connects inflammation, cholesterol homeostasis, and cellular decisions. In this context the present study was addressed to understand the role of LXR-α gene in the selective and specific reprogramming of cancer cells into a state of apoptosis leaving the normal cells unaffected. The results of this study revealed that LXR-α gene when activated in cancerous cells of diverse origin results in the regulation of genes coding for Bcl-2, AATF, and Par-4 in a fashion, forcing these cells to enter into the state of apoptosis leaving the normal cells unaffected. On the basis of this study we propose that in near future LXR-α agonist (Withaferin A) may definitely find its use in the therapeutic interventions directed towards the treatment of cancer.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webb JH (1901) Cancer, its nature and treatment. Lancet ii:976
White C (1909) On the occurrence of crystals in tumours. J Pathol Bacteriol 13:3–10
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2000) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357:539–545
Michael K (2006) NF-kB and cancer: mechanisms and targets. Mol Carcinog 45:355–361
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW (2002) NF-kB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer 2:301–310
Gilmore TD (2003) The Re1/NF-kB/IkB signal transduction pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Res 115:241–265
Joseph SB, Castrillo A, Laffitte BA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Tontonoz P (2003) Reciprocal regulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism by liver X receptors. Nat Med 9:213–219
Repa JJ, Liang G, Ou J, Bashmakov Y, Lobaccaro JM, Shimomura I, Shan B, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Mangelsdorf DJ (2000) Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element- binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXR alpha and LXR beta. Genes Dev 14:2819–2830
Dave VP, Kaul D, Sharma Y, Bhattacharya R (2009) Functional genomics of blood cellular LXR-a gene in human coronary heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46:536–544
Maitra R, Porter MA, Huang S, Gilmour BP (2009) Inhibition of NF-kappaB by the natural product Withaferin A in cellular models of cystic fibrosis inflammation. J Inflamm 6:15. doi:10.1186/1476-9255-6-15
Mandal C, Dutta A, Mallick A, Chandra S, Misra L, Sangwan RS (2008) Withaferin A induces apoptosis by activating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in leukemic cells of lymphoid and myeloid origin through mitochondrial death cascade. Apoptosis 13:1450–1464
Kaul D, Mehrotra A (2007) Functional characterization of AATF transcriptome in human leukemic cells. Mol Cell Biochem 297:215–220
Mehrotra A, Joshi K, Kaul D (2010) E2F–1 RNomics is critical for reprogramming of cancer cells to quiescent state. Int J Cancer 127(4):849–858
Mishra LC, Singh BB, Dagenais S (2000) Scientific basis for the therapeutic use of Withania somnifera (ashwagandha): a review. Altern Med Rev 5:334–346
Schultz JR, Tu H, Luk A, Repa JJ, Medina JC, Li L, Schwendner S, Wang S, Thoolen M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Lustig KD, Shan B (2000) Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev 14:2831–2838
Kaul D, Anand PK (2003) Regulation of PPAR-gamma gene in human promyelocytic HL-60 cell line. Leuk Res 27:683–686
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Blaschke F, Leppanen O, Takata Y, Caglayan E, Liu J, Fishbein MC, Kappert K, Nakayama KI, Collins AR, Fleck E, Hsueh WA, Law RE, Bruemmer D (2004) Liver X receptor agonists suppress vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and inhibit neointima formation in balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Circ Res 95:e110–e123
Lise-Lotte V, Sebastian AL, Paolo P, Jan-Ake G, Steffensen KR (2009) The oxysterol receptor LXR inhibits proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 30:575–579. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp029
Janowski BA, Willy PJ, Devi TR, Falck JR, Mangelsdorf DJ (1996) An oxysterol signalling pathway mediated by the nuclear receptor LXR-α. Nature 383:728–731
Engstrom LD, Youkilis AS, Gorelick JL, Zhen D, Ackley V, Petroff CA, Benson LQ, Coon MR, Zhu X, Hanash SM, Wechsler DS (2004) Mxi-1, an alternatively transcribed Mxi-1 isoform is overexpressed in glioblastomas. Neoplasia 6:660–673
Linda QB, Melissa RC, Leslie MK, Grace CH, Amod A, Sarnaik K, Weschler DS (1999) Expression of Mxi1, a myc antagonist, is regulated by Sp1 and AP2. J Biol Chem 274:28794–28802
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by fellowship grant from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, India. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehrotra, A., Kaul, D. & Joshi, K. LXR-α selectively reprogrammes cancer cells to enter into apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 349, 41–55 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0659-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0659-3