Abstract
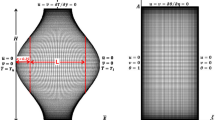
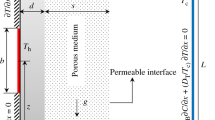
In the present study, the flow field and heat transfer of a water–copper nanofluid with variable properties in a trapezoidal enclosure saturated with porous media are studied. The governing equations are solved by finite volume method and the SIMPLER algorithm. The nanofluid flow is assumed to be laminar, steady and incompressible. Simulations are performed for sidewall (trapezoid legs) angles of 30°, 45° and 60° with respect to horizontal axis, Reynolds numbers from 10 to 1000, Darcy numbers of 10−2, 10−3, 10−4 and volume fractions of 0 to 0.04 of nanoparticles. Numerical results show that the average Nusselt number increases with increasing volume fraction of nanoparticles for all studied Darcy numbers. The convection and motion of the nanofluid decrease by reducing the Darcy number which leads to a reduction in the velocity and local Nusselt number. The average Nusselt number increases by increasing the Darcy number for all aspect ratios. Also, the average Nusselt number increases with increasing Reynolds number for all Darcy numbers, aspect ratios and volume fractions of nanoparticles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nojoomizadeh M, D’Orazio A, Karimipour A, Afrand M, Goodarzi M. Investigation of permeability effect on slip velocity and temperature jump boundary conditions for FMWNT/Water nanofluid flow and heat transfer inside a microchannel filled by a porous media. Phys E. 2018;97:226–38.
Nojoomizadeh M, Karimipour A, Firouzi M, Afrand M. Investigation of permeability and porosity effects on the slip velocity and convection heat transfer rate of Fe3O4/water nanofluid flow in a microchannel while its lower half filled by a porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;119:891–906.
Meghdadi Isfahani AH, Tasdighi I, Karimipour A, Shirani E, Afrand M. A joint lattice Boltzmann and molecular dynamics investigation for thermohydraulical simulation of nano flows through porous media. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2016;55:15–23.
Meghdadi Isfahani AH, Afrand M. Experiment and Lattice Boltzmann numerical study on nanofluids flow in a micromodel as porous medium. Phys E. 2017;94:15–21.
Afrand M, Esfe MH, Abedini E, Teimouri H. Predicting the effects of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and temperature on the thermal conductivity of water using artificial neural network and experimental data. Phys E. 2017;87:242–7.
Afrand M, Karimipour A, Nadooshan AA, Akbari M. The variations of heat transfer and slip velocity of FMWNT-water nano-fluid along the micro-channel in the lack and presence of a magnetic field. Phys E. 2016;84:474–81.
Akbari M, Afrand M, Arshi A, Karimipour A. An experimental study on rheological behavior of ethylene glycol based nanofluid: proposing a new correlation as a function of silica concentration and temperature. J Mol Liq. 2017;233:352–7.
Asadi A, Asadi M, Rezaniakolaei A, Rosendahl LA, Afrand M, Wongwises S. Heat transfer efficiency of Al2O3-MWCNT/thermal oil hybrid nanofluid as a cooling fluid in thermal and energy management applications: an experimental and theoretical investigation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;117:474–86.
Dehkordi RA, Esfe MH, Afrand M. Effects of functionalized single walled carbon nanotubes on thermal performance of antifreeze: an experimental study on thermal conductivity. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;120:358–66.
Esfahani NN, Toghraie D, Afrand M. A new correlation for predicting the thermal conductivity of ZnO–Ag (50%–50%)/water hybrid nanofluid: an experimental study. Powder Technol. 2018;323:367–73.
Esfe MH, Bahiraei M, Hajmohammad MH, Afrand M. Rheological characteristics of MgO/oil nanolubricants: experimental study and neural network modeling. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;86:245–52.
Esfe MH, Motahari K, Sanatizadeh E, Afrand M, Rostamian H, Ahangar MRH. Estimation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-water in low temperature by artificial neural network and correlation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;76:376–81.
Nadooshan AA, Esfe MH, Afrand M. Evaluation of rheological behavior of 10W40 lubricant containing hybrid nano-material by measuring dynamic viscosity. Phys E. 2017;92:47–54.
Nadooshan AA, Esfe MH, Afrand M. Prediction of rheological behavior of SiO2-MWCNTs/10W40 hybrid nanolubricant by designing neural network. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:2741–8.
Nadooshan AA, Eshgarf H, Afrand M. Measuring the viscosity of Fe3O4-MWCNTs/EG hybrid nanofluid for evaluation of thermal efficiency: newtonian and non-Newtonian behavior. J Mol Liq. 2018;253:169–77.
Ranjbarzadeh R, Karimipour A, Afrand M, Isfahani AHM, Shirneshan A. Empirical analysis of heat transfer and friction factor of water/graphene oxide nanofluid flow in turbulent regime through an isothermal pipe. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;126:538–47.
Sepyani K, Afrand M, Esfe MH. An experimental evaluation of the effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the rheological behavior of engine oil. J Mol Liq. 2017;236:198–204.
Shahsavani E, Afrand M, Kalbasi R. Experimental study on rheological behavior of water–ethylene glycol mixture in the presence of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:1177–85.
Shahsavani E, Afrand M, Kalbasi R. Using experimental data to estimate the heat transfer and pressure drop of non-Newtonian nanofluid flow through a circular tube: applicable for use in heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;129:1573–81.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Siavashi M, Taylor RA, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat T, Kolanjiyil A, Kasaeian A, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows—part I: fundamentals and theory. Phys Rep. 2019;790:1–48.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Taylor RA, Abu-Nada E, Rashidi S, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat T, Kasaeian A, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows—part II: applications. Phys Rep. 2019;791:1–59.
Noori Rahim Abadi SMA, Jafari A. Investigating the natural convection heat transfer from two elliptic cylinders in a closed cavity at different cylinder spacings. Heat Transf Res. 2012;43(3):259–84.
Mansour MA, Mohamed RA, Abd-Elaziz MM, Ahmed SE. Numerical simulation of mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity partially heated from below using nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:1504–12.
Ghasemi B, Aminossadati SM. Mixed convection in a lid-driven triangular enclosure filled with nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:1142–8.
Sheikhzadeh GA, Ebrahim Qomi M, Hajialigol N, Fattahi A. Numerical study of mixed convection flows in a lid-driven enclosure filled With nanofluid using variable properties. Int Res Phys. 2012;2:5–13.
Pishkar I, Ghasemi B. Cooling enhancement of two fins in a horizontal channel by nanofluid mixed convection. Int J Therm Sci. 2012;59:141–51.
Chamkha AJ, Abu-Nada E. Mixed convection flow in single- and double-lid driven square cavities filled with water–Al2O3 nanofluid: effect of viscosity models. Eur J Mech B/Fluids. 2012;36:82–96.
Abbasian Arani AA, MazroueiSebdani S, Mahmoodi B, Ardeshiri M, Aliakbari A. Numerical study of mixed convection flow in a lid-driven cavity with sinusoidal heating on sidewalls using nanofluid. Superlattices Microstruct. 2012;51:893–911.
Oztop HF, Al-Salem K, Varol Y, Pop I. Natural convection heat transfer in a partially opened cavity filled with porous media. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:2253–61.
Bourantas GC, Skouras ED, Loukopoulos VC, Burganos VN. Heat transfer and natural convection of nanofluids in porous media. Eur J Mech B/Fluid. 2014;43:45–56.
Hajipour M, Molaei A. DehkordiMixed-convection flow of Al2O3–H2O nanofluid in a channel partially filled with porous metal foam: experimental and numerical study. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci. 2014;51(53):49–56.
Nielda DA, Kuznetsov AV. Forced convection in a parallel-plate channel occupied by a nanofluid or a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;70:430–3.
Abedini E, Zarei T, Rajabnia H, Kalbasi R, Afrand M. Numerical investigation of vapor volume fraction in subcooled flow boiling of a nanofluid. J Mol Liq. 2017;238:281–9.
Afrand M. Using a magnetic field to reduce natural convection in a vertical cylindrical annulus. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;118:12–23.
Afrand M, Farahat S, Nezhad AH, Ali Sheikhzadeh G, Sarhaddi F. 3-D numerical investigation of natural convection in a tilted cylindrical annulus containing molten potassium and controlling it using various magnetic fields. Int J Appl Electromagn Mech. 2014;46:809–21.
Afrand M, Farahat S, Nezhad AH, Sheikhzadeh GA, Sarhaddi F. Numerical simulation of electrically conducting fluid flow and free convective heat transfer in an annulus on applying a magnetic field. Heat Transf Res 2014;45:749–66.
Afrand M, Farahat S, Nezhad AH, Sheikhzadeh GA, Sarhaddi F, Wongwises S. Multi-objective optimization of natural convection in a cylindrical annulus mold under magnetic field using particle swarm algorithm. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;60:13–20.
Afrand M, Rostami S, Akbari M, Wongwises S, Esfe MH, Karimipour A. Effect of induced electric field on magneto-natural convection in a vertical cylindrical annulus filled with liquid potassium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;90:418–26.
Pordanjani AH, Nadooshan AA, Afrand M. Effect of two isothermal obstacles on the natural convection of nanofluid in the presence of magnetic field inside an enclosure with sinusoidal wall temperature distribution. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;121:565–78.
Ali Karimi MA. Numerical study on thermal performance of an air-cooled heat exchanger: effects of hybrid nanofluid, pipe arrangement and cross section. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;164:615–28.
Teimouri H, Afrand M, Sina N, Karimipour A, Isfahani AHM. Natural convection of liquid metal in a horizontal cylindrical annulus under radial magnetic field. Int J Appl Electromagn Mech. 2015;49:453–61.
Abu-Nada E, Masoud Z, Hijazi A. Natural convection heat transfer enhancement in horizontal concentric annuli using nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2008;35:657–65.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solution. J Chem Phys. 1952;20:571–81.
Patel HE, Sundararajan T, Pradeep T, Dasgupta A, Dasgupta N, Das SK. A micro-convection model for thermal conductivity of nanofluids. J Phys. 2005;65:863–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A., Sheikhzadeh, G.A., Aghaei, A. et al. Effect of a porous medium on flow and mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluids with variable properties in a trapezoidal enclosure. J Therm Anal Calorim 139, 741–754 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08404-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08404-4