Abstract
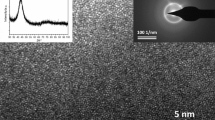
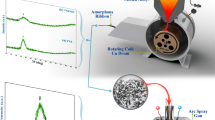
A new Ti-based amorphous alloy without any harmful additions of elements and supplementary Ag content was developed for applications in orthopedics and dentistry. Since complete elimination of toxic elements is reducing the glass-forming ability and direct casting of massive components is no longer possible, the new alloy was produced by melt spinning as thin ribbons, which could be subsequently processed by powder metallurgy. Investigations of X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy evidenced the fully amorphous structure of the new alloy. Differential scanning calorimetry was used to determine the crystallization point and the heating behavior at rates between 5 and 30 K min−1 in order to estimate by Kissinger’s method the activation energy for crystallization. Investigations evidence that the new Ti30Zr32Ag7Pd24Sn7 crystallizes at around 500 °C and the value of activation energy is relatively low in comparison with similar Ti-based alloys that were successfully processed by powder metallurgy; therefore, thermomechanical processing should be performed exclusively below 500 °C during short fabrication cycles, in order to preserve the amorphous structure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geetha M, Singh A, Asokamani R, Gogia A. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—a review. Prog Mater Sci. 2009;54:397–425.
Abdel-Hady MG, Niinomi M. Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;20:407–15.
Basu B, Katti DS, Kumar A. Advanced biomaterials—fundamentals, processing, and applications. Hoboken: Wiley; 2009.
Chen Q, Thouas GA. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mat Sci Eng R. 2015;87:1–57.
Biesiekierski A, Wang J, Gepreel MA-H, Wen C. A new look at biomedical Ti-based shape memory alloys. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:1661–9.
Inoue A, Takeuchi A. Recent development and application products of bulk glassy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011;59:2243–67.
Eckert J, Das J, Pauly S, Duhamel C. Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses and composites. J Mater Res. 2007;22(2):285–301.
Greer AL. Metallic glasses… on the threshold. Mater Today. 2009;12(1–2):14–23.
Oak JJ, Inoue A. Formation, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Ti–Pd base glassy alloys. J Non Cryst Solids. 2008;354:1828–32.
Yavari A, Lewandowski J, Eckert J. Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses. MRS Bull. 2007;32:635–8.
Hornez J, Lefevre A, Joly D, Hildebrand H. Multiple parameter cytotoxicity index on dental alloys and pure metals. Biomol Eng. 2002;19:103–17.
Elshahawy WM, Watanabe I, Kramer P. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of elemental ions released from different prosthodontic materials. Dent Mater. 2009;25:1551–5.
Calin M, Gebert A, Ghinea AC, Gostin PF, Abdi S, Mickel C, Eckert J. Designing biocompatible Ti-based metallic glasses for implant applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2013;33:875–83.
Inoue A, Kong F, Zhu S, Shalaan E, Al-Marzouki F. Production methods and properties of engineering glassy alloys and composites. Intermetallics. 2015;58:20–30.
Ke J, Huang C, Chen Y, Tsai W, Wei T, Huang J. In vitro biocompatibility response of Ti–Zr–Si thin film metallic glasses. Appl Surf Sci. 2014;322:41–6.
Abdi S, Khoshkhoo MS, Shuleshova O, Bönisch M, Calin M, Baró M, Sort J, Gebert A. Effect of Nb addition on microstructure evolution and nanomechanical properties of a glass-forming TiZrSi alloy. Intermetallics. 2014;46:156–63.
Lin H, Tsai P, Ke J, Li J, Jang J, Huang C, Haung J. Designing a toxic-element-free Ti-based amorphous alloy with remarkable supercooled liquid region for biomedical application. Intermetallics. 2014;55:22–7.
Lin C, Huang C, Chuang J, Huang J, Jang J, Chen C. Rapid screening of potential metallic glasses for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2013;33:4520–6.
Zhuravleva K, Chivu A, Teresiak A, Scudino S, Calin M, Schultz L, Eckert J. Porous low modulus Ti40Nb compacts with electrodeposited hydroxyapatite coating for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2013;33:2280–7.
Li J, Lin H, Jang JKC, Huang J. Novel open-cell bulk metallic glass foams with promising characteristics. Mater Lett. 2013;105:140–3.
Karageorgiou V, Kaplan D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26:5474–91.
Xue W, Krishna BV, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S. Processing and biocompatibility evaluation of laser processed porous titanium. Acta Biomater. 2007;3:1007–18.
Wen C, Yamada Y, Hodgson P. Fabrication of novel TiZr alloy foams for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2006;26:1439–44.
Raduta A, Nicoara M, Locovei C, Eckert J, Stoica M. Ti-based bulk glassy composites obtained by replacement of Ni with Ga. Intermetallics. 2016;69:28–34.
Nicoara M, Locovei C, Serban VA, Parthiban R, Calin M, Stoica M. New Cu-free Ti-based composites with residual amorphous matrix. Materials. 2016;331:1–14.
Nicoara M, Raduta A, Parthiban R, Locovei C, Eckert J, Stoica M. Low Young’s modulus Ti-based porous bulk glassy alloy without cytotoxic elements. Acta Biomater. 2016;331:1–14.
Nicoara M, Raduta A, Locovei C, Buzdugan D, Stoica M. About thermostability of biocompatible Ti–Zr–Ta–Si amorphous alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:107–13.
Oak JJ, Louzguine-Luzgin DV, Inoue A. Fabrication of Ni-free Ti-based bulk-metallic glassy alloy having potential for application as biomaterial, and investigation of its mechanical properties, corrosion, and crystallization behavior. J Mater Res. 2007;22:1346–53.
Stohs S, Bagchi D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Bio Med. 1995;18:321–36.
Wataha J, Lockwood P, Schedle A. Effect of silver, copper, mercury, and nickel ions on cellular proliferation during extended, low-dose exposures. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;52:360–4.
Craig R, Hanks C. Cytotoxicity of experimental casting alloys evaluated by cell culture tests. J Dent Res. 1990;69:1539–42.
Secinti KD, Özalp H, Attar A, Sargon MF. Nanoparticle silver ion coatings inhibit biofilm formation on titanium implants. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:391–5.
Choi O, Yu CP, Fernandez GE, Hua Z. Interactions of nanosilver with Escherichia coli cells in planktonic and biofilm cultures. Water Res. 2010;44:6095–103.
Kalishwaralal K, BarathManiKanth S, Pandian SRK, Deepak V, Gurunathan S. Silver nanoparticles impede the biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Colloid Surf B. 2010;79:340–4.
Abdel-Hady M, Hinoshita K, Morinaga M. General approach to phase stability and elastic properties of beta-type Ti-alloys using electronic parameters. Scr Mater. 2006;55:477–80.
Oak JJ, Louzguine-Luzgin DV, Inoue A. Synthetic relationship between titanium and alloying elements in designing Ni-free Ti-based bulk metallic glass alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91:1–4.
Ashby M, Greer A. Metallic glasses as structural materials. Scr Mater. 2006;54:321–6.
Suryanarayana C, Inoue A. Bulk metallic glasses. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2011.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;21:1702–6.
Srivastava AP, Srivastava D, Mazumdar B, Dey GK. Thermoanalytical study of crystallization process in metallic glass of Co69Fe3Si18B10. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1353–61.
Strbac G, Strbac D, Lukic-Petrovic S, Siljegovic M. Thermal characterization of glasses from Fe–Sb–S–I system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127:247–54.
Svoboda R, Malek J. Amorphous-to-crystalline transition in Te-doped Ge2Sb2Se5 glass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117:1073–83.
Svoboda R, Malek J. Is the original Kissinger equation obsolete today? J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1961–7.
Wu J, Pan Y, Pi J. On non-isothermal kinetics of two Cu-based bulk metallic glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:267–74.
Wei HD, Bao QH, Wang CX, Zhang WS, Yuan ZZ, Chen XD. Crystallization kinetics of (Ni0.75Fe0.25)78Si10B12 amorphous alloy. J Non Cryst Solids. 2008;354:1876–82.
Zhang J, Wang W, Ma H, Li G, Lia R, Zhang Z. Isochronal and isothermal crystallization kinetics of amorphous Fe-based alloys. Thermochim Acta. 2010;505:41–6.
Gong P, Wang X, Yao K. Effects of alloying elements on crystallization kinetics of Ti–Zr–Be bulk metallic glass. J Mater Sci. 2016;51:5321–9.
Pratap A, Rao TLS, Lad KN, Dhurandhar HD. Kinetics of crystallization of titanium based binary and ternary amorphous alloys. J Non Cryst Solids. 2007;353:2346–9.
Zhu SL, Wang XM, Qin FX, Yoshimura M, Inoue A. New TiZrCuPd quaternary bulk glassy alloys with potential of biomedical applications. Mater Trans JIM. 2007;48(9):2445–8.
Gong P, Yao K, Zhao S. Cu-alloying effect on crystallization kinetics of Ti41Zr25Be28Fe6 bulk metallic glass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121:697–704.
Huang Y, Shen J, Sun J, Yu X. A new Ti–Zr–Hf–Cu–Ni–Si–Sn bulk amorphous alloy with high glass-forming ability. J Alloy Compd. 2007;427(1–2):171–5.
Xia MX, Zheng HX, Jian L, Ma CL, Li JG. Thermal stability and glass-forming ability of new Ti-based bulk metallic glasses. J Non Cryst Solids. 2005;351:3747–51.
Khalifa HE, Vecchio KS. Thermal stability and crystallization phenomena of low cost Ti-based bulk metallic glass. J Non Cryst Solids. 2011;357:3393–8.
Kasyap S, Patel AT, Pratap A. Crystallization kinetics of Ti20Zr20Cu60 metallic glass by isoconversional methods using modulated differential scanning calorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:1325–36.
Haratian S, Haddad-Sabzevar M. Thermal stability and non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of Ti41.5Cu42.5Ni7.5Zr2.5Hf5Si1 bulk metallic glass. J Non Cryst Solids. 2015;429:164–70.
Lu XC, Li HY. Kinetics of non-isothermal crystallization in Cu50Zr43Al7 and (Cu50Zr43Al7)95Be5 metallic glasses. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1089–97.
Li XP, Roberts MP, O’Keeffe S, Sercombe TB. Selective laser melting of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses: processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater Des. 2016;112:217–26.
Pauly S, Lober L, Petters R, Stoica M, Scudino S, Kuhn U, Eckert J. Processing metallic glasses by selective laser melting. Mater Today. 2013;16:37–41.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Academic Exchange Service (Deutscher Akademischer Austausch Dienst—DAAD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicoara, M., Buzdugan, D., Locovei, C. et al. About thermostability of biocompatible Ti–Zr–Ag–Pd–Sn amorphous alloys. J Therm Anal Calorim 133, 189–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7031-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7031-3