Abstract
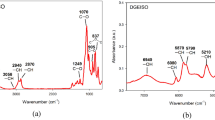
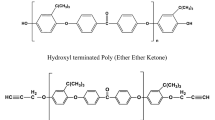
A bio-based epoxy resin was synthesized from cardanol which is natural renewable resource. Subsequently, diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA) was toughened with three different mass proportions of bio-based epoxidized cardanol–formaldehyde resin (ECF) (i.e., 20, 40, 60 mass%). In this study, the curing kinetics of amine-cured modified resin was studied by non-isothermal differential scanning calorimetry analysis. The apparent activation energy obtained by Kissinger and Flynn–Wall–Ozawa methods was 48 and 52 kJ mol−1, respectively. The two-parameter Šesták–Berggren autocatalytic model was used to obtain the reaction orders m and n. The curves obtained by the Malek method show good agreement with the experimental data for bio-based epoxy systems.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothrock HS. Phenol-formaldehyde. United states patent application publication. 1943; 2321627.
Gardziella A, Pilato LA, Knop A. Phenolic resins: chemistry, applications, standardization, safety and ecology. 2nd ed. Heidelberg: Springer; 2000.
Pilato LA. Phenolic resins: a century of progress. Heidelberg: Springer; 2010.
Netravali AN, Chabba S. Composites get greener. Mater Today. 2003;6:22–9.
Kobayashi H, Fukuoka A. Synthesis and utilization of sugar compounds derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2013;15:1740–63.
Zakzeski J, Bruijnincx PCA, Jongerius AL, Weckhuysen BM. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem Rev. 2010;110:3552–99.
Alonso MV, Rodriguez JJ, Oliet M, Rodriguez F, Gilarranz MA. Characterization and structural modification of ammonic lignosulfonate by methylolation. J Appl Polym Sci. 2001;82:2661–8.
Czernik S, Bridgwater AV. Overview of applications of biomass fast pyrolysis oil. Energy Fuels. 2004;18:590–8.
Celzard A, Szczurek A, Jana P, Fierro V, Basso M, Bourbigot S, Stauber M, Pizzi A. Latest progresses in the preparation of tannin-based cellular solids. J Cell Plast. 2015;51:89–102.
Yadav R, Awasthi P, Srivastava D. Studies on synthesis of modified epoxidized novolac resin from renewable resource material for application in surface coating. J Appl Polym Sci. 2009;114:1471–84.
Yadav R, Srivastava D. Blends of cardanol-based epoxidized novolac resin and CTBN for application in surface coating: a study on thermal, mechanical, chemical and morphological characteristics. J Coat Technol Res. 2010;7:557–68.
Shukla SK, Srivatsava D. Studies on the blends of modified epoxy resin and carboxyl-terminated polybutadiene (CTPB)—II: thermal and mechanical characteristics. J Mater Sci. 2007;42:3215–22.
Devi A, Srivatsava D. Studies on the blends of cardanol-based epoxidized novolac type phenolic resin and carboxyl-terminated polybutadiene (CTPB), I. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2007;458:336–47.
Reddy PN, Mohanty D, Nayak SK. Synthesis and modifications of epoxy resins and their composites: a review. Polym Plast Technol Eng. 2014;53:1723–58.
Chruściel JJ, Leśniak E. Modification of epoxy resins with functional silanes, polysiloxanes, silica and silicates. Prog Polym Sci. 2015;41:67–121.
Kumar KD, Kothandaraman B. Modification of (DGEBA) epoxy resin with maleated depolymerised natural rubber. Express Polym Lett. 2008;2:302–11.
Tripathi G, Srivatsava D. Effect of carboxyl-terminated poly(butadiene-co-acrylonitrile) (CTBN) concentration on thermal and mechanical properties of binary blends of diglycidyl ether of bisphenol—a (DGEBA) epoxy resin. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2007;443:262–9.
Sultania M, Srivastava D. Studies on the synthesis and curing of epoxidized novolac vinyl ester resin from renewable resource material. Eur Polym J. 2010;46:2019–32.
Sprenger S. Fiber-reinforced composites based on epoxy resins modified with elastomers and surface-modified silica nanoparticles. J Mater Sci. 2014;49:2391–402.
Wang R, Schuman TP. Vegetable oil-derived epoxy monomers and polymer blends: a comparative study with review. Express Polym Lett. 2013;7:272–92.
Suresh KI, Kishanprasad VS. Synthesis, structure, and properties of novel polyols from cardanol and developed polyurethanes. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2005;44:4504–12.
Sahoo SK, Mohanty S, Nayak SK. Toughened bio-based epoxy blend network modified with transesterified epoxidized soybean oil: synthesis and characterization. RSC Adv. 2015;5:13674–91.
Wuzella G, Mahendran AR, Muller U, Kandelbauer A, Teischinger A. Photocrosslinking of an acrylated epoxidized linseed oil: kinetics and its application for optimized wood coatings. J Polym Environ. 2012;20:1063–74.
Kovarik T, France P, Sestak J, Rieger D, Belsky P, Kadlec J, Roubicek P. A novel approach to polyaluminosialates curing process using electric boosting and temperature profile investigation by DSC. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121:517–24.
Song X, Xu S. Curing kinetics of pre-crosslinked carboxyl-terminated butadiene acrylonitrile (CTBN) modified epoxy blends. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123:319–27.
Bai Y, Yang P, Zhang S, Li Y, Gu Y. Curing kinetics of phenolphthalein–aniline-based benzoxazine investigated by non-isothermal differential scanning calorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120:1755–64.
Li C, Liu MH, Liu ZY, Qing ML, Wang G. DSC and curing kinetics of epoxy resin using cyclohexanediol diglycidyl ether as active diluents. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;116:411–6.
Zhang C, Liu X, Cheng J, Zhang J. Study on curing kinetics of diglycidyl 1,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylate epoxy/episulfide resin system with hexahydro-4-methylphthalic anhydride as a curing agent. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120:1893–903.
Perin DD, Armerigo WLF. Purification of laboratory chemicals. 3rd ed. New York: Pergamon; 1988.
Trivedi MK, Patni MJ, Bindal L. Oligomerisation of cardanol. Indian J Tech. 1989;27:281–5.
Lee H, Neville K. Handbook of epoxy resins. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1967.
Montserrrat A, Malek JA. A kinetic analysis of the curing reaction of an epoxy resin. Thermochim Acta. 1993;228:47–60.
Durga G, Narula AK. Curing kinetics and thermal stability of epoxy blends containing phosphorous-oxirane with aromatic amide-amine as curing agents. Chin J Polym Sci. 2012;30:694–704.
Mousa G, Bazzar M, Farshad RB. Curing of DGEBA/ZnO nanocomposites with new fluorinated curing agents: study of kinetics, water absorption, thermal and photophysical properties. High Perform Polym. 2011;24:632–45.
Sestak J, Berggren G. Study of the kinetics of mechanism of solid state reactions at increasing temperatures. Thermochim Acta. 1971;3:1–12.
Malek J. Kinetic analysis of crystallization processes in amorphous materials. Thermochim Acta. 2000;239:239–53.
Senum GI, Yang RT. Rational approximations of the integral of the Arrhenius function. J Thermal Anal. 1977;11:445–7.
Haines PJ. Principles of thermal analysis and calorimetry. Cambridge: Royal society of chemistry; 2002.
Dominguez JC, Grivel JC, Madsen B. Study on the non-isothermal curing kinetics of a polyfurfuryl alcohol bioresin by DSC using different amount of catalyst. Thermochim Acta. 2012;529:29–35.
Rosu D, Cascaval CN, Mustata F, Ciobanu C. Cure kinetics of epoxy resins studied by non-isothermal DSC data. Thermochim Acta. 2002;383:119–27.
Kun H, Pei Z, Zhang J, Li S, Li M, Xia J, Zhou Y. Preparation of biobased epoxies using tung oil fatty acid- derivated c21 diacid and c22 triacid and study of epoxy properties. Green Chem. 2013;15:2466–75.
Nayef EIT, Tizazu M, Paolo M, David B, Phillip C. Nonisothermal DSC study of epoxy resins cured with hydrolyzed specified risk material. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52:8189–99.
Um MK, Daniel IM, Hwang BS. A study of cure kinetics by the use of dynamic differential scanning calorimetry. Compos Sci Technol. 2002;62:29–40.
Saad GR, Elhamid EEA, Elmenyawy SA. Dynamic cure kinetics and thermal degradation of brominated epoxy resin-organoclay based nanocomposites. Thermochim Acta. 2011;524:186–93.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Principal and Management, PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore, for providing the necessary facilities. Sincere thanks are also due to IIT (Madras), Chennai, for NMR spectral studies.
Funding
This work was supported by the University Grants Commission (UGC), India, for financial assistance [Grant No. F. No. 39-804/2010 (SR)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natarajan, M., Murugavel, S.C. Cure kinetics of bio-based epoxy resin developed from epoxidized cardanol–formaldehyde and diglycidyl ether of bisphenol–A networks. J Therm Anal Calorim 125, 387–396 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5417-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5417-7