Abstract
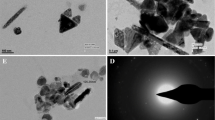
A sol–gel route to synthesize copper oxide nanoparticles with an average size of ca. 63 nm from copper acetate precursor and monoethanolamine as the capping agent is reported. Structural characterization showed the formation of a cubic phase for CuO. The effect of annealing temperature on formation of crystalline phases was investigated. Characterization of the products was performed using thermo-gravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and diffuse reflectance. The results showed that there are significant differences in the morphological, crystallographic, structural, and optical properties of the nanostructures prepared at different annealing temperatures. The optical properties and band gap of CuO nanoparticles were studied by UV–Vis spectroscopy. According to the results of the optical measurements, the band gap is estimated to be 1.41 eV. These results showed that the band gap energy changed with increase of annealing temperature, which can be attributed to the change in grain size of the samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramezanzadeh B, Attar M. Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the thermal and mechanical properties of epoxy-based nanocomposite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;103:731–9.
Habibi MH, Askari E. Thermal and structural studies of zinc zirconate nanoscale composite derived from sol–gel process: the effects of heat-treatment on properties. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:227–33.
Baji S, Labadi Z, Horvath Z, Fried M, Szentpali B, Barsony I. Temperature dependent in situ doping of ALD ZnO. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;105(1):93–9.
Habibi MH, Habibi AH. Effect of the thermal treatment conditions on the formation of zinc ferrite nanocomposite, ZnFe2O4, by sol–gel method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012. doi:10.1007/s10973-012-2830-4.
Lv M, Xiu X, Pang Z, Dai Y, Ye L, Cheng C, Han S. Structural, electrical and optical properties of zirconium-doped zinc oxide films prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films. 2008;516:2017–21.
Habibi MH, Askari E. Synthesis of nanocrystalline zinc manganese oxide by thermal decomposition of new dinuclear manganese(III) precursors. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:1345–9.
Singh I, Bedi RK. Influence of pH on the synthesis and characterization of CuO powder for thick film room-temperature NH3 gas sensor. J Mater Sci. 2011;46:5568–80.
Chen T, Zhang T, Wang G, Zhou J, Zhang J, Liu Y. Effect of CuO on the microstructure and electrical properties of piezoceramic. J Mater Sci. 2012;47:4612–9.
Yu Q, Wang M, Chen H. Fabrication of highly ordered TiO2 nanobelt arrays by electrospinning. Mater Lett. 2010;64:428–30.
Habibi MH, Kamrani R, Mokhtari R. Fabrication and characterization of copper nanoparticles using thermal reduction: the effect of nonionic surfactants on size and yield of nanoparticles. Microchim Acta. 2010;171:91–5.
Rehman S, Mumtaz A, Hasanain SK. Size effects on the magnetic and optical properties of CuO nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. 2011;13:2497–507.
Alikhanzadeh-Arani S, Salavati-Niasari M, Almasi-Kashi M. Growth of the dysprosium–barium–copper oxide superconductor nanoclusters in biopolymer gels. J Inorg Organomet Polym. 2012;22:1081–6.
Fan XY, Wu ZG, Yan PX, Geng BS, Li HJ, Li C, Zhang PJ. Fabrication of well-ordered CuO nanowire arrays by direct oxidation of sputter-deposited Cu3N film. Mater Lett. 2008;62:1805–8.
Wang G, Huang J, Chen S, Gao Y, Cao D. Preparation and supercapacitance of CuO nanosheet arrays grown on nickel foam. J Power Sources. 2011;196:5756–60.
Zhao JG, Liu SJ, Yang SH, Yang SG. Hydrothermal synthesis and ferromagnetism of CuO nanosheets. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;257:9678.
Chen LB, Lu N, Xu CM, Yu HC, Wang TH. Electrochemical performance of polycrystalline CuO nanowires as anode material for Li ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2009;54:4198–201.
Zhang H, Zhang M. Synthesis of CuO nanocrystalline and their application as electrode materials for capacitors. Mater Chem Phys. 2008;108:184–7.
Jia W, Reitz E, Shimpi P, Rodriguez EG, Gao PX, Lei Y. Spherical CuO synthesized and its electrocatalytic application. Mater Res Bull. 2009;44:1681–8.
Wang H, Xu J-Z, Zhu J-J, Chen H-Y. Preparation of CuO nanoparticles by microwave irradiation. J Cryst Growth. 2002;244:88–94.
Mukherjee N, Show B, Maji SK, Madhu U, Bhar SK, Mitra BC, Khan GG, Mondal A. CuO nano-whiskers: electrodeposition, Raman analysis, photoluminescence study and photocatalytic activity. Mater Lett. 2011;65:3248–50.
Chen XY, Cui H, Liu P, Yang GW. Shape induced ultraviolet absorption of CuO shuttle like nano-particles. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;90:183118–21.
Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A, Hushmandrad S. Solar photodecolorization of methylene blue by CuO/X. Appl Catal A. 2010;388:149–59.
Yan X, Hu D, Li H, Li L, Chong X, Wang Y. Nanostructure and optical properties of M doped ZnO (M = Ni, Mn) thin films prepared by sol–gel process. Phys B. 2011;406:3956–62.
Murphy AB. Band-gap determination from diffuse reflectance measurements of semiconductor films, and application to photoelectrochemical water-splitting. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2007;91:1326–37.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the University of Isfahan for financially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habibi, M.H., Karimi, B. Effect of the annealing temperature on crystalline phase of copper oxide nanoparticle by copper acetate precursor and sol–gel method. J Therm Anal Calorim 115, 419–423 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3255-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-013-3255-4