Abstract
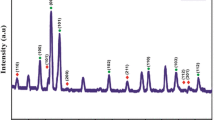
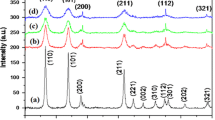
Mixed metal oxides of tin with strontium (xSnO2.SrO) in different molar ratio {where x = 1 (1), 2 (2), 4(3); SnO2 doped with Sr+2(4), SnO2 doped with Sr+2 and co-doped with F−(5)} have been prepared by sol–gel technology in basic medium using SnCl2.2H2O as precursor in isopropanol as solvent. Structural analysis by XRD patterns have shown formation of particles at nanoscale and phase separation of SnO2 in tetragonal rutile framework in these mixed metal oxides. This fact was further supported by TEM. SEM images of all these samples have shown formation of various geometrical patterns ranging from spherical particles to nanorods. In the IR spectra of all these oxides, Sr–O absorption bands were present only in sample (1). UV–Vis spectroscopy has shown reduction in optical band gap in mixed metal oxides and the lowest value of band gap was observed for sample (3). Photoluminescence spectra of all these derivatives are found to be almost similar again indicated retention of tetragonal rutile SnO2 framework. I–V curves of all these oxides are non-linear and lowest resistance was observed for sample (3). This fact was further supported by impedance measurements.

Highlights
-
Mixed metal oxides of SnO2 and SrO in different stoichiometric ratios have been prepared by sol–gel technology in basic medium.
-
XRD patterns have shown separation of phases and retention of tetragonal rutile framework in SnO2.
-
SEM images have shown formation of various geometrical patterns ranging from spherical particles to nanorods.
-
UV–Vis spectroscopy has shown reduction in optical band gap in these mixed metal oxides.
-
IV curves and impedance measurements have shown comparatively high conductance in sample (3).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thangaraju B (2002) Thin Solid Films 402:71–78
Baker PGL, Sanderson RD, Crouch AM (2007) Thin Solid Films 515:6691–6697
Liu Y, Li Y, Zeng H (2013) J Nanomater 2013:1–9
Bargougui R, Oueslati A, Schmerber G, Ulhaq-Bouillet C, Colis S, Hlel F, Ammar S, Dinia A (2014) J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25:2066–2071
Banyamin ZY, Kelly PJ, West G, Boardman J (2014) Coatings 4:732–746
Sagadevan S, Podder J (2015) Soft Nanosci Lett 5:55–64
Khan N, Athar T, Foud H, Umar A, Ansari ZA, Ansari SG (2017) Scientific reports 7, Article No. 42510. p 11
Sharma V (2017) J Sol-gel Sci Technol 84:231–238
Patil GE, Kajale DD, Gaikwad VB, Jain GH (2012) Int Nano Lett 2:46–51
Helwig A, Muller G, Svervegkieri G, Faglia G (2008) Sens Actuators B130:193–199
Kadhim IH, Hassan HA, Abdullah QN (2016) Nano Micro Lett 8:20–28
Zhao Q, Ma L, Zhang Q, Wang C, Xu X (2015) J Nanomater 2015:1–15
Kalpana D, Omkumar KS, Kumar SS, Ranganathan N (2006) Electrochim Acta 52(3):1309–1315
Yadav AA, Masumdar EU, Moholkar AV, Neumann-Spallart M, Rajpure KY, Bhosle CH (2009) J Alloy Compd 488:350–355
He Z, Zhou J (2013) Mod Res Catal 2:13–18
Liu Y, Koep E, Liu M (2005) Chem Meter 17(15):3997–4000
Chacko S, Bushiri MJ, Vaidyan VK (2006) J Phys D-Appl Phys 39:4540–4543
Elangovan E, Ramamurthi K (2005) Thin Solid Films 476:231–236
Nütz T, Haase M (2000) J Phys Chem B 104:8430–8437
Blessi S, Sonia MML, Vijayalakshmi S, Pauline S (2014) Int J Res (IJCRGG) 6(3):2153-2155
Bhagwat AD, Sawant SS, Ankamwar BG, Mahajan CM (2015) J Nano Electron Phys 7(4):4037. (4pp)
Agrawal S, Sharma V, Bohra R (2006) J Chem Res 7:426–430
Sharma N, Sharma V, Bohra R, Raju VS (2007) Appl Org -Met Chem 21:763–771
Sharma N, Sharma V, Bohra R, Raju VS, Lorenz I-P, Krinninger C, Mayer P (2007) Inorg Chim Acta 360:3002–3012
Dhayal V, Sharma N, Sharma V, Bohra R, Drake JE, McDonald CLB (2007) Polyhedron 26:3168–3174
Mishra S, Daniele S (2015) Chem Rev 115:8379–8448
Nemade KR, Waghuley SA (2013) J Results Phys 3:52–54
Hamedani HA, Allam NK, Garmestani H, EI-Sayed MA (2011) J Phys Chem C 115:13480–13486
Kim S, Yang Y, Oh WK, Kim C, Jang J (2014) Adv Healthc Mater 3:1097–1106
Ueno S, Nakashima K, Sakamoto Y, Wad S (2015) Nanomaterials 5:386–397
Luo J, Shen P, Yao W, Jiang C, Xu J (2016) Nanoscale Res Lett 11: 141(14 pp).
Thompson S, Shirtcliffe NJ, O’Keefe ES, Appleton S, Perry CC (2005) J Magn Magn Mater 292:100–107
Jose R, Suzuki T, Ohishi Y (2006) J Non-Cryst Solids 352:5564–5568
Veverka P, Knižek K, Pollert E, Bohaček J, Vasseur S, Duguet D, Portier J (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 309(1):106–112
Luo J, Xu Y, Gao D (2015) Solid State Sci 37:40–46
Lashanizadegan M, Mousavi F, Mirzazahed H (2016) J Ceram Process Res 17:586–590
Wong-Ng W, Cline JP, Cook LP, Greenwood W (2000) Adv X-ray Anal 42:355–365
Smith MB, Page K, Siegrist T, Redmond PL, Walter EC, Sheshadry R, Brus LE, Steigerwald ML (2008) J Am Chem Soc 130:6955–6963
Zou GL, Liu R, Chen WX, Zu ZD (2007) Mater Res Bull 42:1153–1158
Zhang J, Gao L (2004) J Solid State Chem 4-5:1425–1430
Pasierb P, Komornicki S, Rokita M, Rekas M (2001) J Mol Struct 596:151–156
Bonu V, Das A, Amirthapandian S, Dhara S, Tyagi AK (2015) Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:9794–9801
Sudhaparimala S, Gnanamania A, Mandal AB (2014) Am J Nanosci Tech 2:75–83
Rajeshwaran P, Shivarajan A (2015) J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26:539–546
Mazumder N, Bharti A, Saha S, Sen D, Chattopadhyay KK (2012) Curr Appl Phys 12:975–982
Chu CW, F. Chen, Shulman J, Tsui S, Xue YY, Wen W, Sheng P (2005) Proc. SPIE 5932, Strongly Correlated Electron Materials: Physics and Nanoengineering, 59320X. arXiv: cond-mat/0511166[cond.mat.Supr.con] p 9
Acknowledgements
V Sharma is thankful to UGC- New Delhi for financial support (No. MS-37/304004/XII/13-14/CRO dated 19 January 2015). We are thankful to Material Research Center, MNIT, Jaipur Rajasthan for providing all technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
sharma, V., Prajapati, R.C. Synthesis of mixed metal oxide nanoparticles of SnO2 with SrO via sol–gel technology: their structural, optical, and electrical properties. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 87, 41–49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4718-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4718-7