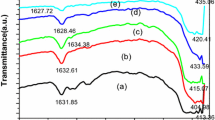
Abstract
Photoluminescent nano material has been reported as an intriguing field during the past few decades. In this article, tartaric-templated silica nanotubes were conveniently synthesized by sol–gel method. X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, fourier transform infrared spectra and photoluminescence spectra analysis were employed to characterize the growth, structure, morphology and optical property of the products. It is found that tartaric templates can form spindle/spherical-like aggregates composed of many sheets under static/stirring condition, which lead to the different shapes of silica nanotubes. Then the probable strategies for silica nanotubes templating with tartaric acid were described particularly. Hydrogen-bond interaction, supramolecular interaction and a competition of various effects may be the reasons of the nanotubes formation. Moreover, under ultraviolet light excitation, the silica nanotubes exhibited blue emission and luminescent intensity of the tubes prepared under the static condition is much stronger than the stirring ones, mostly because of more defect centers in the structures obtained under stirring condition.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ying JY (1997) Preface to the special issue: sol–gel derived materials. Chem Mater 9(11):2247–2248. doi:10.1021/cm970999y
Lee KG, Wi R, Imran M, Park TJ, Lee J, Lee SY, Kim DH (2010) Functionalization effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes as templates for the synthesis of silica nanorods and study of growing mechanism of silica. ACS Nano 4(7):3933–3942
Nakamura H, Matsui Y (1995) Silica gel nanotubes obtained by the sol–gel method. J Am Chem Soc 117(9):2651–2652
Delclos T, Aimé C, Pouget E, Brizard A, Huc I, Delville M-H, Oda R (2008) Individualized silica nanohelices and nanotubes: tuning inorganic nanostructures using lipidic self-assemblies. Nano Lett 8(7):1929–1935
Chen Y, Wang S, Liu X, Li Y, Li B, Yang Y (2010) Formation of left-handed double twisted silica nanoribbons. Chin J Chem 28(10):1941–1945
Geltmeyer J, Van der Schueren L, Goethals F, De Buysser K, De Clerck K (2013) Optimum sol viscosity for stable electro spinning of silica nano fibres. J Solgel Sci Technol 67(1):188–195. doi:10.1007/s10971-013-3066-x
Su X, Zhao J, Zhao X, Guo Y, Zhu Y, Wang Z (2008) A facile synthesis of Cu2O/SiO2 and Cu/SiO2 core–shell octahedral nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 19(36):365610
Han WS, Kang Y, Lee SJ, Lee H, Do Y, Lee Y-A, Jung JH (2005) Fabrication of color-tunable luminescent silica nanotubes loaded with functional dyes using a sol–gel co condensation method. J Phys Chem B 109(44):20661–20664
García-Calzón JA, Díaz-García ME (2012) Synthesis and analytical potential of silica nanotubes. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 35:27–38. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2012.01.003
Dong W, Zhao H, Li C, Mei J, Chen B, Tang W, Shi Z, Feng S (2011) Hetero-nanostructure of silver nanoparticles on MOx (M = Mo, Ti and Si) and their applications. Sci China Chem 54(6):865–875
Mitchell DT, Lee SB, Trofin L, Li N, Nevanen TK, Söderlund H, Martin CR (2002) Smart nanotubes for bioseparations and biocatalysis. J Am Chem Soc 124(40):11864–11865
Chen CC, Liu YC, Wu CH, Yeh CC, Su MT, Wu YC (2005) Preparation of fluorescent silica nanotubes and their application in gene delivery. Adv Mater 17(4):404–407
Clavier GM, Pozzo JL, Bouas-Laurent H, Liere C, Roux C, Sanchez C (2000) Organogelators for making porous sol-gel derived silica at two different length scales. J Mater Chem 10(7):1725–1730. doi:10.1039/B000525H
Huang X, Weiss RG (2006) Silica structures templated on fibers of tetraalkylphosphonium salt gelators in organogels. Langmuir 22(20):8542–8552
Xue P, Lu R, Li D, Jin M, Bao C, Zhao Y, Wang Z (2004) Rearrangement of the aggregation of the gelator during sol–gel transcription of a dimeric cholesterol-based viologen derivative into fibrous silica. Chem Mater 16(19):3702–3707
Lin Y, Qiao Y, Gao C, Tang P, Liu Y, Li Z, Yan Y, Huang J (2010) Tunable one-dimensional helical nanostructures: from supramolecular self-assemblies to silica nanomaterials. Chem Mater 22(24):6711–6717. doi:10.1021/cm102181e
Gundiah G, Mukhopadhyay S, Tumkurkar UG, Govindaraj A, Maitra U, Rao C (2003) Hydrogel route to nanotubes of metal oxides and sulfates. J Mater Chem 13(9):2118–2122
Yuwono VM, Hartgerink JD (2007) Peptide amphiphile nanofibers template and catalyze silica nanotube formation. Langmuir 23(9):5033–5038
Dickerson MB, Sandhage KH, Naik RR (2008) Protein-and peptide-directed syntheses of inorganic materials. Chem Rev 108(11):4935
Caruso RA, Antonietti M (2001) Sol–gel nanocoating: an approach to the preparation of structured materials. Chem Mater 13(10):3272–3282. doi:10.1021/cm001257z
Fan R, Wu Y, Li D, Yue M, Majumdar A, Yang P (2003) Fabrication of silica nanotube arrays from vertical silicon nanowire templates. J Am Chem Soc 125(18):5254–5255
Nakamura H, Matsui Y (1995) The preparation of novel silica gel hollow tubes. Adv Mater 7(10):871–872
Lim A, Schueneman G, Novak B (1999) Solid state NMR of SiO2 nanotube coated ammonium tartrate crystal. Solid State Commun 110(6):333–338
Anastasescu C, Zaharescu M, Balint I (2009) Unexpected photocatalytic activity of simple and platinum modified tubular SiO2 for the oxidation of oxalic acid to CO2. Catal Lett 132(1–2):81–86. doi:10.1007/s10562-009-0066-0
Xiao Q-G, Tao X, Chen J-F (2007) Silica nanotubes based on needle-like calcium carbonate: fabrication and immobilization for glucose oxidase. Ind Eng Chem Res 46(2):459–463
Khoabane K, Mokoena EM, Coville NJ (2005) Synthesis and study of ammonium oxalate sol–gel templated silica gels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 83(1–3):67–75. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.04.002
Anastasescu C, Anastasescu M, Teodorescu VS, Gartner M, Zaharescu M (2010) SiO2 nanospheres and tubes obtained by sol–gel method. J Non Cryst Solids 356(44–49):2634–2640. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.03.038
Banerjee S, Datta A (2010) Photoluminescent silica nanotubes and nanodisks prepared by the reverse micelle sol–gel method. Langmuir 26(2):1172–1176. doi:10.1021/la902265e
Shen J, Chen P, Lee Y, Cheng C (2002) Red-light emission in MCM-41 meso-porous nanotubes. Solid State Commun 122(1):65–68
Lee YC, Liu YL, Wang CK, Shen JL, Cheng PW, Cheng CF, Ko CH, Lin TY (2005) Decay dynamics of blue–green luminescence in meso-porous MCM-41 nanotubes. J Lumin 113(3–4):258–264. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2004.10.026
Zhang M, Ciocan E, Bando Y, Wada K, Cheng LL, Pirouz P (2002) Bright visible photoluminescence from silica nanotube flakes prepared by the sol–gel template method. Appl Phys Lett 80(3):491. doi:10.1063/1.1434309
Liu H, Huang J, Li X, Liu J, Zhang Y (2012) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like SnO2/carbon nanotubes composite and its electrochemical properties. J Solgel Sci Technol 63(3):569–572
Mokoena E, Datye A, Coville N (2003) A systematic study of the use of DL-Tartaric acid in the synthesis of silica materials obtained by the sol–gel method. J Solgel Sci Technol 28(3):307–317. doi:10.1023/A:1027418230211
Uchino T, Kurumoto N, Sagawa N (2006) Structure and formation mechanism of blue-light-emitting centers in silicon and silica-based nanostructured materials. Phys Rev B 73(23). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.73.233203
Thomas V, Jose G, Jose G, Biju P, Rajagopal S, Unnikrishnan N (2005) Structural evolution and fluorescence properties of Dy3+: silica matrix. J Solgel Sci Technol 33(3):269–274
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51272085) and the Opening Research Funds Projects of the State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry and College of Chemistry, Jilin University (2010–05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F., Song, Y., Sheng, Y. et al. Growth, structure and optical properties of tartaric acid-templated silica nanotubes by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 68, 204–212 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3152-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-013-3152-0