Abstract
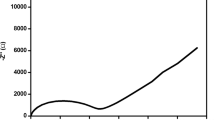
Polyvinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene(PVdF-HFP) and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and sodium triflate(NaTf) were used to prepare P(VdF-HFP)-PMMA-NaTf electrolytes using solution casting technique. The liquid plasticizer ethylene carbonate (EC) was added to the electrolytes in different concentrations say 10, 20, 30 and 40 wt% to achieve the enhancement of Na+ ion conduction at room temperature. Ionic conductivity of the samples was determined using AC impedance analysis and it was 7.86 × 10−8 S cm−1 for the polymer blend electrolyte at room temperature. Inclusion of EC was found to enhance the Na+ ion conduction and maximum value of ionic conductivity, 1.86 × 10−4 S cm−1, was obtained for the EC concentration of 30 wt%. This observation was explained on the basis of FTIR, XRD and AFM analysis of the samples which revealed the enhanced EC-polymer interaction and hence fast ion transport. Larger increase of dielectric constants and the reduced dielectric loss of EC added polymer blend electrolytes revealed the increase of the number of free Na+ ions. Thermal analysis of the samples was done through TGA-DTG technique and the thermal stability was found to decrease after the addition of EC.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ponrouch D, Monti A, Steen BB, Johansson P, Palacin MR (2015) Non-aqueous electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:22–42
Xuel Y, Li X, Quesnel DJ (2017). Int J Electrochem Sci 12:10674–10686
Zhu Y, Yang Y, Fu L, Wu Y (2017) A porous gel-type composite membrane reinforced by nonwoven: promising polymer electrolyte with high performance for sodium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 224:405–411
Xue Y, Quesnel DJ (2016) Synthesis and electrochemical study of sodium ion transport polymer gel electrolytes. RSC Adv 6:7504–7510
Cisnerosa CSM, Levenfelda B, Vareza A, Sancheza JY (2016) Development of sodium-conducting polymer electrolytes: comparison between film-casting and films obtained via green processes. Electrochim Acta 192:456–466
Aravindan V, Lakshmi C, Vickraman P (2009) Investigations on Na+ ion conducting polyvinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene/poly ethylmethacrylate blend polymer electrolytes. Curr Appl Phys 9:1106–1111
Tripathi SK, Gupta A, Kumari M (2012) Studies on electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PVdF–HFP–PMMA–NaI polymer blend electrolyte. Bull Mater Sci 35(6):969–975
Tripathi SK, Jain A, Gupta A, Kumari M, Pure IJ (2013) Appl. Physics 51:315–319
Mindemark J, Mogensen R, Michael Smith J, Manuela Silva M, Brandell D (2017) Polycarbonates as alternative electrolyte host materials for solid-state sodium batteries. Electrochem Commun 77:58–61
Noor SAM, Su NC, Mohamad NS, Ahmad A, Yahya MZA, Zhu HM, Forsyth DR, MacFarlane (2017). Electrochimica Acta 247:983–993
Austen Angell C (2017) Polymer electrolytes—Some principles, cautions, and new practices. Electrochim Acta 250:368–375
Zhua X, Zhao R, Deng W, Ai X, Yang H, Cao Y (2015) An All-solid-state and All-organic Sodium-ion Battery based on Redox-active Polymers and Plastic Crystal Electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 178:55–59
Singh P, Bharati DC, Gupta PN, Saroj AL (2018) Vibrational, thermal and ion transport properties of PVA-PVP-PEG-MeSO 4 Na based polymer blend electrolyte films. J Non-Cryst Solids 494:21–30
Jayanthi S, Arulsankar A, Sundaresan B (2016). Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 122(109):1–11
Rajendran S, Prabhu MR, Rani M (2008). Int J Electrochem Sci 3:282–290
Chaurasia SK, Saroj AL, Singh S, VK TAK, Gupta AK, Verma YL, Singh RK (2015) Studies on structural, thermal and AC conductivity scaling of PEO-LiPF6polymer electrolyte with added ionic liquid [BMIMPF6]. AIP Adv 5(077178):1–13
Saroj AL, Singh RK (2012) Thermal, dielectric and conductivity studies on PVA/Ionic liquid [EMIM][EtSO4] based polymer electrolytes. J Phys Chem Solids 73:162–168
Liew CW, Arifin KH, Kawamura J, Iwai Y, Ramesh S, Arof AK (2015) J. Non-cyst. Solids 425:163–172
Ramesh S, Liew CW, Arof AK (2011) Ion conducting corn starch biopolymer electrolytes doped with ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J Non-Cyst Solids 357:3654–3660
Ning W, Xingxiang Z, Haihuib L, Benqiao H (2009) 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride plasticized-corn starch as solid biopolymer electrolytes. Carbohydr Polym 76:482–484
Ji KS, Moon HS, Kim JW, Park JW (2003) Role of functional nano-sized inorganic fillers in poly(ethylene) oxide-based polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 117:124–130
Isa KBM, Othman L, Zainol NH, Samin SM, Chong WG, Osman Z, Arof AK (2014) Key Eng. Mater. 594-595:786–792
Zidan HM, El-Ghamaz NA, Abdelghany AM, Lotfy A (2016). Int JElectrochem Sci 11:9041–9056
Othman L, Md Isa KB, Osman Z, Yahya R (2017) Ionic Transport Studies of Gel Polymer Electrolytes Containing Sodium Salt. Mater Today Proc 4:5122–5129
Zebardastan N, Khanmirzaei MH, Ramesh S, Ramesh K (2017) Presence of NaI in PEO/PVdF-HFP blend based gel polymer electrolytes for fabrication of dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater Sci Semicond Process 66:144–148
Vignarooban K, Badami P, Dissanayake KL, Ravirajan P, Kannan AM (2017) Poly-acrylonitrile-based gel-polymer electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. Ionics 23:2817–2822
Hashmi SA, Bhat MY, Singh MK, Kalyana Sundaram NT, Raghupathy PC, Tanaka H (2016) Ionic liquid-based sodium ion-conducting composite gel polymer electrolytes: effect of active and passive fillers. J Solid State Electrochem 20(10):2817–2826
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ionic liquid based sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 181:416–423
KarthikeyanS, Sikkanthar S, Selvasekarapandian S, Arunkumar D, Nithya H, Kawamura J (2016) Structural, electrical and electrochemical properties of polyacrylonitrile-ammonium hexaflurophosphate polymer electrolyte system. J Polym Res 23:51
Shmukler LE, Van Thuc N, Fadeeva YA, Safonova LP (2012) Proton conducting gel electrolytes based on polymethylmethacrylate doped with sulfuric acid solutions in N,N-dimethylformamide. J Polym Res 19:9770
Chandra MVL, Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2017) Sampath Monisha. J Polym Eng 37(6):617–631
Rhodes CP, Frech R (1999) Cationâ anion and cationâ polymer interactions in (PEO)nNaCF3SO3 (n=1â 80). Solid State Ionics 121:91–99
Saika D, Kumar A (2004) Ionic conduction in P(VDF-HFP)/PVDF–(PC + DEC)–LiClO 4 polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 49:2581–2589
Kumar GG, Kim P, Kim AR, Nahm KS, Elizabeth RN (2009). Mater Chem Phys 11:40–46
Johnscher AK (1977) The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267:673–679
Natesan B, Karan NK, Katiyar RS (2006). Phys Rev E 74(0420801):1–4
Sudhakar YN, Selvakumar M, Krishna Bhat D (2018) Biopolymer Electrolytes: Fundamentals and Applications in Energy Storage. Elsevier ISBN: 978–0–12-813447-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjana, P.A.B., S, J., S, A. et al. Enhancement of Na+ ion conduction in polymer blend electrolyte P(VdF-HFP) – PMMA- NaTf by the inclusion of EC. J Polym Res 26, 38 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1704-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1704-x