Abstract
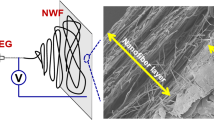
Present paper deals with the effect of gelatin on the structure, phase composition, and morphology of the electrospun chitosan/PEO nanofibers. Special attention is paid to the surface chemistry, surface structure and surface morphology of nanocomposite fibers, as these parameters are crucial for biomedical applications and for eventual subsequent surface modification. Gelatin prevents the crystallization of PEO and chitosan and has significant effect on the surface properties of chitosan/PEO/gelatin nanofibers, especially after the cross-linking. During the heating at 130 °C, gelatin appears on the surface of the nanofibers, what results in a large amount of the surface cracks, as well as in the dramatic changes of the surface chemistry and consequently surface adhesion properties. In addition, we observe regions with a continuous gelatin layer between fibers after the cross-linking, what leads to a significant decrease of the porosity of the nanofiber textile. Special attention has been paid to the complex characterization of the structure and surface chemistry of composite nanofibrous materials in order to predict their surface properties, crucial for wound dressing and tissue engineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun K, Li ZH (2011) Preparations, properties and applications of chitosan based nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning. eXPRESS Polym Lett 4(5):342–361
Gudjónsdóttir M, Gacutan MD Jr, Mendes AC, Chronakis IS, Jespersen L, Karlsson AH (2015) Effects of electrospun chitosan wrapping for dry-ageing of beef, as studied by microbiological, physicochemical and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. Food Chem 184:167–175
Mi F-L, Tan Y-C, Liang H-F, Sung H-S (2002) In vivo biocompatibility and degradability of a novel injectable- chitosan-based implant. Biomaterials 23:181–191
Angelova N, Manolova N, Rashkov I, Maximova V, Bogdanova S, Domard A (1995) Preparation and properties of modified chitosan films for drug release. J Bioact Compat Polym 10:285–298
Selmer-Olsen E, Ratnaweera HC, Pehrson R (1996) A novel treatment process for dairy wastewater with chitosan produced from shrimp-shell waste. Water Sci Technol 34:33–40
Leceta I, Guerrero P, Ibarburu I, Duenas MT, de la Caba K (2013) Characterization and antimicrobial analysis of chitosan-based films. J Food Eng 116:889–899
Min BM, Lee SW, Lim JN, You Y, Lee TS, Kang PH, Park WH (2004) Chitin and chitosan nanofibers: electrospinning of chitin and deacetylation of chitin nanofibers. Polymer 45:7137–7142
Ohkawa K, Cha D, Kim H, Nishida A, Yamamoto H (2004) Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol Rapid Commun 25:1600–1605
Hasegawa M, Isogai A, Onabe F, Usuda M (1992) Dissolving states of cellulose and chitosan in trifluoroacetic acid. J Appl Polym Sci 45:1857–1863
Ohkawa K, Minato K-I, Kumagai G, Hayashi S, Yamamoto H (2006) Chitosan nanofiber. Biomacromolecules 7:3291–3294
Sangsanoh P, Suwantong O, Neamnark A, Cheepsunthornc P, Pavasantd P, Supaphola P (2010) In vitro biocompatibility of electrospun and solvent-cast chitosan substrata towards Schwann, osteoblast, keratinocyte and fibroblast cells. Eur Polym J 46:428–440
Sangsanoh P, Supaphol P (2006) Stability improvement of electrospun chitosan nanofibrous membranes in neutral or weak basic aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 7:2710–2714
Haider S, Park S-Y (2009) Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. J Membr Sci 328:90–96
Geng X, Kwon O-H, Jang J (2005) Electrospinning of chitosan dissolved in concentrated acetic acid solution. Biomaterials 26:5427–5432
Vrieze SD, Westbroeak P, Camp TV, van Langenhove L (2007) Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibrous structures: Feasibility study. J Mater Sci 42:8029–8034
Spasova M, Manolova N, Paneva D, Rashkov I (2004) Preparation of chitosan-containing nanofibres by electrospinning of chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) blend solutions. E-polymers 56:1–12
Duan B, Dong C, Yuan X, Yao K (2004) Electrospinning of chitosan solutions in acetic acid with poly(ethylene oxide). J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 15(6):797–811
Bhattarai N, Edmondson D, Veiseh O, Matsen FA, Zhang M (2005) Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials 26(31):6176–6184
Ohkawa K, Kitagawa T, Yamamoto H (2004) Preparation and characterization of chitosan-gellan hybrid capsules formed by self-assembly at an aqueous solution interface. Macromol Mater Eng 289(1):33–40
Li L, Hsieh Y-L (2006) Chitosan biocomponent nanofibers and nanoporous fibers. Carbohydr Res 341(3):374–381
Park WH, Jeong L, Yoo DI, Hudson S (2004) Effect of chitosan on morphology and conformation of electrospun silk fibroin nanofibers. Polymer 45(21):7151–7157
Bao W-W, He L, Zhang Y-Z, Chang L-N (2006) Influence of blend on the electrospun silk fibroin nanofibers’ morphology. J Soochow Univ Eng Sci Ed 26(1):20–23
Peesan M, Rujiravanit R, Supaphol P (2006) Electrospinning of hexanoyl chitosan/polylactide blends. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 17(5):547–565
Chen Z, Mo X, Qing F (2006) Electrospinning of collagen-chitosan complex. Mater Lett 61(16):3490–3494
Zeugolis DI, Khew ST, Yew ESY, Ekaputra AK, Tong YW, Yung LYL, Hutmacher DW, Shepard C, Raghunath M (2008) Electro-spinning of pure collagen nano-fibers – just an expansive way to make gelatin. Biomaterials 29:2293–2305
Rho KS, Jeong L, Lee G, Seo BM, Park YJ, Hong SD, Roh S, Cho JJ, Park WH, Min BM (2006) Electtrospinning of collagen nanofibers: effects on the behavior of normal human keratinocytes and early-stage wound healing. Biomaterials 27:1452–1461
Yang L, Fitie CFC, van der Werf KO, Bennink ML, Dijkstra PJ, Feijen J (2008) Mechanical properties of single elctrospun collagen type I fibers. Biomaterials 29:955–962
Chen JP, Chang GY, Chen JK (2008) Electrospun collagen/chitosan nanofibrous membrane as wound dressing. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 313–314:183–188
Weadock KS, Miller EJ, Bellincampi LD, Zawadsky JP, Dunn MG (1995) Physical cross-linking of collagen fibers: comparison of ultraviolet irradiation and dehydrothermal treatment. J Biomed Mater Res 29(11):1373–1379
Fujimori E (1965) Ultraviolet light-induced change in collagen macromolecules. Biopolymers Pept Sci Section 3(2):115–119
Cooper DR, Davidson RJ (1965) The effect of ultraviolet irradiation on soluble collagen. Biochem J 97:139–147
Sionkowska A, Skopinska-Wisniewska J, Gawron M, Kozlowska J, Planecka A (2010) Chemical and thermal cross-linking of collagen and elastin hydrolysates. Int J Biol Macromol 47:570–577
Jorge-Herrero E, Fernández P, Turnay J, Olmo N, Calero P, García R, Freile I, Castillo-Olivares JL (1999) Influence of different chemical cross-linking treatments on the properties of bovine pericardium and collagen. Biomaterials 20:539–545
Čapková P, Čajka A, Kolská Z, Kormunda M, Pavlík J, Munzarová M, Dopita M, Rafaja D (2015) Phase composition and surface properties of nylon-6 nanofiber prepared by nanospider technology at various electrode distances. J Polym Res 22:101
Kolská Z, Řezníčková A, Švorčík V (2012) Surface characterization of polymer foils. E-polymers 083:1–13
Yui T, Imada K, Okuyama K, Obata Y, Suzuki K, Ogawa K (1994) Molecular and crystal structures of the anhydrous form of chitosan. Macromolecules 27:7601–7605
Zhang C, Gamble S, Ainsworth D, Slawin AMZ, Andreev YG, Bruce PG (2009) Alkali metal crystalline polymer electrolytes. Nat Mater 8:580–584
Hall MM, Veeraraghavan VG, Rubin H, Winchell PG (1977) The approximation of symmetric X-ray peaks by Pearson type VII distributions. J Appl Crystallogr 10:66
Švorčík V, Makajová Z, Kasálková N, Kolská Z, Bačáková L (2012) Plasma-modified and polyethylene glycol-grafted polymers for potential tissue engineering applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:6665–6671
Kolská Z, Řezníčková A, Nagyová M, Slepičková Kasálková N, Sajdl P, Slepička P, Švorčík V (2014) Plasma activated polymers grafted with cyteamine for bio-application. Polym Degrad Stab 101:1–9
Arima Y, Iwata H (2007) Effect of wettability and surface functional groups on protein adsorption and cell adhesion using well-defined mixed self-assembled monolayers. Biomaterials 28:3074–3082
Faucheux N, Schweiss R, Lutzow K, Werner C, Groth T (2004) Self-assembled monolayers with different terminating groups as model substrates for cell adhesion studies. Biomaterials 25:2721–2730
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support by the project LO1509 of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic and by Operational Program Prague – Competitiveness project (CZ.2.16/3.1.00/24023) supported by EU EU and the SGS project of Internal grant agency UJEP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barchuk, M., Čapková, P., Kolská, Z. et al. Structure and surface properties of chitosan/PEO/gelatin nanofibrous membrane. J Polym Res 23, 20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0906-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0906-0