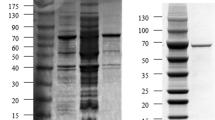
Abstract
SPase is widely used in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries. Previously, a SPase gene was cloned from Bifidobacterium longum JCM1217 and constructed into Escherichia coli BL21. In this paper, its expression conditions were optimized. The results showed that several induction factors determined the expression efficiency of SPase. The initial cell density, IPTG concentration, and induction time and temperature significantly (p < 0.01) affected the total protein content and activity of expressed SPase. The highest expression efficiency was obtained at an initial cell density of OD600 = 0.5, with 0.05 mM IPTG, followed by shaking at 180 rpm and incubation at 30 °C for 15 h. The purified SPase had a specific activity of 122.1 U/mg, which was raised by 1.85 -fold more than that before optimization, and its recovery yield was 86%. Furthermore, SPase also showed higher thermostability. The results of this study provide essential information for the industrial production of SPase.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SPase:
-
Sucrose phosphorylase
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside
- Glc 1-P:
-
α-d-Glucose 1-phosphate
References
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280(Pt 2):309
An C, Winter KD, Desmet T, Soetaert W (2010) Sucrose phosphorylase as cross-linked enzyme aggregate: improved thermal stability for industrial applications. Biotechnol J 5(11):1192–1197
Lee JH, Moon YH, Kim N, Kim YM, Kang HK, Jung JY, Abada E, Kang SS, Kim D (2008) Cloning and expression of the sucrose phosphorylase gene from Leuconostoc mesenteroides in Escherichia coli. Biotech Lett 30(4):749–754
Kitao S, Sekine H (1994) α-d-Glucosyl Transfer to phenolic compounds by sucrose phosphorylase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides and production of α-arbutin. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58(1):38
Minhye S, Namyong C, Jonghoon L, Kyoungheon K (2009) Transglucosylation of caffeic acid by a recombinant sucrose phosphorylase in aqueous buffer and aqueous-supercritical CO2 media. Food Chem 115(3):1028–1033
Kwon T, Kim CT, Lee JH (2007) Transglucosylation of ascorbic acid to ascorbic acid 2-glucoside by a recombinant sucrose phosphorylase from Bifidobacterium longum. Biotech Lett 29(4):611–615
Goedl C, Schwarz A, Minani A, Nidetzky B (2007) Recombinant sucrose phosphorylase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides: characterization, kinetic studies of transglucosylation, and application of immobilised enzyme for production of alpha-d-glucose 1-phosphate. J Biotechnol 129(1):77–86
Nishimoto M, Kitaoka M (2007) Practical preparation of lacto-N-biose I, a candidate for the bifidus factor in human milk. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(8):2101–2104. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70320
Nihira T, Nakajima M, Inoue K, Nishimoto M, Kitaoka M (2007) Colorimetric quantification of α- d -galactose 1-phosphate. Anal Biochem 371(2):259–261
Kitaoka M, Aoyagi C, Hayashi K (2001) Colorimetric quantification of cellobiose employing cellobiose phosphorylase. Anal Biochem 292(1):163–166
Marbach A, Bettenbrock K (2012) lac operon induction in Escherichia coli: systematic comparison of IPTG and TMG induction and influence of the transacetylase LacA. J Biotechnol 157(1):82–88
Malakar P, Venkatesh KV (2012) Effect of substrate and IPTG concentrations on the burden to growth of Escherichia coli on glycerol due to the expression of Lac proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(6):2543–2549
Fernándezcastané A, Caminal G, Lópezsantín J (2012) Direct measurements of IPTG enable analysis of the induction behavior of E. coli in high cell density cultures. Microb Cell Fact 11(1):1–9
Castellanosmendoza A, Castroacosta RM, Olvera A, Zavala G, Mendozavera M, Garcíahernández E, Alagón A, Trujilloroldán MA, Valdezcruz NA (2014) Influence of pH control in the formation of inclusion bodies during production of recombinant sphingomyelinase-D in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 13(1):1–14
Kawasaki H, Nakamura N, Ohmori M, Sakai T (1996) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of sucrose phosphorylase gene from Leuconostoc mesenteroides No. 165. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60(2):322–324
Weickert MJ, Best DEA, Olins PO (1996) Optimization of heterologous protein production in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7(5):494–499
Blanch HW, Prausnitz JM, Curtis RA, Bratko D (2002) Molecular thermodynamics and bioprocessing: from intracellular events to bioseparations. Fluid Phase Equilib 194:31–41
Nomura K, Sugimoto K, Nishiura H, Ohdan K, Nishimura T, Hayashi H, Kuriki T (2008) Glucosylation of acetic acid by sucrose phosphorylase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72(1):82–87
Funkenstein B, Rebhan Y, Funkenstein B, Rebhan Y (2007) Expression, purification, renaturation and activation of fish myostatin expressed in Escherichia coli: facilitation of refolding and activity inhibition by myostatin prodomain. Protein Express Purif 54(1):54–65
Yeh SR, Rousseau DL (1998) Folding intermediates in cytochrome c. Nat Struct Biol 5(3):222
Li ZY, Liu CP, Zhu LQ, Jing GZ, Zhou JM (2001) The chaperone activity of trigger factor is distinct from its isomerase activity during co-expression with adenylate kinase in Escherichia coli. Febs Lett 506(2):108–112
Singh S, Du PJ, Pillay B, Prior BA (2000) The production of hemicellulases by Thermomyces lanuginosus strain SSBP: influence of agitation and dissolved oxygen tension. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54(5):698–704
Shioya S, Morikawa M, Kajihara Y, Shimizu H (1999) Optimization of agitation and aeration conditions for maximum virginiamycin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51(2):164–169
Lee JH, Yoon SH, Nam SH (2006) Molecular cloning of a gene encoding the sucrose phosphorylase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides B-1149 and the expression in Escherichia coli. Enzyme Microbial Technol 39(4):612–620
Lee JH, Moon YH, Kim N, Kim YM, Kang HK, Jung JY, Abada E, Kang SS, Kim D (2008) Cloning and expression of the sucrose phosphorylase gene from Leuconostoc mesenteroides in Escherichia coli. Biotech Lett 30(4):749
Silverstein R, Voet J, Reed D, Abeles RH (1967) Purification and mechanism of action of sucrose phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 242(242):1338–1346
Broek LAMVD., Boxtel ELV, Kievit RP, Verhoef R, Beldman G, Voragen AGJ (2004) Physico-chemical and transglucosylation properties of recombinant sucrose phosphorylase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis DSM20083. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65(2):219
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the program for International S & T Cooperation Projects of Shenyang (F16-219-6-00), the research Grants of Shenyang Kay Laboratory (F17-158-1-00), and the research foundation of Shenyang Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Sun, X., Li, W. et al. Expression and Characterization of Recombinant Sucrose Phosphorylase. Protein J 37, 93–100 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-017-9754-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-017-9754-6