Abstract
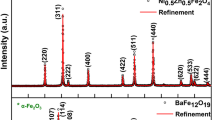
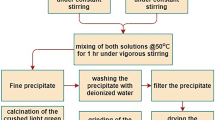
The strontium ferrite nano-crystals were prepared via co-precipitation method in different synthesis media including a mixture of ethanol and water (with a volume ratio equal to 3:1) and water. In this way, the iron and strontium chlorides with various molar ratios were utilized as sources for Fe3+ and Sr2+ ions, respectively. Phase analyses, structural properties and morphology of the SrFe12O19 powders were characterized by various techniques including X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer and Fourier transform infrared spectra. Thermal decomposition behaviors of the as-synthesized precursors were monitored by DTA/TGA (differential thermal analysis/thermo-gravimetric analysis). The effects of molar ratio, calcination temperature and co-precipitation media of the strontium ferrite powder were investigated. The results of DTA indicated that the strontium hexaferrite prepared by co-precipitation in ethanol/water media was formed at a lower temperature. The maximum saturation magnetization of the strontium ferrite powder with the value of 58 emu/g was achieved at a temperature of 950 °C by a Fe3+/Sr2+ molar ratio of 12. Wide coercivity in the range of 1512–5764 Oe was observed by tuning calcination temperatures. Furthermore, the photocatalytic properties of the resultant optimum SrFe12O19 particles were assessed. The destruction of methylene blue dye was about 46% in the presence of the strontium ferrite under UV light irradiation for 120 min.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Cunningham, G. Al-Sayyed, S. Srijaranai, Adsorption of model pollutants onto TiO2 particles in relation to photoremediation of contaminated water, in Aquatic and Surface Photochemistry, ed. by G.R. Helz, R.G. Zepp, D.G. Crosby (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1994), pp. 317–348. (Reissued 2018)
R.J. Tayade, P.K. Surolia, R.G. Kulkarni, R.V. Jasra, Photocatalytic degradation of dyes and organic contaminants in water using nanocrystalline anatase and rutile TiO2. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 8, 455–462 (2007)
C. Hariharan, Photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants in water by ZnO nanoparticles: revisited. Appl. Catal. Gen. 304, 55–61 (2006)
P. Shukla, I. Fatimah, S. Wang, H.M. Ang, M.O. Tadé, Photocatalytic generation of sulphate and hydroxyl radicals using zinc oxide under low-power UV to oxidise phenolic contaminants in wastewater. Catal. Today 157, 410–414 (2010)
R.L. Pozzo, M.A. Baltanás, A.E. Cassano, Supported titanium oxide as photocatalyst in water decontamination: state of the art. Catal. Today 39, 219–231 (1997)
T. Xin, M. Ma, H. Zhang, J. Gu, S. Wang, M. Liu, Q. Zhang, A facile approach for the synthesis of magnetic separable Fe3O4@TiO2, core–shell nanocomposites as highly recyclable photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 288, 51–59 (2014)
Z. Teng, X. Su, G. Chen, C. Tian, H. Li, L. Ai, G. Lu, Superparamagnetic high-magnetization composite microspheres with Fe3O4@SiO2 core and highly crystallized mesoporous TiO2 shell. Colloid Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 402, 60–65 (2012)
F. Ghasemy-Piranloo, F. Bavarsiha, S. Dadashian and M. Rajabi, Synthesis of core/shell/shell Fe3O4/SiO2/ZnO nanostructure composite material with cubic magnetic cores and study of the photo-degradation ability of methylene blue. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00359-x
F. Bavarsiha, M. Rajabi, M. Montazeri-Pour, Synthesis of SrFe12O19/SiO2/TiO2 composites with core/shell/shell nano-structure and evaluation of their photo-catalytic efficiency for degradation of methylene blue. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 1877–1887 (2018)
A. Xia, C. Zuo, L. Chen, C. Jin, Y. Lv, Hexagonal SrFe12O19 ferrites: hydrothermal synthesis and their sintering properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 332, 186–191 (2013)
O. Mohanta, Y. Singhbabu, S. Giri, D. Dadhich, N. Das, R.K. Sahu, Degradation of Congo red pollutants using microwave derived SrFe12O19: an efficient magnetic photocatalyst under visible light. J. Alloys Compd. 564, 78–83 (2013)
K. Mohammadi, M. Sadeghi, R. Azimirad, Facile synthesis of SrFe12O19 nanoparticles and its photocatalyst application. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 10042–10047 (2017)
A. Farghali, M. Khedr, A. Moustafa, Photocatalytic activity and magnetic properties of nanocrystallite strontium hexaferrite prepared by self-flash combustion. Mater. Technol. 23, 104–109 (2008)
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
S. Rowley, Y.-S. Chai, S.-P. Shen, Y. Sun, A. Jones, B. Watts, J.F. Scott, Uniaxial ferroelectric quantum criticality in multiferroic hexaferrites BaFe12O19 and SrFe12O19. Sci. Rep. 6, 25724 (2016)
H. Stäblein, Hard ferrites and plastoferrites. Handb. Ferromagn. Mater. 3, 441–602 (1982)
V. Pankov, M. Pernet, P. Germi, P. Mollard, Fine hexaferrite particles for perpendicular recording prepared by the coprecipitation method in the presence of an inert component. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 120, 69–72 (1993)
H. Lu, R. Hong, H. Li, Influence of surfactants on co-precipitation synthesis of strontium ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 10127–10131 (2011)
M. Montazeri-Pour, A. Ataie, R. Nikkhah-Moshaie, Synthesis of nano-crystalline barium hexaferrite using a reactive co-precipitated precursor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 44, 4239–4242 (2008)
C. Surig, K. Hempel, D. Bonnenberg, Hexaferrite particles prepared by sol-gel technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30, 4092–4094 (1994)
A. Drmota, M. Drofenik, A. Žnidaršič, Synthesis and characterization of nano-crystalline strontium hexaferrite using the co-precipitation and microemulsion methods with nitrate precursors. Ceram. Int. 38, 973–979 (2012)
A. Ataie, S. Heshmati-Manesh, Synthesis of ultra-fine particles of strontium hexaferrite by a modified co-precipitation method. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1951–1955 (2001)
H. Kojima, Fundamental properties of hexagonal ferrites with magnetoplumbite structure. Handb. Ferromagn. Mater. 3, 305–391 (1982)
H.-F. Yu, K.-C. Huang, Effects of pH and citric acid contents on characteristics of ester-derived BaFe12O19 powder. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 260, 455–461 (2003)
S. Kulkarni, J. Shrotri, C. Deshpande, S. Date, Synthesis of chemically coprecipitated hexagonal strontium-ferrite and its characterization. J. Mater. Sci. 24, 3739–3744 (1989)
H. Su, Y. Xie, B. Li, X. Liu, Y. Qian, A novel one-step solvothermal route to nanocrystalline Sn4P3. J. Solid State Chem. 146, 110–113 (1999)
M. Montazeri-Pour, A. Ataie, Synthesis of nanocrystalline barium ferrite in ethanol/water media. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25, 465–469 (2009)
A. Ataie, M. Montazeri-Pour, Formation mechanism of BaFe12O19 nanoparticles processed via wet chemical route using mixed solvent. Int. J. Nanosci. 10, 1083–1086 (2011)
A. Davoodi, B. Hashemi, Investigation of the effective parameters on the synthesis of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles by chemical coprecipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 512, 179–184 (2012)
G. Tan, X. Chen, Structure and multiferroic properties of barium hexaferrite ceramics. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 327, 87–90 (2013)
M. Kari, M. Montazeri-Pour, M. Rajabi, V. Tizjang, S. Moghadas, Maximum SiO2 layer thickness by utilizing polyethylene glycol as the surfactant in synthesis of core/shell structured TiO2–SiO2 nano-composites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 5560–5569 (2014)
M. Ganjali, M. Ganjali, A. Eskandari, M. Aminzare, Effect of heat treatment on structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline SrFe12O19 hexaferrite synthesized by Co-precipitation method. J. Adv. Mater. Process 1, 41–48 (2013)
E. Kiani, A.S. Rozatian, M.H. Yousefi, Synthesis and characterization of SrFe12O19 nanoparticles produced by a low-temperature solid-state reaction method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 2485–2492 (2013)
S. Tyagi, R.C. Agarwala, V. Agarwala, A comparative study on the morphology and magnetic properties of barium and strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Adv. Mater. Res. 67, 203–208 (2009)
M. Hessien, M. Rashad, K. El-Barawy, Controlling the composition and magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrite synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 336–343 (2008)
N. Kumar, A. Kumar, R. Jha, A. Dogra, R. Pasricha, R. Kotnala, H. Kishan, V. Awana, Impact of particle size on room temperature ferrimagnetism of SrFe12O19. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 23, 423–427 (2010)
L. Lutterotti, H. Pilliere, C. Fontugne, P. Boullay, D. Chateigner, Full-profile search-match by the Rietveld method. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 52, 587–598 (2019)
T.T.V. Nga, N.P. Duong, T.T. Loan, T.D. Hien, Key step in the synthesis of ultrafine strontium ferrite powders (SrFe12O19) by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 610, 630–634 (2014)
Z.F. Zi, Y.P. Sun, X.B. Zhu, Z.R. Yang, J.M. Dai, W.H. Song, Structural and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 hexaferrite synthesized by a modified chemical co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2746–2751 (2008)
V. Harikrishnan, P. Saravanan, R. Ezhil Vizhi, D.R. Babu, V.T.P. Vinod, P. Kejzlar, M. Černík, Effect of annealing temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of CTAB-capped SrFe12O19 platelets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 775–783 (2016)
B.H. Toby, R factors in Rietveld analysis: how good is good enough? Powder Diffr. 21, 67–70 (2012)
E. Roohani, H. Arabi, R. Sarhaddi, S. Sudkhah, A. Shabani, Effect of annealing temperature on structural and magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29, 1550190 (2015)
M.A. Ahmed, N. Helmy, S.I. El-Dek, Innovative methodology for the synthesis of Ba-M hexaferrite BaFe12O19 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 3394–3398 (2013)
G.B. Teh, Y.C. Wong, R.D. Tilley, Effect of annealing temperature on the structural, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of sol–gel derived Magnetoplumbite-type (M-type) hexagonal strontium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2318–2322 (2011)
T.R. Wagner, Preparation and crystal structure analysis of magnetoplumbite-type BaGa12O19. J. Solid State Chem. 136, 120–124 (1998)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc, Reading, 1978)
M. Hessien, M. Radwan, M. Rashad, Enhancement of magnetic properties for the barium hexaferrite prepared through ceramic route. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 78, 282–287 (2007)
Z. Mosleh, P. Kameli, M. Ranjbar, H. Salamati, Effect of annealing temperature on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40, 7279–7284 (2014)
W. Roos, Formation of chemically coprecipitated barium ferrite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 63, 601–603 (1980)
Y.-P. Fu, C.-H. Lin, Fe/Sr ratio effect on magnetic properties of strontium ferrite powders synthesized by microwave-induced combustion process. J. Alloys Compd. 386, 222–227 (2005)
X. Meng, Y. Zhu, S. Xu, T. Liu, Facile synthesis of shell–core polyaniline/SrFe12O19 composites and magnetic properties. RSC Adv. 6, 4946–4949 (2016)
T. Ben Ghzaiel, W. Dhaoui, A. Pasko, F. Mazaleyrat, Effect of non-magnetic and magnetic trivalent ion substitutions on BaM-ferrite properties synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 671, 245–253 (2016)
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, H. Güngüneş, A. Baykal, S.V. Trukhanov, A.V. Trukhanov, Manganese/Yttrium codoped strontium nanohexaferrites: evaluation of magnetic susceptibility and mossbauer spectra. Nanomaterials 9, 24 (2018)
M. Asghari, A. Ghasemi, E. Paimozed, Microwave and magnetic analysis of substituted SrFe12O19/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Curr. Nanosci. 8, 239–243 (2012)
V. Tizjang, M. Montazeri-Pour, M. Rajabi, M. Kari, S. Moghadas, Surface modification of sol–gel synthesized TiO2 photo-catalysts for the production of core/shell structured TiO2–SiO2 nano-composites with reduced photo-catalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 3008–3019 (2015)
S. Xing, Z. Zhou, Z. Ma, Y. Wu, Characterization and reactivity of Fe3O4/FeMnOx core/shell nanoparticles for methylene blue discoloration with H2O2. Appl. Catal. B 107, 386–392 (2011)
W. Zhanyong, Z. Liuming, L. Jieli, Q. Huichun, Z. Yuli, F. Yongzheng, J. Minglin, X. Jiayue, Microwave-assisted synthesis of SrFe12O19 hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2782–2785 (2010)
M. Bahgat, F. Awan, H. Hanafy, The influence of reaction parameters on magnetic properties of synthesized strontium ferrite. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Nucl. Mater. Metall. Eng. 9, 1043–1047 (2015)
M. George, A. Mary John, S.S. Nair, P.A. Joy, M.R. Anantharaman, Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 190–195 (2006)
S. Cho, K. Jeon, J. Kim, K.H. Kim, J. Kim, Synthesis and Ferromagnetic Properties of Magnetic Ink for Direct Printing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47, 3157–3159 (2011)
D. Lisjak, M. Drofenik, The influence of the coprecipitation conditions on the low-temperature formation of barium hexaferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 8606–8612 (2007)
S.E. Jacobo, L. Civale, M.A. Blesa, Evolution of the magnetic properties during the thermal treatment of barium hexaferrite precursors obtained by coprecipitation from barium ferrate (VI) solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 260, 37–41 (2003)
D.D. Mishra, G. Tan, Visible photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue on magnetic SrFe12O19. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 123, 157–161 (2018)
A. Houas, H. Lachheb, M. Ksibi, E. Elaloui, C. Guillard, J.-M. Herrmann, Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl. Catal. B 31, 145–157 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for financially supporting this research work under Contract Number of 94/sad/42699 on 9/11/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bavarsiha, F., Montazeri-Pour, M. & Rajabi, M. Effect of Non-aqueous Media on Nano-crystalline SrFe12O19 Particles Produced by Co-precipitation with Metal Chlorides and Evaluation of Their Magnetic and Photocatalytic Properties. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 2386–2396 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01414-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01414-7