Abstract
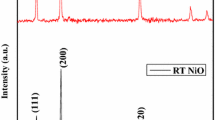
In the present work, NiO nanoparticles are synthesized using chemical co-precipitation method which is an easy and cost-effective approach. Aqueous solutions of the precursors containing Ni(NO3)2.6H2O and NaOH pellets are calcined at 300 °C for 2 h. The structural, morphological, compositional, optical study, and thermal analysis of the synthesized powdered product was investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), UV–vis absorption spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermo-gravimetric analysis. FTIR study shows the presence of functional groups in the synthesized NiO nanoparticles. The powder XRD pattern along with Rietveld refinement data reveals that the prepared sample is NiO with face-centered cubic (fcc) structure (Fm-3 m space group) having average crystallite size ranging from 4 to 6 nm. The optical band gap of the synthesized NiO nanoparticles (estimated from Tauc’s plot) is found to be ~ 3.20 eV which is less than the bulk NiO clearly showing red shift. This could be attributed due to the presence of chemical defects or vacancies resulting in the formation of some trap states.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Meyer, A.M. Albrecht-Gary, C.O. Dietrich-Buchecker, J.P. Sauvage, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 4599 (1997)
V.T. Liveri, Controlled Synthesis of Nanoparticles in Microheterogeneous Systems (Springer, New York, 2006)
Y. Wu, Y. He. T. Wu, T. Chen, W. Weng, H. Wan, Mater. Lett. 61(14–15), 3174 (2007)
H. Yang, Q. Tao, X. Zhang, A. Tang, J. Ouyang, J. Alloys Compds. 459, 98 (2008)
J. He, H. Lindstrom, A. Hagfeldt, E.S. Lindquist, J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 8940 (1999)
K. Yoshimura, T. Miki, S. Tanemura, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 2440 (1995)
K. Liu, M. Anderson, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 124 (1966)
I. Hotovy, V. Rehacek, P. Siciliano, S. Capone, L. Spiess, Thin Solid Films 418, 9 (2002)
H. Sato, T. Minami, S. Takata, T. Yamada, Thin Solid Films 236(1–2), 27 (1993)
C.R. Makkus, K. Hemmes, D.W.H.J. Wit, J. Electrochem. Soc. 141, 3429 (1994)
M.I. Chan, Y.T. Hsu, C.F. Hong, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1899 (2002)
M. Alagiri, S. Ponnusamy, C. Muthamizhchelvam, J. Mater Sci: Mater Electron 23, 728 (2012)
L. Xiang, X.Y. Deng, Y. Jin, Scrip. Materialia 47, 219 (2002)
S. Takami, R. Hayakawa, Y. Wakayama, T. Chikyow, Nanotech. 21, 134009 (2010)
D.V. Lyso, D.V. Kuznetsov, A.G. Yudin, D.S. Muratov, V.V. Levina, D.I. Ryzhonkov, Nanotechnol. Res. 5, 493 (2010)
W. Wang, Y. Liu, C. Xu, C. Zheng, G. Wang, Chem. Phys. Lett. 362, 119 (2002)
N.M. Hosny, Polyhedron 30, 470 (2011)
A. Jena, S.A. Shivashankar, A.I.P. Conf, Proc. 1063, 211 (2008)
P. Palanisamy, A.M. Raichur, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29, 199 (2009)
S.S.L. Irudaya, D.M. Priya, V. Shally, J. Gerardin, Inter. Res. J. Adv. Engg. Sci. 2, 55 (2016)
A. Kalam, A.G. Al-Sehemi, A.S. Al-Shihri, G. Du, T. Ahmad, Mater. Charac. 68, 77 (2012)
N. Srivastava, P.C. Srivastava, Bull. Mater. Sci. 33, 653 (2010)
K. Nakamoto, Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compound, 4th edn. (Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 1991)
Z. Wei, H. Qiao, H. Yang, C. Zhang, X. Yan, J. Alloy Compd. 479, 855 (2009)
Y.B.M. Mahaleh, S.K. Sadrnezhaad and D. Hosseini, Journal of Nanomaterials 2008, 4 pages (2008)
A.M. Abdeen, O.M. Hemeda, E.E. Assem, M.M. Elsehly, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 238, 75 (2002)
S. Carbonin, F. Martignago, G. Menegazzo, A. Negro, Phys. Chem. Miner. 29, 503 (2002)
C. Suryanarayana, M.G. Nortan, X-Ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach (Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, 1998)
L. Kumar, P. Kumar, A. Narayan, M. Kar, Intern. Nano Lett. 3, 8 (2013)
T. Shahid, T.M. Khan, M. Zakria, R.I. Shakoor, M. Arfan, S. Khursheed, J. Mater. Sci. Engg. 5, 287 (2016)
S. Rakshit, S. Ghosh, S. Chall, S.S. Mati, S.P. Moulik, S.C. Bhattacharya, RSC Adv. 3, 19348 (2013)
A. Hagfeldt, M. Gratzel, Chem. Rev. 95, 49 (1995)
A.J. Varkey, A.F. Fort, Thin Solid Films 235, 47 (1993)
N. Srivastava, P.C. Srivastava, Physica E 42, 2225 (2010)
X. Song, L. Gao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 346 (2008)
L. Kumari, W.Z. Li, C.H. Vannoy, R.M. Leblanc, D.Z. Wang, Cryst. Res. Technol. 44, 495 (2009)
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Prof. Rajendra K. Singh, Department of Physics, BHU for getting FTIR, UV-vis, and TG-DTA measurements done on our samples. The authors are much thankful to Dr. O.P. Sinha (Director, Amity Institute of Nanotechnology, Noida) for extending us the XRD facility. Thanks are also due to Dr. Manish K. Srivastava (Department of Physics, Banasthali Vidyapith, Rajasthan) for doing FE-SEM measurements of our samples. Mr. Anadi Krishna Atul also wants to acknowledge the University for providing the financial assistance in the form of UGC-Research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atul, A.K., Srivastava, S.K., Gupta, A.K. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of NiO Nanoparticles by Chemical Co-precipitation Method: an Easy and Cost-Effective Approach. Braz J Phys 52, 2 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-021-01006-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-021-01006-2