Abstract
Current study was aimed to determine the antibacterial, antioxidant and cytotoxic potential of Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) and Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs). Nanoparticles were characterized by UV–Vis spectrophotometry, particle size analyzer (PSA), fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined by standard agar dilution method. Antibacterial potential of nanoparticles was analyzed by standard disc diffusion method against bacterial strains including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumonia. Different concentrations of NPs (0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.4 mg/mL) were incorporated to evaluate the antimicrobial activity. Antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity of these NPs was analyzed by DPPH method and brine shrimp cytotoxicity assay, respectively. The MIC of TiO2NPs against E. coli, P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae was 0.04, 0.08 and 0.07 mg/mL respectively while the MIC of ZnONPs against the above strains was 0.01, 0.015 and 0.01 mg/mL. The maximum zone of inhibition was observed for K. pneumoniae i.e., 20mm and 25mm against TiO2 and ZnO NPs respectively, at 1.4 mg/mL concentration of NPs. The susceptibility of NPs against bacterial strains was evaluated in the following order: K. pneumoniae > P. aeruginosa > E. coli. The antioxidant activity of nanoparticles increased by increasing the concentration of NPs while cytotoxic analysis exhibited non-toxic effect of ZnO NPs while TiO2 had toxic effects on 1.2 and 1.4 mg/mL concentrations. Results revealed that ZnO NPs have more antibacterial and negligible cytotoxic potential in contrast to TiO2 NPs.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All the appropriate data and material regarding the current study is present within the manuscript.
References
Chau TP, Brindhadevi K, Krishnan R, Alyousef MA, Almoallim HS, Whangchai N, Pikulkaew S (2022) A novel synthesis, analysis and evaluation of Musa coccinea based zero valent iron nanoparticles for antimicrobial and antioxidant. Environ Res 209:112770
Gangwar R, Ghosh A, Kumar S, Maurya VK (2023) Antibacterial, antioxidant and nutraceutical potential of new culinary-medicinal mushroom Russula lakhanpalii (Agaricomycetes) from India. Int J Med Mushrooms 25.
Martelli G, Giacomini D (2018) Antibacterial and antioxidant activities for natural and synthetic dual-active compounds. Eur J Med Chem 158:91–105
Rajeswari VD, Eed EM, Elfasakhany A, Badruddin IA, Kamangar S, Brindhadevi K (2021) Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Laurus nobilis (bay leaf): Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Appl Nanosci 1–8
Yuan S, Xue Z, Zhang S, Wu C, Feng Y, Kou X (2023) The characterization of antimicrobial nanocomposites based on chitosan, Cinnamon essential oil, and TiO2 for fruits preservation. Food Chem 135446
Ghosh C, Sarkar P, Issa R, Haldar J (2019) Alternatives to conventional antibiotics in the era of antimicrobial resistance. Trends Microbiol 27(4):323–338
Habib S, Rashid F, Tahir H, Liaqat I, Latif AA, Naseem S, ... Jefri OA (2023) Antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of biosynthesized zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Microorganisms 11(6):1363
Anupong W, On-Uma R, Jutamas K, Salmen SH, Alharbi SA, Joshi D, Jhanani GK (2023) Antibacterial, antifungal, antidiabetic, and antioxidant activities potential of Coleus aromaticus synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Res 216:114714
Joshi KM, Shelar A, Kasabe U, Nikam LK, Pawar RA, Sangshetti J, ... Chaskar MG (2022) Biofilm inhibition in Candida albicans with biogenic hierarchical zinc-oxide nanoparticles. Biomater Adv 134:112592
Archana P, Janarthanan B, Bhuvana S, Rajiv P, Sharmila S (2022) Concert of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Cucumis melo by green synthesis and the antibacterial activity on pathogenic bacteria. Inorg Chem Commun 137:109255
Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Ahmad R, Mahmood T, Ali B, Khalil AT, ... Munir A (2018) Nanomedicines for developing cancer nanotherapeutics: From benchtop to bedside and beyond. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:9449–9470
Jan H, Shah M, Andleeb A, Faisal S, Khattak A, Rizwan M, ... Abbasi BH (2021) Plant-based synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) using aqueous leaf extract of aquilegia pubiflora: Their antiproliferative activity against HepG2 cells inducing reactive oxygen species and other in vitro properties. Oxid Med Cell Longev
Naiel B, Fawzy M, Halmy MWA, Mahmoud AED (2022) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Sea Lavender (Limonium pruinosum L. Chaz.) extract: characterization, evaluation of anti-skin cancer, antimicrobial and antioxidant potentials. Sci Rep 12(1):20370
Han Y, Zhang S, Shen N, Li D, Li X (2017) MOF-derived porous NiO nanoparticle architecture for high performance supercapacitors. Mater Lett 188:1–4
Gudkov SV, Burmistrov DE, Serov DA, Rebezov MB, Semenova AA, Lisitsyn AB (2021) A mini review of antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Front Phys 9:641481
Iravani S (2011) Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem 13(10):2638–2650
Subhani AA, Irshad M, Ali S, Jawad M, Akhtar MF, Summer M (2023) UV-spectrophotometric optimization of temperature, pH, concentration and time for eucalyptus globulus capped silver nanoparticles synthesis, their characterization and evaluation of biological applications. J Fluoresc 1–12
Summer M, Ali S, Tahir HM, Abaidullah R, Tahir H, Mumtaz S, ... Tariq M (2023) Silk sericin protein: Turning discarded biopolymer into ecofriendly and valuable reducing, capping and stabilizing agent for nanoparticles synthesis using sonication. Macromol Chem Phys 2300124
Faisal S, Ullah R, Alotaibi A, Zafar S, Rizwan M, Tariq MH (2023) Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles employing biomolecules of Paraclostridium benzoelyticum strain: Its characterization and their in-vitro antibacterial, anti-aging, anti-cancer and other biomedical applications. Microsc Res Tech
Shafiee A, Rabiee N, Ahmadi S, Baneshi M, Khatami M, Iravani S, Varma RS (2022) Core-shell nanophotocatalysts: Review of materials and applications. ACS Appl Nano Mater 5:55–86
Sarfraz N, Khan I (2021) Plasmonic gold nanoparticles (AuNPs): Properties, synthesis and their advanced energy, environmental and biomedical applications. Chem Asian J 16:720–742
Rai P, Pandey A (2022) Role of emerging green technology in remediation of toxic pollutants. Innov Environ Biotechnol 183–201
Zafar S, Faisal S, Jan H, Ullah R, Rizwan M, Abdullah, … & Khattak, A. (2022) Development of Iron nanoparticles (FeNPs) using biomass of enterobacter: Its Characterization, antimicrobial, anti-Alzheimer’s, and enzyme inhibition potential. Micromachines 13(8):1259
Thema FT, Manikandan E, Dhlamini MS, Maaza MJML (2015) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via Agathosma betulina natural extract. Mater Lett 161:124–127
Saqib S, Nazeer A, Ali M, Zaman W, Younas M, Shahzad A, ... Nisar M (2022) Catalytic potential of endophytes facilitates synthesis of biometallic zinc oxide nanoparticles for agricultural application. BioMetals 35(5): 967–985
Alavi M, Nokhodchi A (2021) Synthesis and modification of bio-derived antibacterial Ag and ZnO nanoparticles by plants, fungi, and bacteria. Drug Discov Today 26(8):1953–1962
Al-Radadi NS, Faisal S, Alotaibi A, Ullah R, Hussain T, Rizwan M, ... Ali Z (2022) Zingiber officinale driven bioproduction of ZnO nanoparticles and their anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-Alzheimer, anti-oxidant, and anti-microbial applications. Inorg Chem Commun 140:109274
Eadi SB, Kim S, Jeong SW, Jeon HW (2017) Novel preparation of Fe doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their application for gas sensor and photocatalytic degradation. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2017:1–6
Manzoor M, Rafiq A, Ikram M, Nafees M, Ali S (2018) Structural, optical, and magnetic study of Ni-doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. Int Nano Lett 8:1–8
Khairy M, Zakaria W (2014) Effect of metal-doping of TiO2 nanoparticles on their photocatalytic activities toward removal of organic dyes. Egypt J Pet 23:419–426
Nithya N, Bhoopathi G, Magesh G, Kumar CDN (2018) Neodymium doped TiO2 nanoparticles by sol-gel method for antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. Mater Sci Semicond Process 83:70–82
Salehi P, Babanouri N, Roein-Peikar M, Zare F (2018) Long-term antimicrobial assessment of orthodontic brackets coated with nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide against Streptococcus mutans. Prog Orthod 19:35
Ahmad MA, Yuesuo Y, Ao Q, Adeel M, Hui ZY, Javed R (2019) Appraisal of comparative therapeutic potential of undoped and nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Molecules 24(21):3916
Ahamed M, Khan MAM, Akhtar MJ, Alhadlaq HA, Alshamsan A (2017) Ag-doping regulates the cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles via oxidative stress in human cancer cells. Sci Rep 7:17662
Ahmad J, Siddiqui M, Akhtar M, Alhadlaq H, Alshamsan A, Khan S, Wahab R, Al-Khedhairy A, Al-Salim A, Musarrat J et al (2018) Copper doping enhanced the oxidative stress–mediated cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles in A549 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 37:496–507
Caratto V, Locardi F, Alberti S, Villa S, Sanguineti E, Martinelli A, Balbi T, Canesi L, Ferretti M (2016) Different sol–gel preparations of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles: Characterization, photocatalytic activity and cytotoxicity. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 80:152–159
Liu Z, Jian Z, Fang J, Xu X, Zhu X, Wu S (2012) Low-temperature reverse microemulsion synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic performance of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Int J Photoenergy
Ahmad W, Kalra D (2020) Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of ZnO nanoparticles using Euphorbia hirta leaf extract. J King Saud Univ-Sci 32(4):2358–2364
Ajmal N, Saraswat K, Bakht MA, Riadi Y, Ahsan MJ, Noushad M (2019) Cost-effective and eco-friendly synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles using fruit’s peel agro-waste extracts: characterization, in vitro antibacterial, antioxidant activities. Green Chem Lett Rev 12(3):244–254
Ullah R, Shah S, Muhammad Z, Shah SA, Faisal S, Khattak U, ... Taj Akbar M (2021) In vitro and in vivo applications of Euphorbia wallichii shoot extract-mediated gold nanospheres. Green Process Synth 10(1):101–111
Simorangkir M, Nainggolan B, Juwitaningsih T, Silaban S (2021, March) The toxicity of n-hexane, ethyl acetate and ethanol extracts of sarangbanua (Clerodendrumfragrans Vent Willd) leaves by brine shrimp lethality test (BSLT) method. J Phys Conf Ser 1811(1):012053. IOP Publishing
Imran M, Jan H, Faisal S, Shah SA, Shah S, Khan MN, ... Syed S (2021) In vitro examination of anti-parasitic, anti-Alzheimer, insecticidal and cytotoxic potential of Ajuga bracteosa Wallich leaves extracts. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(5):3031–3036
Summer M, Tahir HM, Ali S (2023) Sonication and heat-mediated synthesis, characterization and larvicidal activity of sericin-based silver nanoparticles against dengue vector (Aedes aegypti). Microsc Res Tech. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.24333
Summer M, Tahir HM, Ali S, Abaidullah R, Mumtaz S, Nawaz S (2023) Bactericidal potential of different size sericin-capped silver nanoparticles synthesized by heat, light, and sonication. J Basic Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202200632
Mumtaz S, Ali S, Tahir HM, Mumtaz S, Mughal TA, Kazmi SAR, ... Zulfiqar A (2023) Biological applications of biogenic silk fibroin–chitosan blend zinc oxide nanoparticles. Polym Bull 1–24
Durairaj B, Xavier T, Muthu S (2014) Fungal generated titanium dioxide nanopartilces for UV Protective and bacterial resistant fabrication. Int J Eng Sci Technol 6(9):621
Panda J, Singh UP, Sahu R (2018, September) Synthesis, characterization of TiO2 nano particles for enhancement of electron transport application in DSSC with Cu-BPCA Dye. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 410(1):012008. IOP Publishing
Fadillah R, Rati Y, Dewi R, Farma R, Rini AS (2021, February) Optical and structural studies on bio-synthesized ZnO using Citrullus lanatus peel extract. J Phys Conf Ser 1816(1):012019. IOP Publishing
Muhammad W, Ullah N, Haroon M, Abbasi BH (2019) Optical, morphological and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Papaver somniferum L. RSC Adv 9(51):29541–29548
Zak AK, Razali R, Majid WA, Darroudi M (2011) Synthesis and characterization of a narrow size distribution of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 1399–1403
Baker C, Pradhan A, Pakstis L, Pochan DJ, Shah SI (2005) Synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5(2):244–249
Tang S, Zheng J (2018) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: structural effects. Adv Healthc Mater 7(13):170–178
Le Ouay B, Stellacci F (2015) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: a surface science insight. Nano Today 10(3):339–354
Russel WB (1989) Formulation and processing of colloidal dispersions. MRS Proc Cambridge University Press 177:281
Muhammad Tahir H, Saleem F, Ali S, Ain QU, Fazal A, Summer M, ... Murtaza G (2020) Synthesis of sericin-conjugated silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial activity. J Basic Microbiol 60(5):458–467
Mumtaz S, Ali S, Kazmi SAR, Mughal TA, Mumtaz S, Tahir HM, ... Rashid MI (2022) Analysis of the antimicrobial potential of sericin-coated silver nanoparticles against human pathogens. Microsc Resd Tech
Alamdari S, Sasani Ghamsari M, Lee C, Han W, Park HH, Tafreshi MJ, ... Ara MHM (2020) Preparation and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl Sci 10(10):3620
Handore K, Bhavsar S, Horne A, Chhattise P, Mohite K, Ambekar J, ... Chabukswar V (2014) Novel green route of synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by using natural biodegradable polymer and its application as a catalyst for oxidation of aldehydes. J Macromol Sci Part A 51(12):941–947
León A, Reuquen P, Garín C, Segura R, Vargas P, Zapata P, Orihuela PA (2017) FTIR and Raman characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles coated with polyethylene glycol as carrier for 2-methoxyestradiol. Appl Sci 7(1):49
Patil, P. R., & Joshi, S. S. (2007). Polymerized organic–inorganic synthesis of nanocrystalline zinc oxide. Mater Chem Phys 105(2–3):354–361
Look DC (2001) Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater Sci Eng B 80(1–3):383–387
Sangkhaprom N, Supaphol P, Pavarajarn V (2010) Fibrous zinc oxide prepared by combined electrospinning and solvothermal techniques. Ceram Int 36(1):357–363
Masoumi S, Shakibaie MR, Gholamrezazadeh M, Monirzadeh F (2018) Evaluation synergistic effect of TiO2, ZnO nanoparticles and amphiphilic peptides (Mastoparan-B, indolicidin) against drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiellapneumoniae and acinetobacterbaumannii. Arch Pediatr Infect Dis 6(3)
Rosi H, Kalyanasundaram S (2018) Synthesis, characterization, structural and optical properties of titanium-dioxide nanoparticles using Glycosmiscochinchinensis Leaf extract and its photocatalytic evaluation and antimicrobial properties. World News Nat Sci 17:1–15
Hoseinzadeh E, Alikhani MY, Samarghandi MR, Shirzad-Siboni M (2014) Antimicrobial potential of synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles against gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Desalin Water Treat 52(25–27):4969–4976
Yusof NAA, Zain NM, Pauzi N (2019) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with chitosan as stabilizing agent and their antibacterial properties against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Int J Biol Macromol 124:1132–1136
Rashid Y, Ahmad I, Ahmad N, Aslam M, Alotaibi A (2022) Affective antidepressant, cytotoxic activities, and characterization of phyto-assisted zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Sanvitalia procumbens aqueous extract. BioMed Res Int 2022.
Faisal S, Jan H, Shah SA, Shah S, Khan A, Akbar MT, ... Syed S (2021) Green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using aqueous fruit extracts of Myristica fragrans: Their characterizations and biological and environmental applications. ACS Omega 6(14):9709–9722
Crisan CM, Mocan T, Manolea M, Lasca LI, Tăbăran FA, Mocan L (2021) Review on silver nanoparticles as a novel class of antibacterial solutions. Appl Sci 11(3):1120
Chen F, Shi Z, Neoh KG, Kang ET (2009) Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of eugenol and carvacrol‐grafted chitosan nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioeng 104(1):30–39
Faisal S, Rizwan M, Ullah R, Alotaibi A, Khattak A, Bibi N, Idrees M (2022) Paraclostridium benzoelyticum bacterium-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles and their in vivo multiple biological applications. Oxid Med Cellr Longev
Khan MI, Shah S, Faisal S, Gul S, Khan S, Abdullah, … & Shah, W. A. (2022) Monotheca buxifolia driven synthesis of zinc oxide nano material its characterization and biomedical applications. Micromachines 13(5):668
Nigussie GY, Tesfamariam GM, Tegegne BM, Weldemichel YA, Gebreab TW, Gebrehiwot DG, Gebremichel GE (2018) Antibacterial activity of Ag-doped TiO2 and Ag-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Int J Photoenergy
Boroumand Moghaddam A, Moniri M, Azizi S, Abdul Rahim R, Bin Ariff A, ZuhainisSaad W, ... Mohamad R (2017) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by a new Pichiakudriavzevii yeast strain and evaluation of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Molecules 22(6):872
Santhoshkumar T, Rahuman AA, Jayaseelan C, Rajakumar G, Marimuthu S, Kirthi AV, ... Kim SK (2014) Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Psidiumguajava extract and its antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Asian Pac J Trop Med 7(12):968–976
Rajabi S, Ramazani A, Hamidi M, Naji T (2015) Artemiasalina as a model organism in toxicity assessment of nanoparticles. DARU J Pharm Sci 23:1–6
Kumar P, Selvi SS, Praba AL, Selvaraj M, Rani LM, Suganthi P, ... Govindaraju M (2012) Antibacterial activity and in-vitro cytotoxicity assay against brine shrimp using silver nanoparticles synthesized from Sargassumilicifolium. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 7(4):1447–1455
Supraja N, Prasad TNVKV, Gandhi AD, Anbumani D, Kavitha P, Babujanarthanam R (2018) Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy and brine shrimp lethality assay of Alstoniascholaris stem bark extract mediated ZnONPs. Biochem Biophys Rep 14:69–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hunaiza Tahir performed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. Farzana Rashid supervised the experiment and edited the manuscript. Shaukat Ali edited the manuscript and evaluated the manuscript. Muhammad Summer edited the manuscript and did the characterization analysis. Rimsha Abaidulah assisted in writeup and reference management.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
As no animal is being used/sacrificed in present study, ethical approval was not applicable
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest of author regarding the present study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Research Highlights
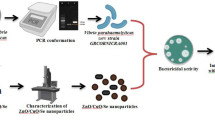
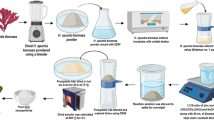
• 1st Comparative study of TiO2NPs and ZnONPs regarding their bactericidal, antioxidative and cytotoxic potential as shown in Fig. 1.
• Complete characterization of smaller (18 nm) TiO2NPs and ZnONPs using, SEM, FTIR, UV–Vis and PSA.
• Study of thermal behavior of both TiO2NPs and ZnONPs for their working efficiency at variable temperatures.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tahir, H., Rashid, F., Ali, S. et al. Spectrophotometrically, Spectroscopically, Microscopically and Thermogravimetrically Optimized TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles and their Bactericidal, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential: A Novel Comparative Approach. J Fluoresc (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03367-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03367-0