Abstract
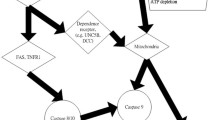
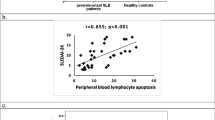
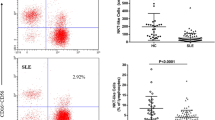
Autoantibody production and leukocytopenia may be linked in patients with lupus erythematosus (LE). Unclear is the ability of different autoantibody species to induce apoptosis and cell loss. Laboratory routine analyses (white blood cell counts, autoantibody detection), and flow cytometry (annexin V, CD3, CD4, CD8) have been performed in 126 consecutive LE-patients. Nuclei of PBMC were investigated flow cytometrically for the presence of the 85 kDa poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase (PARP) fragment. Peripheral total white blood cells (WBC), lymphocytes, T-cells, CD3+ CD4+, and CD3+ CD8+ cells were significantly decreased in patients with LE (P from 1.2 × 10−14 to P < .0008). In the presence of either antinuclear (P from 1.2 × 10−14 to P < .0008) or anti-dsDNA antibodies (P from 2.9 × 10−12 to P < .007) were significantly diminished. Differences in cell numbers in LE patients with versus without anti-Ro/SSA were less pronounced: significant differences could be only obtained in lymphocytes and T-cells (P < .02). Anti-La/SSB antibodies were accompanied by significant increased leukocytes (P < .02). PARP cleavage (85 kDa) in nuclei was preferentially observed in cases with nuclear targeting autoantibodies. These results indicate that nuclear targeting autoantibodies are associated to lower peripheral blood cells counts than Ro/SSA, and La/SSB cytoplasmic targeting autoantibodies. This provides an explanation for the pathogenesis of cytopenias associated with SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Navratil JS, Ahearn JM: Apoptosis, clearance mechanisms, and the development of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 3:191–198, 2001
Stollar BD, Stephenson F: Apoptosis and nucleosomes. Lupus 11:787–789, 2002
Ramirez-Sandoval R, Sanchez-Rodriguez SH, Herrera-van Oostdam D, Avalos-Diaz E, Herrera-Esparza R: Antinuclear antibodies recognize cellular autoantigens driven by apoptosis. Joint Bone Spine 70:187–194, 2003
Ohlsson M, Jonsson R, Brokstad KA: Subcellular redistribution and surface exposure of the Ro52, Ro60 and La48 autoantigens during apoptosis in human ductal epithelial cells: a possible mechanism in the pathogenesis of Sjogren’s syndrome. Scand J Immunol 56:456–469, 2002
Böhm I: Disruption of the cytoskeleton after apoptosis induction with autoantibodies. Autoimmunity 36:183–189, 2003
Starkebaum G: Chronic neutropenia associated with autoimmune disease. Semin Hematol 39:121–127, 2002
Guma M, Krakauer R: CD4+ lymphocytopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med 120:168–169, 1994
Yu CL, Huang MH, Tsai CY, Tsai YY, Tsai ST, Sun KH, Han SH, Yu HS: The effect of human polyclonal anti-dsDNA autoantibodies on apoptotic gene expression in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Scand J Rheumatol 27:54–60, 1998
Amasaki Y, Kobayashi S, Takeda T, Ogura N, Jodo S, Nakabayashi T, Tsutsumi A, Fujisaku A, Koike T: Up-regulated expression of Fas antigen (CD95) by peripheral naive and memory T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): a possible mechanism for lymphopenia. Clin Exp Immunol 99:245–250, 1995
Portales-Perez D, Alarcon-Segovia D, Llorente L, Ruiz-Arguelles A, Abud-Mendoza C, Baranda L, de la Fuente H, Ternynck T, Gonzalez-Amaro R: Penetrating anti-DNA monoclonal antibodies induce activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Autoimmun 11:563–571, 1998
Ruiz-Arguelles A, Rivadeneyra-Espinoza L, Alarcon-Segovia D: Antibody penetration into living cells: pathogenic, preventive and immuno-therapeutic implications. Curr Pharm Des 9:1881–1887, 2003
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ: The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277, 1982
Zhan X, Hu X, Friedman S, Maciag T: Analysis of endogenous and exogenous nuclear translocation of fibroblast growth factor-1 in NIH 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 188:982–991, 1992
Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, James JA, Harley JB: Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349:1526–1533, 2003
Cabral AR, Alarcon-Segovia D: Autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 9:387–392, 1997
Meilof JF, Veldhoven CH, Swaak AJ, Smeenk RJ: Production of anti-Ro/SS-A and anti-La/SS-B autoantibodies is closely coordinated in systemic lupus erythematosus and independent of anti-dsDNA production. J Autoimmun 10:67–75, 1997
Franceschini F, Calzavara-Pinton P, Quinzanini M, Cavazzana I, Bettoni L, Zane C, Facchetti F, Airo P, McCauliffe DP, Cattaneo R: Chilblain lupus erythematosus is associated with antibodies to SSA/Ro. Lupus 8:215–219, 1999
Parodi A, Drosera M, Barbieri L, Rebora A: Counterimmunoelectrophoresis, ELISA and immunoblotting detection of anti-Ro/SSA antibodies in subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. A comparative study. Br J Dermatol 138:114–117, 1998
Chien JW, Lin CY: Autoantibodies to dsDNA, Ro/SSA, and La/SSB in systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Clin Chem 37:129–172, 2003
Gorson KC, Ropper AH: Positive salivary gland biopsy, Sjogren syndrome, and neuropathy: clinical implications. Muscle Nerve 28:553–560, 2003
Meyer O: Anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies. What’s new? Ann Med Interne (Paris). 153:520–529, 2002
Hsieh SC, Yu HS, Lin WW, Sun KH, Tsai CY, Huang DF, Tsai YY, Yu CL: Anti-SSB/La is one of the antineutrophil autoantibodies responsible for neutropenia and functional impairment of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 131:506–516, 2003
Courtney PA, Crockard AD, Williamson K, Irvine AE, Kennedy RJ, Bell AL: Increased apoptotic peripheral blood neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus: relations with disease activity, antibodies to double stranded DNA, and neutropenia. Ann Rheum Dis 58:309–314, 1999
Frank MB, Itoh K, McCubbin V: Epitope mapping of the 52-kDa Ro/SSA autoantigen. Clin Exp Immunol 95:390–396, 1994
Miranda ME, Tseng CE, Rashbaum W, Ochs RL, Casiano CA, Di Donato F, Chan EK, Buyon JP: Accessibility of SSA/Ro and SSB/La antigens to maternal autoantibodies in apoptotic human fetal cardiac myocytes. J Immunol 161:5061–5069, 1998
Hasan T, Nyberg F, Stephansson E, Puska P, Hakkinen M, Sarna S, Ros AM, Ranki A: Photosensitivity in lupus erythematosus, UV photoprovocation results compared with history of photosensitivity and clinical findings. Br J Dermatol 136:699–705, 1997
Tiefenthaler M, Bacher N, Linert H, Muhlmann O, Hofer S, Sepp N, Amberger A, Geisen F, Obermoser G, Konwalinka G: Apoptosis of CD34+ cells after incubation with sera of leukopenic patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2:471–478, 2003
Alarcon-Segovia D, Ruiz-Arguelles A, Fishbein E: Antibody penetration into living cells. I. Intranuclear immunoglobulin in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in mixed connective tissue disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 35:364–375, 1979
Ruiz-Arguelles A, Perez-Romano B, Llorente L, Alarcon-Segovia D, Castellanos JM: Penetration of anti-DNA antibodies into immature live cells. J Autoimmun 11:547–556, 1998
Weisbart RH, Stempniak M, Harris S, Zack DJ, Ferreri K: An autoantibody is modified for use as a delivery system to target the cell nucleus: therapeutic implications. J Autoimmun 11:539–546, 1998
Reichlin M: Cellular dysfunction induced by penetration of autoantibodies into living cells: cellular damage and dysfunction mediated by antibodies to dsDNA and ribosomal P proteins. J Autoimmun 11:557–561, 1998
Tran HB, Ohlsson M, Beroukas D, Hiscock J, Bradley J, Buyon JP, Gordon TP: Subcellular redistribution of la/SSB autoantigen during physiologic apoptosis in the fetal mouse heart and conduction system: a clue to the pathogenesis of congenital heart block. Arthritis Rheum 46:202–208, 2002
Pourmand N, Blange I, Ringertz N, Pettersson I: Intracellular localisation of the Ro 52 kDa auto-antigen in HeLa cells visualised with green fluorescent protein chimeras. Autoimmunity 28:225–233, 1998
Zhang J, Xu Z, Jin J, Zhu T, Ma S. Induction of Ro/SSA antigen expression on keratinocyte cell membrane by heat shock and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate as well as estradiol and ultraviolet B. J Dermatol Sci 24:92–98, 2000
Song Q, Lees-Miller SP, Kumar S, Zhang Z, Chan DW, Smith GC, Jackson SP, Alnemri ES, Litwack G, Khanna KK, Lavin MF: DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit: a target for an ICE-like protease in apoptosis. EMBO J 15:3238–3246, 1996
Böhm I, Schild H: Apoptosis: the complex scenario for a silent cell death Molecular Imaging and Biology 5:2–14, 2003
Jeoung D, Lim Y, Lee EB, Lee S, Kim HY, Lee H, Song YW: Identification of autoantibody against poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) fragment as a serological marker in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 22:87–94, 2004
McConnell JR, Crockard AD, Cairns AP, Bell AL: Neutrophils from systemic lupus erythematosus patients demonstrate increased nuclear DNA damage. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:653–660, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böhm, I. Nuclear-Targeting Autoantibodies Induced Nuclear PARP Cleavage Accompanied by More Pronounced Decrease of Peripheral White Blood Cells Than Ro/SSA and La/SSB Antigen-Targeting Autoantibodies. J Clin Immunol 25, 99–105 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-2815-1
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-005-2815-1