Abstract
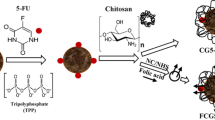
The development of smart targeted nanoparticle that can deliver drugs to direct cancer cells, introduces better efficacy and lower toxicity for treatment. We report the development and characterizations of pH-sensitive carboxymethyl chitosan modified folic acid nanoparticles and manifest their feasibility as an effective targeted drug delivery vehicle. The nanoparticles have been synthesized from carboxymethyl chitosan with covalently bonded bifunctional 2,2′-(ethylenedioxy)-bis-(ethylamine) (EDBE) through the conjugation with folic acid. The conjugation has been analyzed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The resultant nanoparticles with an average size less then 200 nm measured by dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy. Confocal microscopy and flow cytometric analysis have revealed that folate-mediated targeting significantly enhances the cellular uptake of the nanoparticle and thus facilitates apoptosis of cancer cells (HeLa, B16F1). For the application of the nanoparticles as a drug carrier, Doxorubicin a potent anticancer drug has been loaded into the nanoparticles, with the drug loading amount and the drug release pattern observed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uhrich KE, Cannizzaro SM, Langer RS, Shakesheff KM. Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem Rev. 1999;99:3181–98.
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:329–47.
Marin RV, Ng CH, Wilke M, Tiersch B, Fratzl P, Peter MG. Size-controlled hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as self-organized organic–inorganic composite materials. Biomaterials. 2005;26:5414–26.
Marinakos SM, Anderson MF, Ryan JA, Martin LD, Feldheim DL. Encapsulation, permeability, and cellular uptake characteristics of hollow nanometer-sized conductive polymer capsules. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:8872–6.
Maeda H, Bharate GY, Daruwalla J. Polymeric drugs for efficient tumor-targeted drug delivery based on EPR-effect. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;71:409–19.
Faraji AH, Wipf P. Nanoparticles in cellular drug delivery. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:2950–62.
Singh R, Lillard JW Jr. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp Mol Pathol. 2009;86:215–23.
Breunig M, Bauer S, Goepferich A. Polymers and nanoparticles: intelligent tools for intracellular targeting. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;68:112–28.
Brannon-Peppas L, Blanchester JO. Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56:1649–59.
Vauthier C, Dubernet C, Chauvierre C, Brigger I, Couvreur P. Drug delivery to resistant tumors: the potential of poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2003;93:151–60.
Liang HF, Chen CT, Chen SC, Kulkarni AR, Chiu YL, Chen MC, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded poly(g-glutamic acid)-poly(lactide) nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for the treatment of liver cancer. Biomaterials. 2006;27:2051–9.
Sheikh FA, Barakat NAM, Kanjwal MA, Aryal S, Khil MS, Kim HY. Novel self-assembled amphiphilic poly (epsilon-caprolactone)-grafted-poly (vinyl alcohol) nanoparticles: hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs carrier nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20:821–31.
Mitra S, Gaur U, Ghosh PC, Maitra AN. Tumour targeted delivery of encapsulated dextran–doxorubicin conjugate using chitosan nanoparticles as carrier. J Control Release. 2001;74:317–23.
Ravi Kumar MNV, Muzzarelli RAA, Muzzarelli C, Sashiwa H, Domb AJ. Chitosan chemistry and pharmaceutical perspectives. Chem Rev. 2004;104:6017–84.
Yinsong W, Lingrong L, Jian W, Zhang Q. Preparation and characterization of self-aggregated nanoparticles of cholesterol-modiWed O-carboxymethyl chitosan conjugates. Carbohydr Polym. 2007;69:597–606.
Weitman SD, Lark RH, Coney LR, Fort DW, Frasca V, Zurawski VRJ, et al. Distribution of the folate receptor GP38 in normal and malignant cell lines and tissues. Cancer Res. 1992;52:3396–401.
Lee RJ, Low PS. Delivery of liposomes into cultured KB cells via folate receptor- mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:3198–204.
Guo W, Hinkle GH, Lee RJ. Folate: a novel receptor-based targeted radiopharmaceutical for tumor imaging. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:1563–9.
Van Steenis JH, Van Maarseveen EM, Verbaan FJ, Verrijk R, Crommelin DJA. Preparation and characterization of folate-targeted pEG-coated pDMAEMA-based polyplexes. J Control Release. 2003;87:167–76.
Dauty E, Remy JS, Zuber G, Behr JP. Intracellular delivery of nanometric DNA particles via the folate receptor. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13:831–9.
Aronov O, Horowitz AT, Gabizon A, Gibson D. Folate-targeted PEG as a potential carrier for carboplatin analogs. Synthesis and in vitro Studies. Bioconjug Chem. 2003;14:563–74.
Yoo HS, Park TG. Folate receptor targeted biodegradable polymeric doxorubicin micelles. J Control Release. 2004;96:273–83.
Hattori Y, Maitani Y. Enhanced in vitro DNA transfection efficiency by novel folate-linked nanoparticles in human prostate cancer and oral cancer. J Control Release. 2004;97:173–83.
Ishida T, Kirchmeier MJ, Moase EH, Zalipsky S, Allen TM. Targeted delivery and triggered release of liposomal doxorubicin enhances cytotoxicity against human B lymphoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1515:144–58.
Yang Y, Jiang JS, Du B, Gan ZF, Qian M, Zhang P. Preparation and properties of a novel drug delivery system with both magnetic and biomolecular targeting. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20:301–7.
Minkoa T, Batrakovab EV, Lib S, Lib Y, Pakunlua RI, Alakhovc VY, et al. Pluronic block copolymers alter apoptotic signal transduction of doxorubicin in drug-resistant cancer cells. J Control Release. 2005;105:269–78.
Wang Y, Bansal V, Zelikin AN, Frank C. Templated synthesis of single-component polymer capsules and their application in drug delivery. Nano Lett. 2008;8:1741–5.
Engin K, Leeper DB, Cater JR, Thistlethwaite AJ, Tupchong L, McFarlane JD. Extracellular pH distribution in human tumors. Int J Hyperth. 1995;11:211–6.
Ojugo ASE, Mesheehy PMJ, McIntyre DJO, McCoy C, Stubbs M, Leach MO, et al. Measurement of the extracellular pH of solid tumors in mice by magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a comparison of exogenous 19F and 31P probes. NMR Biomed. 1999;12:495–504.
Van Sluis R, Bhujwalla ZM, Ballerteros P, Alverez J, Cerdan S, Galons JP, et al. In vivo imaging of extracellular pH using 1H MSRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;41:743–50.
Decuzzi P, Ferrari M. The role of specific and non-specific interactions in receptor-mediated endocytosis of nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2007;28:2915–22.
Park JS, Han TH, Lee KY, Han SS, Hwang JJ, et al. N-acetyl histidine-conjugated glycol chitosan self-assembled nanoparticles for intracytoplasmic delivery of drugs: endocytosis, exocytosis and drug release. J Control Release. 2006;115:37–45.
Mellman I, Fuchs R, Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:773–800.
Mohapatra S, Mallick SK, Maiti TK, Ghosh SK, Pramanik P. Synthesis of highly stable folic acid conjugated magnetite nanoparticles for targeting cancer cells. Nanotechnology. 2007;18:385102–11.
Das M, Mishra D, Maiti TK, Basak A, Pramanik P. Bio-functionalization of magnetite nanoparticles using an aminophosphonic acid coupling agent: new, ultradispersed, iron-oxide folate nanoconjugates for cancer-specific targeting. Nanotechnology. 2008;19:415101–15.
Chen XG, Park HJ. Chemical characteristics of O-carboxymethyl chitosans related to the preparation conditions. Carbohydr Polym. 2003;53:355–9.
Gabizon A, Horowitz AT, Goren D, Tzemach D, Shavit FM, Qazen MM, et al. Targeting folate receptor with folate linked to extremities of poly (ethylene glycol)-grafted liposomes: in vitro studies. Bioconjug Chem. 1999;10:289–98.
Zhang Z, Lee SH, Feng SS. Folate-decorated poly (lactide-co-glycolide)-vitamin E TPGS nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1889–99.
Acknowledgment
The authors express gratefulness to the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for funding and Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur for execution of these studies. Acknowledgements are also due to FIST program, DST, Govt. of India for Confocal microscope facility, and Central Research Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, S.K., Mallick, S.K., Santra, S. et al. In vitro evaluation of folic acid modified carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin for targeted delivery. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 21, 1587–1597 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-3998-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-3998-4