Abstract
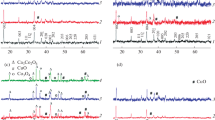
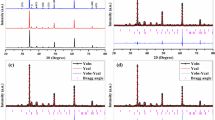
In the present study, calcium cobalt oxide-based ceramic oxide (Ca3Co4O9±δ) is synthesized by various reducing agent method by metal complex-assisted sol–gel assisted followed by combustion method using various reducing agents. The reducing agents adopted in the study are citric acid, starch polymer, and polyethylene glycol. The detailed structural and surface characterizations of as-prepared Ca3Co4O9+δ have demonstrated by XRD, TGA, and diffuse UV–visible spectral analysis. Hydrothermal method-prepared Iron-doped Ca3Co4O9± δ ceramic shows the Nanorods’ morphology. Electrical properties such as conductivity, Hall co-efficient, and electron mobility studies have been demonstrated. The density of the prepared materials by changing the stoichiometry ranges from 2.72 g/cm3 (relative density 55%) to 2.91 g/cm3 (relative density 58.9%). The density is found to be improved by decreasing the amount of calcium. The higher density is obtained for Ca2.90 Co3.91O9±δ which is 2.91 g/cm3 (58.9% of theoretical density). The effect of foreign metal ion doping in bulk calcium carbonate has studied and compared their electronic properties. The various reducing agent method-prepared Ca3Co4O9±δ shows the promising thermoelectric features. Polymer method-prepared Ca3Co4O9±δ sample with various transition metal ion substitution shows (calcium-doped ceramic oxide) the higher electron mobility and conducting activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Change history
23 November 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11648-4
13 April 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10416-8
References
D. Marxer, P. Furler, J. Scheffe, H. Geerlings, C. Falter, V. Batteiger, A. Sizmann, A. Steinfeld, Demonstration of the entire production chain to renewable kerosene via solar thermochemical splitting of H2O and CO2. Energy Fuels 29, 3241–3250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5b00351
D. Duan, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. Lei, Q. Wang, R. Ruan, Production of renewable jet fuel and gasoline range hydrocarbons from catalytic pyrolysis of soapstock over corn cob-derived activated carbons. Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118454
T. Radhika, K.R. Anju, M.S. Silpa, R.J. Ramalingam, H.A. Al-Lohedan, Cellulose acetate/N-TiO2 biocomposite flexible films with enhanced solar photochromic properties. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 4567–4574 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5442-8
T. Radhika, N. Raghu, N. Powrnami, R. Jothi Ramalingam, H.A. Al-Lohedan, Effect of synthesis conditions on formation, electrical properties, and seebeck coefficient of p-type Ca3Co4O9±δ thermoelectric ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1787–1793 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5229-3
R.J. Ramalingam, H.A. Al-Lohedan, T. Radhika, Synthesis, surface and textural characterization of ag doped polyaniline-SiO2(Pan-Ag/RHA) nanocomposites derived from biomass materials. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 11, 731–740 (2016)
Y.F. Wang, K.H. Lee, H. Ohta, K. Koumoto, Fabrication and thermoelectric properties of heavily rare-earth metal-doped SrO(SrTiO3)n (n = 1, 2) ceramics. Ceram. Int. 34, 849–852 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.09.034
M.K. Mohanta, A. Rawat, N. Jena, R. Dimple, A.D. Ahammed, Sarkar, Interfacing boron monophosphide with molybdenum disulfide for an ultrahigh performance in thermoelectrics, two-dimensional excitonic solar cells, and nanopiezotronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 3114–3126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b16866
K. Liu, T. Ding, J. Li, Q. Chen, G. Xue, P. Yang, M. Xu, Z.L. Wang, J. Zhou, thermal-electric nanogenerator based on the electrokinetic effect in porous carbon film. Adv. Energy Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201702481
A.S. Santhosh, K.M. Sahana, S. Sandeep, P.N. Prashanth Kumar, N.S. Alsaiari, K.M. Katubi, K.M. Abualnaja, J.R. Rajabathar, Synthesis and application of a 0D/2D nanocomposite for the nanomolar level detection of an antiandrogen drug. New J. Chem. 46, 16068–16077 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2nj01967a
P. Iyyappa Rajan, J. Judith Vijaya, S.K. Jesudoss, K. Kaviyarasu, S.C. Lee, L. John Kennedy, R. Jothiramalingam, H.A. Al-Lohedan, M. Mahamad Abdullah, Investigation on preferably oriented abnormal growth of CdSe nanorods along (0002) plane synthesized by henna leaf extract-mediated green synthesis. R. Soc. Open Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.171430
A.I. Klyndyuk, I.V. Matsukevich, Synthesis and properties of disubstituted derivatives of layered calcium cobaltite. Glass Phys. Chem. 41, 545–550 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659615050077
T. Silva, V. Silva, J. Santos, T. Simões, D. Macedo, Effect of Cu-doping on the activity of calcium cobaltite for oxygen evolution reaction. Mater. Lett. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130026
F. Ahmed, A. Munir, A.S. Khan, A.A. Chaudhry, M. Anis-ur Rehman, Facile synthesis and conduction mechanism in re-substituted oxide systems for enhanced thermoelectric performance, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(10), 7460–7467 (2015).
M.D. Daivajna, N. Kumar, V.P.S. Awana, B. Gahtori, J. Benedict Christopher, S.O. Manjunath, K.Z. Syu, Y.K. Kuo, A. Rao, Electrical, magnetic and thermal properties of Pr0.6-xBixSr0.4MnO3 manganites. J. Alloy. Compd. 588, 406–412 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.033
Y. Li, G. Wang, M. Akbari-Saatlu, M. Procek, H.H. Radamson, Si and SiGe nanowire for micro-thermoelectric generator: a review of the current state of the art. Front. Mater. 8, 1–24 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2021.611078
Chinese Materials Conference on Materials and Technologies for Energy Supply and Environmental Engineering, 2015, Mater. Sci. Forum. 847 (2016) 1–546. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-84962182347&partnerID=40&md5=b5f76c6bc5be7b0f9af9d4db6eea6e13.
R. Jothiramalingam, S. Devasanan, H.A. Lohedan, M.R. Muthumareeswaran, H.M. Alqahtani, K. Abdalnaser, Green chemistry method prepared effective copper nanoparticles by lemon flower (citrus) extract and its anti-microbial activity. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostr. 17, 145–151 (2022)
M.U. Sajid, H.M. Ali, Thermal conductivity of hybrid nanofluids: a critical review. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 126, 211–234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.05.021
G. Constantinescu, M.A. Sh Rasekh, M.A. Torres, J.C. Diez, M.A. Madre, A. Sotelo, Effect of Sr substitution for Ca on the Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric properties.". J. Alloy. Compd. 577, 511–515 (2013)
J.C. Diez, M.A. Torres, S. Rasekh, G. Constantinescu, M.A. Madre, A. Sotelo, Enhancement of Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric properties by Cr for Co substitution. Ceram. Int. 39(6), 6051–6056 (2013)
M.A. Torres, F.M. Costa, D. Flahaut, K. Touati, Sh. Rasekh, N.M. Ferreira, J. Allouche, M. Depriester, M.A. Madre, A.V. Kovalevsky, J.C. Diez, A. Sotelo, Significant enhancement of the thermoelectric performance in Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric materials through combined strontium substitution and hot-pressing process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39(4), 1186–1192 (2019)
Sh. Rasekh, M.A. Torres, G. Constantinescu, M.A. Madre, J.C. Diez, A. Sotelo, Effect of Cu by Co substitution on Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24(7), 2309–2314 (2013)
D. Kenfaui, D. Chateigner, M. Gomina, J.G. Noudem, Texture, mechanical and thermoelectric properties of Ca3Co4O9 ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 490(1–2), 472–479 (2010)
M.A. Torres, G. Garcia, I. Urrutibeascoa, M.A. Madre, J.C. Diez, A. Sotelo, Fast preparation route to high-performances textured Sr-doped Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric materials through precursor powder modification. Sci. China Mater. 62(3), 399–406 (2019)
H. Fukutomi, Y. Konno, K. Okayasu, M. Hasegawa, H. Nakatsugawa, Texture development of Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric oxide by high temperature plastic deformation and its contribution to the improvement in electric conductivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527(1–2), 61–64 (2009)
A. Sotelo, G. Constantinescu, Sh. Rasekh, M.A. Torres, J.C. Diez, M.A. Madre, Improvement of thermoelectric properties of Ca3Co4O9 using soft chemistry synthetic methods. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32(10), 2415–2422 (2012)
M.A. Madre, S. Rasekh, M.A. Torres, J.C. Diez, A. Sotelo, Improving bulk Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric materials through Zr doping. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 117, 142–146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/17436753.2017.1386409
F. Delorme, C.F. Martin, P. Marudhachalam, D. Ovono Ovono, G. Guzman, Effect of Ca substitution by Sr on the thermoelectric properties of Ca3Co4O9 ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 2311–2315 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.209
K. Obata, Y. Chonan, T. Komiyama, T. Aoyama, H. Yamaguchi, S. Sugiyama, Grain-oriented Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric oxide ceramics prepared by solid-state reaction. J. Electron. Mater. 42(7), 2221–2226 (2013)
M. Sundararajan, J. Vidhya, R. Revathi, M. Sukumar, B. Arunadevi, R. Rajkumar, S. Ramachandran, M. Kamalakannan, C.S. Dash, J.R. Rajabathar, Rapid synthesis and magnetic property characterization of Mg2+ doped Co3O4 nanostructures. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2021.2025400
P.S. Selvamani, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, A. Mustafa, M. Bououdina, P.J. Sophia, R.J. Ramalingam, Synergic effect of Cu2O/MoS2/rGO for the sonophotocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin antibiotics. Ceram. Int. 47, 4226–4237 (2021)
J.R. Rajabathar, J.R. Rajabathar, H.A. Al-Lohedan, S. Arokiyaraj, Z.A. Issa, C.S. Dash, S. Murugesan, S.K.K. Pasha, D.M. Al-dhayan, J.N. Appaturi, Characterization of pure rutile titania nanoparticle prepared by feasible method for coatings and visible light-driven dye removal application. Coatings (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11101150
M. Govindasamy, S.-F. Wang, R. Jothiramalingam, S. Noora Ibrahim, H.A. Al-lohedan, A screen-printed electrode modified with tungsten disulfide nanosheets for nanomolar detection of the arsenic drug roxarsone. Microchim. Acta. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3535-1
M. Govindasamy, S.-F. Wang, W.C. Pan, B. Subramanian, R.J. Ramalingam, H. Al-lohedan, Facile sonochemical synthesis of perovskite-type SrTiO3 nanocubes with reduced graphene oxide nanocatalyst for an enhanced electrochemical detection of -amino acid (tryptophan). Ultrason. Sonochem. 56, 193–199 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors (RJ and HA) extend their appreciation to the financial support through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R354), King Saud university, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
This work was supported by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R354).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JRR, development of design of methodology, creation of models, conducting a research work, specifically performing experiments, and data collections. Writing—original draft. RT, formal analysis, validation. HA-L, methodology, formal analysis, writing—review & editing, supervision. HA-S, validation, formal analysis, critical review, commentary and revision, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent to participate
The authors agreed that they participating in the research work.
Consent to publish
The authors agreed to publish this research paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajabathar, J.R., Thankappan, R., AL-Lohedan, H. et al. Structural and electrical property characterization of thermoelectric (Ca3Co4O9±δ) ceramic oxide fabrication by various reducing agent method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 585 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09986-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09986-4