Abstract
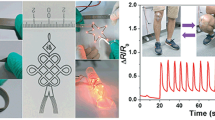
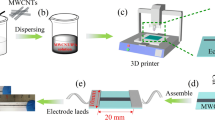
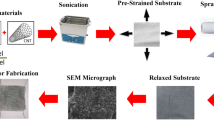
Recently, the fabrication of strain sensors with high sensitivity and high stretchability, which can precisely monitor subtle strains and large mechanical deformations exhibited by the human bodily motions, is critical for healthcare, human–machine interfaces, and biomedical electronics. However, a great challenge still exists i.e. achieving strain sensors with both high sensitivity and high stretchability by a facile, low-cost and scalable fabrication technique. Herein, this work reports Silver nanowires (AgNWs)/Ecoflex based composite strain sensors via inkjet printing technique which precisely deposits functional materials in a rapid, non-contact and maskless approach allowing high volume production. Noteworthily, the fabricated strain sensor display many fascinating features, including high sensitivity (a gauge factor of 13.7), a broad strain sensing range over 30%, excellent stability and reliability (>1000 cycles), and low monitoring limit (<5% strain). These remarkable features allow the strain sensor to effectively monitor various human motions. This work opens up a new path for fabricating nanocomposite thin film-based strain sensors for wearable electronics.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 September 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09087-8
References
C. Luo, B. Tian, Yu. Qun Liu, W.W. Feng, One-step-printed, highly sensitive, textile-based, tunable performance strain sensors for human motion detection. Adv Mater Technol 5(2), 1900925 (2020)
J. Ma, P. Wang, H. Chen, S. Bao, W. Chen, H. Lu, Highly sensitive and large-range strain sensor with a self-compensated two-order structure for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 8527–8536 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b20902
W. Liu, Y. Huang, Y. Peng, M. Walczak, D. Wang, Q. Chen, Z. Liu, L. Li, Stable wearable strain sensors on textiles by direct laser writing of graphene. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 283–293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01937
Z.F. Liu, S. Fang, F.A. Moura, J.N. Ding, N. Jiang, J. Di, M. Zhang, X. Lepro, D.S. Galvao, C.S. Haines et al., Hierarchically buckled sheath-core fibers for superelastic electronics, sensors, and muscles. Science 349, 400–404 (2015)
Yin Cheng, Ranran Wang, Kwok Hoe Chan, Lu. Xin, Jing Sun, Ghim Wei Ho, A biomimetic conductive tendril for ultrastretchable and integratable electronics, muscles, and sensors. ACS Nano 12(4), 3898–3907 (2018)
Vu. Chicuong, J. Kim, Muscle activity monitoring with fabric stretch sensors. Fibers Polym 18(10), 1931–1937 (2017)
T. Giorgino, P. Tormene, F. Lorussi, D.D. Rossi, S. Quaglini, Sensor evaluation for wearable strain gauges in neurological rehabilitation IEEE trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 17, 409–415 (2009)
F. Porciuncula, A.V. Roto, D. Kumar, et al., Wearable movement sensors for rehabilitation: a focused review of technological and clinical advances [published correction appears in PM R. 2018 Dec;10(12):1437]. PM R. 10(9 Suppl 2), S220–S232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2018.06.013 (2018)
S.-E. Park, Y.-J. Ho, M.H. Chun, J. Choi, Y. Moon, Measurement and analysis of gait pattern during stair walk for improvement of robotic locomotion rehabilitation system. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2019, 1495289 (2019)
Zewei Luo, Hu. Xiaotong, Xiyue Tian, Chen Luo, Xu. Hejun, Quanling Li, Qianhao Li, Jian Zhang, Fei Qiao, Wu. Xing, V. Borisenko, Junhao Chu, Structure-property relationships in graphene-based strain and pressure sensors for potential artificial intelligence applications. Sensors 19(5), 1250 (2019)
S. Yao, P. Swetha, Y. Zhu, Nanomaterial-enabled wearable sensors for healthcare. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 7(1), 1700889 (2018)
J. Guo, B. Zhou, R. Zong, L. Pan, X. Li, Yu. Xinguang, C. Yang, L. Kong, Q. Dai, Stretchable and highly sensitive optical strain sensors for human-activity monitoring and healthcare. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(37), 33589–33598 (2019)
R. Rahimi, M. Ochoa, W. Yu, B. Ziaie, Highly stretchable and sensitive unidirectional strain sensor via laser carbonization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 4463–4470 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/am509087u
J. Huang, J. Zhou, Y. Luo, G. Yan, Yi. Liu, Y. Shen, Xu. Yong, H. Li, L. Yan, G. Zhang, Fu. Yongqing, H. Duan, Wrinkle-enabled highly stretchable strain sensors for wide-range health monitoring with a big data cloud platform. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12(38), 43009–43017 (2020)
X. Ye, Z. Yuan, H. Tai, W. Li, X. Du, Y. Jiang, A wearable and highly sensitive strain sensor based on a polyethylenimine–rGO layered nanocomposite thin film. J. Mater. Chem. C. 5, 7746–7752 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TC01872J
D.J. Cohen, D. Mitra, K. Peterson, M.M. Maharbiz, A highly elastic, capacitive strain gauge based on percolating nanotube networks. Nano Lett. 12, 1821–1826 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl204052z
J.T. Muth, D.M. Vogt, R.L. Truby, Y. Mengüç, D.B. Kolesky, R.J. Wood, J.A. Lewis, Embedded 3D printing of strain sensors within highly stretchable elastomers. Adv. Mater. 26, 6307–6312 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201400334
S. Liu, L. Li, Ultrastretchable and self-healing double-network hydrogel for 3D printing and strain sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 26429–26437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07445
D. Zhang, Y. Tang, Y. Zhang, F. Yang, Y. Liu, X. Wang, J. Yang, X. Gong, J. Zheng, Highly stretchable, self-adhesive, biocompatible, conductive hydrogels as fully polymeric strain sensors. J Mater Chem A 8(39), 20474–20485 (2020)
J. Lin, X. Cai, Z. Liu, N. Liu, M. Xie, BingPu Zhou, H. Wang, Z. Guo, Anti-liquid-interfering and bacterially antiadhesive strategy for highly stretchable and ultrasensitive strain sensors based on Cassie-Baxter Wetting State. Adv. Func. Mater. 30(23), 2000398 (2020)
H. Zhang, N. Liu, Y. Shi, W. Liu, Y. Yue, S. Wang, Y. Ma, Li. Wen, L. Li, F. Long, Z. Zou, Y. Gao, Piezoresistive sensor with high elasticity based on 3D hybrid network of Sponge@CNTs@Ag NPs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(34), 22374–22381 (2016)
P. Feng, Y. Yuan, M. Zhong, J. Shao, X. Liu, Xu. Jie, J. Zhang, K. Li, W. Zhao, Integrated resistive-capacitive strain sensors based on polymer-nanoparticle composites. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3(5), 4357–4366 (2020)
Z. Zhang, Q. Liao, X. Zhang, G. Zhang, P. Li, S. Lu, S. Liu, Y. Zhang, Nanoscale 7, 1796–1801 (2015)
X. Liao, Z. Zhang, Z. Kang, F. Gao, Q. Liao, Y. Zhang, Mater. Horiz. 4, 502 (2017)
J. Chen, J. Zheng, Q. Gao, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, O.M. Omisore, L. Wang, H. Li, Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based flexible resistive strain sensors for wearable applications. Appl. Sci. 8, 345 (2018)
J. Chen, Q. Yu, X. Cui, M. Dong, J. Zhang, C. Wang, J. Fan, Y. Zhu, Z. Guo, J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 11710–11730 (2019)
S. Wang, P. Xiao, Y. Liang, J. Zhang, Y. Huang, S. Wu, S.-W. Kuo, T. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 5140–5147 (2018)
Z. Zeng, Y. Yu, Y. Song, N. Tang, L. Ye, J. Zang, Precise engineering of conductive pathway by frictional direct-writing for ultrasensitive flexible strain sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 41078–41086 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b14501
T. Nguyen, M. Chu, R. Tu, M. Khine, The effect of encapsulation on crack-based wrinkled thin film soft strain sensors. Materials 14, 364 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020364
Lim Wei Yap, Shu Gong, Yue Tang, Yonggang Zhu, Wenlong Cheng, Soft piezoresistive pressure sensing matrix from copper nanowires composite aerogel. Sci. Bull. 61(20), 1624–1630 (2016)
G.-Y. Lee, M.-S. Kim, S.-H. Min, H.-S. Kim, H.-J. Kim, R. Keller, J.-B. Ihn, S.-H. Ahn, Highly sensitive solvent-free silver nanoparticle strain sensors with tunable sensitivity created using an aerodynamically focused nanoparticle printer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(29), 26421–26432 (2019)
H.B. Liu, H. Jiang, F. Du, D.P. Zhang, Z.J. Li, H.W. Zhou, Flexible and degradable paper-based strain sensor with low cost. ACS Sustain Chem. Eng. 5, 10538–10543 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02540
L. Cai, L. Song, P. Luan, Q. Zhang, N. Zhang, Q. Gao, D. Zhao, X. Zhang, M. Tu, F. Yang, W. Zhou, Q. Fan, J. Luo, W. Zhou, P.M. Ajayan, S. Xie, Super-stretchable transparent carbon nanotube-based capacitive strain sensors for human motion detection. Sci. Rep. 3, 3048 (2013)
J. Lee, S. Kim, J. Lee, D. Yang, B.C. Park, S. Ryu, I. Park, Nanoscale 6, 11932 (2014)
G. Keulemans, P. Pelgrims, M. Bakula, F. Ceyssens, R. Puers, An ionic liquid based strain sensor for large displacements. Procedia Eng. 87, 1123–1126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.362
G.-J. Zhu, P.-G. Ren, H. Guo, Y.-L. Jin, D.-X. Yan, Z.-M. Li, Highly sensitive and stretchable polyurethane fiber strain sensors with embedded silver nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(26), 23649–23658 (2019)
S. Yao, Y. Zhu, Wearable multifunctional sensors using printed stretchable conductors made of silver nanowires. Nanoscale 6, 2345–2352 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr05496a
Yi Xi. Song, Xu. Wei Min, Min Zhi Rong, Ming Qiu Zhang, A sunlight self-healable transparent strain sensor with high sensitivity and durability based on a silver nanowire/polyurethane composite film. J Mater Chem A. 7(5), 2315–2325 (2019)
D.J. Finn, M. Lotya, J.N. Coleman, Inkjet printing of silver nanowire networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7(17), 9254–9261 (2015)
M.A.U. Karim, S. Chung, E. Alon, V. Subramanian, Fully inkjet-printed stress-tolerant microelectromechanical Reed relays for large-area electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2(5), 1–8 (2016)
M. Gao, L. Li, Y. Song, J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 2971–2993 (2017)
M.F. Farooqui, A. Shamim, Sci. Rep. 6, 28949 (2016)
S. Ammu, V. Dua, S.R. Agnihotra, S.P. Surwade, A. Phulgirkar, S. Patel, S.K. Manohar, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 4553–4556 (2012)
B. Ando, S. Baglio, All-inkjet printed strain sensors. IEEE Sensors J. 13, 4874–4879 (2013)
S. Cruz, D. Dias, J.C. Viana, L.A. Rocha, Inkjet printed pressure sensing platform for postural imbalance monitoring. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 64(10), 2813–2820 (2015)
P. Giannakou, M.O. Tas, B. Le Borgne, M. Shkunov, Water-transferred, inkjet-printed supercapacitors toward conformal and epidermal energy storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12(7), 8456–8465 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21283
Szymon Sollami Delekta, Mikael Östling, Jiantong Li, Wet transfer of inkjet printed graphene for microsupercapacitors on arbitrary substrates. ACS Appl Energ Mater. 2(1), 158–163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01225
E. Sowade, K.Y. Mitra, E. Ramon, C. Martinez-Domingo, F. Villani, F. Loffredo, H.L. Gomes, R.R. Baumann, Up-scaling of the manufacturing of all-inkjet-printed organic thin-film transistors: device performance and manufacturing yield of transistor arrays. Org. Electron. 30, 237–246 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2015.12.018
S. Singh, Y. Takeda, H. Matsui, S. Tokito, Flexible inkjet-printed dual-gate organic thin film transistors and PMOS inverters: noise margin control by top gate. Org. Electron. 85, 105847 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2020.105847
M. Min, R.F. Hossain, N. Adhikari, A.B. Kaul, Inkjet-printed organohalide 2D layered perovskites for high-speed photodetectors on flexible polyimide substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12(9), 10809–10819 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21053
Lu. Zhou, L. Yang, Yu. Mengjie, Yi. Jiang, C.-F. Liu, W.-Y. Lai, W. Huang, Inkjet-printed small-molecule organic light-emitting diodes: halogen-free inks, printing optimization, and large-area patterning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9(46), 40533–40540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13355
F. Villani, P. Vacca, G. Nenna, O. Valentino, G. Burrasca, T. Fasolino, C. Minarini, D. della Sala, Inkjet printed polymer layer on flexible substrate for OLED applications. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113, 13398–13402 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8095538
Z. Wang, H. Zhou, J. Lai, B. Yan, H. Liu, X. Jin, A. Ma, G. Zhang, W. Zhao, W. Chen, Extremely stretchable and electrically conductive hydrogels with dually synergistic networks for wearable strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 9200–9207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tc02505c
J. Lai, H. Zhou, Z. Jin, S. Li, H. Liu, X. Jin, C. Luo, A. Ma, W. Chen, Highly stretchable, fatigue-resistant, electrically conductive, and temperature-tolerant ionogels for high-performance flexible sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 26412–26420 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b10146
Chang-Ge. Zhou, Wen-Jin. Sun, Li-Chuan. Jia, Xu. Ling, Kun Dai, Ding-Xiang. Yan, Zhong-Ming. Li, Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensor with porous segregated conductive network. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 11(40), 37094–37102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b12504
M. Amjadi, K.U. Kyung, I. Park, M. Sitti, Stretchable, skin-mountable, and wearable strain sensors and their potential applications: a review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 1678–1698 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201504755
J.H. Kim, J.Y. Hwang, H.R. Hwang, H.S. Kim, J.H. Lee, J.W. Seo, U.S. Shin, S.H. Lee, Simple and cost-effective method of highly conductive and elastic carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane composite for wearable electronics. Sci. Rep. 8, 1375 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18209-w
T. Borca-Tasciuc, M. Mazumder, Y. Son, S.K. Pal, L.S. Schadler, P.M. Ajayan, Anisotropic thermal diffusivity characterization of aligned carbon nanotube-polymer composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7, 1581–1588 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2007.657
Y.R. Jeong, H. Park, S.W. Jin, S.Y. Hong, S.S. Lee, J.S. Ha, Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensors using fragmentized graphene foam. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 4228–4236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201501000
J.H. Kong, N.S. Jang, S.H. Kim, J.M. Kim, Simple and rapid micropatterning of conductive carbon composites and its application to elastic strain sensors. Carbon 77, 199–207 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.022
S.-H. Bae, Y. Lee, B.K. Sharma, H.-J. Lee, J.-H. Kim, J.-H. Ahn, Graphene-based transparent strain sensor. Carbon 51, 236–242 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.08.048
X. Wang, J. Sparkman, J. Gou, Strain sensing of printed carbon nanotube sensors on polyurethane substrate with spray deposition modelling. CompComm. 3, 1–6 (2017)
H. Zhao, Y. Zhang, P.D. Bradford, Q. Zhou, Q. Jia, F.G. Yuan, Y. Zhu, Carbon nanotube yarn strain sensors. Nanotechnology. 21, 305502 (2010)
S. Li, J.G. Park, S. Wang, R. Liang, C. Zhang, B. Wang, Working Mechanisms of Strain Sensors Utilizing Aligned Carbon Nanotube Network and Aerosol Jet Printed Electrodes. Carbon 73, 303–309 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.02.068
H. Lee, D. Lee, J. Hwang, D. Nam, C. Byeon, S.H. Ko, S. Lee, Silver nanoparticle piezoresistive sensors fabricated by roll-to-roll slot-die coating and laser direct writing. Opt. Express 22, 8919–8927 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.22.008919
B. Thompson, H.S. Yoon, Aerosol-printed strain sensor using PEDOT: PSS. IEEE Sens. J. 13, 4256–4263 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2013.2264482
M.Q. Le, F. Ganet, D. Audigier, J.F. Capsal, P.J. Cotttinet, Printing of microstructure strain sensor for structural health monitoring. Appl. Phys. A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0970-x (2017).
J. Park, D. Nam, S. Park, D. Lee, Fabrication of flexible strain sensors via roll-to-roll gravure printing of silver ink. Smart Mater Struct. 27, 085014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/aacbb8
S. Gong, W. Schwalb, Y.W. Wang, Y. Chen, Y. Tang, J. Si, B. Shirinzadeh, W.L. Cheng, A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires. Nat. Commun. 5, 3132 (2014)
J. Lee, S. Kim, J. Lee, D. Yang, B.C. Park, S. Ryu, I. Park, A stretchable strain sensor based on a metal nanoparticle thin film for human motion detection. Nanoscale 6, 11932 (2014)
K.K. Kim, S. Hong, H.M. Cho, J. Lee, Y.D. Suh, J. Ham, S.H. Ko, Highly sensitive and stretchable multidimensional strain sensor with prestrained anisotropic metal nanowire percolation networks. Nano Lett. 15, 5240 (2015)
J. Eom, J.S. Heo, M. Kim, J.H. Lee, S.K. Park, Y.H. Kim, Highly sensitive textile-based strain sensors using poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): polystyrene sulfonate/silver nanowire-coated nylon threads with poly-L-lysine surface modification. RSC Adv 7(84), 53373–53378 (2017)
C. Pang, G.Y. Lee, Ti. Kim et al., A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibers. Nat Mater 11, 795–801 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Madhavan, R. Flexible and stretchable strain sensors fabricated by inkjet printing of silver nanowire-ecoflex composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 3465–3484 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07540-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07540-8