Abstract
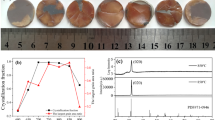
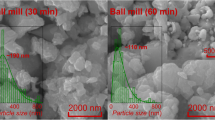
A high-quality KCl0.5Br0.5 crystal has been grown by using the resistance heating Czochralski (Cz) method under the best process parameters (rotating speed: 6–8 r/min, pulling speed: 1–2 mm/h, circulating water temperature: 28 ± 1 °C, cooling rate: 8–10 °C/h, and axial temperature gradient: 1–2 °C/mm). The deliquescence analysis of the KCl0.5Br0.5 crystal indicates that the deliquescence of KCl0.5Br0.5 crystal strongly depends on the temperature and humidity and the deliquescence of the crystal has been proved to be a physical process by carrying out X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopic (AFM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopic (EDX) measurements. The results of the polishing fluid composition experiment have shown that the best polishing fluid composition is ‘water + ethanol + surfactant X’, and the best ratio between them is 87.5:9.5:3.0. The effects of polishing pressure, polishing disk speed, polishing fluid flow rate, and polishing time on the removal rate and roughness of the KCl0.5Br0.5 crystal surface have been analyzed. The best parameters found for the crystal processing are the optimal pressure is 0.1042 MPa, the polishing fluid flow rate is 15 ml/min, the rotating speed of the polishing disk is 30 r/min, and the polishing time is 20 min. The performance test of the polished crystal element has shown that the transmittance of the crystal with a thickness of 4 mm is 91.7%, and the surface roughness of the crystal is 3.96 nm. Results obtained in the present study provide the technical route and experimental support for the processing of soft and moisture-prone crystals.











Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 January 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09813-w
References
Y. Li, Y. Li, Z. Yang, X. Zhang, F. Zeng, C. Li, H. Lin, Z. Su, C.K. Mahadevan, J. Liu, The structure and liquid flow effect of melt during NaCl crystal growth. Cryst. Res. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.201900229
M. Priya, C.K. Mahadevan, Studies on multiphased mixed crystals of NaCl. KCl and KI. Cryst. Res. Technol. 44, 92–102 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200800220
K. Jayakumari, C. Mahadevan, Growth and X-ray studies of (NaCl)x(KCl)y-x(KBr)1-y single crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 66, 1705–1713 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2005.07.008
Y. Li, Y. Li, C. Li, X. Zhang, F. Zeng, H. Lin, Z. Su, Optical and mechanical properties of NaCl:Ce3+ crystal grown by the Czochralski method. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 13070–13077 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03857-y
C.M. Padma, C.K. Mahadevan, Growth and characterization of multiphased mixed crystals of NaBr and KBr. Mater. Manuf. Proc. 23, 144–151 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910701774585
Y. Li, Y. Li, Z. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Liu, F. Zeng, J. Yao, C. Li, H. Lin, Z. Su, C.K. Mahadevan, Structural, optical and mechanical properties and cracking factors of large-sized KBr:Ce3+ single crystal. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 4785–4793 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08173-z
L. Guo, W. Jin, Z. Chen, J. Liu, P. Murugasen, C.K. Mahadevan, Large size crystal growth and structural, thermal, optical and electrical properties of KCl1-xBrx mixed crystals. J. Cryst. Growth. 480, 154–163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2017.10.005
D.B. Sirdeshmukh, L. Sirdeshmukh, K.G. Subhadra, Alkali Halides - A Handbook of Physical Properties, Springer Series in Materials Science-49 (Springer, Berlin, 2001).
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Baladi, M. Salavati-Niasari, Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance for degradation of organic contaminants using PbWO4 nanostructure fabricated by a new, simple and green sonochemical approach. Ultrason. Sonochem. 72, 105420 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105420
M. Mousavi-Kamazani, S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Ghodrati, One-step sonochemical synthesis of Zn(OH)2/ZnV3O8 nanostructures as a potent material in electrochemical hydrogen storage. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 17332–17338 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04289-4
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, N. Ghasemian, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Effect of zirconia on improving NOx reduction efficiency of Nd2Zr2O7 nanostructure fabricated by a new, facile and green sonochemical approach. Ultrason. Sonochem. 71, 105376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105376
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, Effect of copper on improving the electrochemical storage of hydrogen in CeO2 nanostructure fabricated by a simple and surfactant-free sonochemical pathway. Ceram. Int. 46, 26548–26556 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.121
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Sadat-Morassaei, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, Green synthesis of dysprosium stannate nanoparticles using Ficus carica extract as photocatalyst for the degradation of organic pollutants under visible irradiation. Ceram. Int. 46, 6095–6107 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.072
Y. Li, Y. Li, C. Li, X. Zhang, F. Zeng, H. Lin, Z. Su, C.K. Mahadevan, Luminescent and mechanical properties of cerium doped potassium chloride single crystal. Cryst. Res. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.202000060
S. Perumal, C.K. Mahadevan, Growth and characterization of multiphased mixed crystals of KCl, KBr and KI – Part 2: Electrical measurements. Phys. B 367, 172–181 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.06.013
M. Priya, C.K. Mahadevan, Formation of multiphased mixed crystals from miscible NaBr KBr and KCl. Cryst. Res. Technol. 43, 1069–1073 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200800189
C.K. Mahadevan, K. Jayakumari, Electrical measurements on multiphased (NaCl)x(KCl)y-x(KBr)1-y single crystals. Phys. B 403, 3990–3996 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.07.041
P. Easwaran, A. Anbagi, S. Nagarajan, Optical studies on KBr: Tl and KCl-Br: Tl mixed crystals. E-J. Chem. 7, 425–432 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/971465
F. Samavat, E. Haji-Ali, S. Shahmaleki, S. Solgi, Growth of KCl1-xBrx mixed crystals with different composition percent and study of KBr concentration effect on optical characteristics of mixed crystals. Adv. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2, 19978 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2012.22015
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S. Ali Heidari-Asil, M. Salavati-Niasari, Recyclable magnetic ZnCo2O4-based ceramic nanostructure materials fabricated by simple sonochemical route for effective sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic pollution. Ceram. Int. 47, 8959–8972 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.018
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S. Ali Heidari-Asil, M. Salavati-Niasari, Simple and eco-friendly synthesis of recoverable zinc cobalt oxide-based ceramic nanostructure as high-performance photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic removal of organic contamination under solar light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 267, 118667 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118667
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M.S. Morassaei, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, L.K. Foong, Nd2Sn2O7 nanostructures: Green synthesis and characterization using date palm extract, a potential electrochemical hydrogen storage material. Ceram. Int. 46, 17186–17196 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.014
M.S. Morassaei, S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Salavati-Niasari, Simple salt-assisted combustion synthesis of Nd2Sn2O7-SnO2 nanocomposites with different amino acids as fuel: an efficient photocatalyst for the degradation of methyl orange dye. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 11698–11706 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5306-7
S.A. Heidari-Asil, S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, Amino acid assisted-synthesis and characterization of magnetically retrievable ZnCo2O4eCo3O4 nanostructures as high activity visible-light-driven photocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 45, 22761–22774 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.122
F. Samavat, E. Haji-Ali, S. Shahmaleki, S. Solgi, Growth of KCl1-xBrx mixed crystals with different composition percent and study of KBr concentration effect on optical characteristics of mixed crystals. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2, 85–89 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2012.22015
V.G. Kononenko, V.V. Bogdanov, M.A. Volosyuk, A.V. Volosyuk, Interdiffusion under pressure in KBr-KCl single-crystals system. Funct. Mater. 23, 158–164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.15407/fm23.02.158
N. Beaudoin, A. Hamilton, D. Koehn, Z.K. Shipton, U. Kelka, Reaction-induced porosity fingering: replacement dynamic and porosity evolution in the KBr-KCl system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 232, 163–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.04.026
S. Perumal, C.K. Mahadevan, Growth and characterization of multiphased mixed crystals of KCl, KBr and KI: 1. Growth and X-ray diffraction studies. Phys. B 369, 89–99 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.07.034
L. Sirdeshmukh, G. Sathaiah, P. Devi, Dielectric properties of the KCl-KBr mixed crystal system. Phys. Status Solidi A 99, 631–639 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2210990235
A. Smakula, N. Maynard, A. Repucci, Defects in mixed crystals of KCl-KBr. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 453–455 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1777140
R. Ananda Kumari, R. Chandramani, Thermoluminescence, optical absorption and ESR studies in (KCl)1–x(KBr)x mixed alkali halide crystals doped with gold. Radiat. Meas. 43, 278–282 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2007.11.074
Kh. Rezaee Ebrahim Saraee, S.A. Hosseini, H. Faripour, M.R. Faiez, M.R. Abdi, N. Soltani, A. Aghay Khareiky, Thermoluminescence behavior of KClXBr1-X: In mixed crystals exposed to gamma radiation. J. Cryst. Growth. 402, 161–168 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2014.04.017
B.M. Moreno-Calles, A. Pérez-Rodríguez, R. Pérez-Salas, T.M. Piters, R. Rodriguez-Mijangos, Reorientation of Eu2+-cation vacancy dipolar complex in KCl/KBr binary crystals. J. Phys. 32, 165901 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/ab60e3
T. Ohgaku, N. Takeuchi, Dielectric loss of KCl-KBr mixed crystals doped with Sr2+. Phys. Stat. Sol. 42, K83–K85 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2210420167
L. Lu, Y.C. Wu, F.D. Fan, G.C. Zhang, P.Z. Fu, Study on the hygroscopic mechanism and moisture-proof protection of CsB3O5 crystal. J. Synth. Cryst. 01, 1–6 (2009)
H. Dong, L. Wang, W. Gao, X. Li, C. Wang, J. Fang, J. Pan, B. Wang, KDP aqueous solution-in-oil microemulsion for ultra-precision chemical–mechanical polishing of KDP crystal. Mater. 10, 271 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10030271
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis of pure nanocrystalline ZrO2 via a simple sonochemical assisted route. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20, 3313–3319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.12.013
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir, M. Salavati-Niasari, Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline praseodymium oxide via a simple precipitation approach. J. Mater Sci. 26, 5812–5821 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3141-x
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
J.I. Langford, A.J.C. Wilson, Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Cryst. 11, 102–113 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889878012844
J.M. Steigerwald, S.P. Murarka, R.J. Gatmann, Chemical Mechanical Planarization of Microelectronics Materials, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1997.
B.L. Wang, H. Gao, X.J. Teng, R.K. Kang, Effect of polishing parameter on material removal and surface quality of KDP crystal. J. Synth. Cryst. 39, 29–33 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(11)60006-6
F. Zhang, S. Guo, Z. Yong, D. Luan, Effect of several processing parameters on material removal ratio in the deliquescent polishing of KDP crystals. Proc. SPIE (2009). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.830905
S.L. Wang, Y.L. Liu, X.H. Niu, B.M. Tan, Slurry and processing technique of CLBO crystal. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 16, s692–s695 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(06)60280-X
Z. Cheng, H. Gao, Z. Liu, D. Guo, Investigation of the trajectory uniformity in water dissolution ultraprecision continuous polishing of large-sized KDP crystal. Int. J. Extreme Manuf. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-7990/abaabe
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology (Grant Nos. 20200801038GH, 20200403158SF) and Education (Grant Nos. 202010191150, JJKH20200271K, JJKH20200272KJ) Departments of the Jilin Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Sun, X., Li, Y. et al. Study on the growth and processing technology of large-size KCl0.5Br0.5 crystal. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 16432–16444 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06196-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06196-8