Abstract
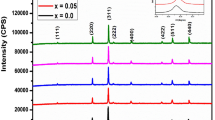
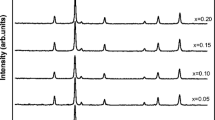
The structure, morphology, temperature dependent electrical and frequency dependent dielectric behavior of Cu2+ substituted Ni–Zn spinel ferrite nanoparticles having generic formula Ni0.70−xCuxZn0.30Fe2O4 (x = 0.00, 0.05, 0.15 and 0.25) prepared by sol–gel auto combustion technique with citric acid as a chelating agent is reported here. The XRD patterns revealed the presence of cubic spinel structure. The crystallite size was obtained using Scherrer’s formula which varies between 29 and 34 nm. The lattice parameter was found to increase with an increase in copper concentration. FTIR spectra show the characteristic bands for tetrahedral and octahedral sites. The morphology investigated by SEM technique demonstrates the nanocrystalline grain formation with almost spherical geometry. The grain size obtained from SEM analysis is in the range of 69–88 nm. The particle size obtained through TEM image analysis varies from 30 to 35 nm. The electrical and dielectric behavior was studied using a two-probe technique as a function of temperature and frequency respectively. Various electrical parameters like DC resistivity, activation energy, drift mobility, charge carrier concentration, diffusion coefficient were obtained as a function of copper concentration ‘x’. Arrhenius plot indicates the semiconducting nature of Cu2+ substituted Ni–Zn spinel ferrite. The dielectric constant and dielectric loss tangent both decreases with increase in frequency and concentration of Cu2+.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Lee, T. Hyeon, Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 2575–2589 (2012)
M. Mishra, A.P. Singh, B.P. Singh, V.N. Singh, S.K. Dhawan, Conducting ferrofluid: a high-performance microwave shielding material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 13159–13168 (2014)
S. Mohapatra, S.R. Rout, S. Maiti, T.K. Maiti, A.B. Panda, Monodisperse mesoporous cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and application in targeted delivery of antitumor drugs. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 9185–9193 (2011)
A.R.O. Rodrigues, I.T. Gomes, B.G. Almeida, J.P. Araujo, E.M.S. Castanheira, P.J.G. Coutinho, Magnetic liposomes based on nickel ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 18011–18021 (2015)
Y. Yang, X. Liu, Y. Yang, W. Xiao, Z. Li, D. Xue et al., Synthesis of nonstoichiometric zinc ferrite nanoparticles with extraordinary room temperature magnetism and their diverse applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 2875–2885 (2013)
S.P. Dalawai, T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, P.N. Vasambekar, Ni–Zn ferrite thick film gas sensors. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 9016–9025 (2015)
B.J. Rani, R. Mageswari, G. Ravi, V. Ganesh, R. Yuvakkumar, Physico-chemical properties of pure and zinc incorporated cobalt nickel mixed ferrite (ZnxCo0.005 – xNi0.005Fe2O4, where x = 0, 0.002, 0.004 M) nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2017)
M. Hashim, S.E. Shirsath, S.S. Meena, M.L. Mane, S. Kumar, P. Bhatt et al., Manganese ferrite prepared using reverse micelle process: structural and magnetic properties characterization. J. Alloy. Compd. 642, 70–77 (2015)
R. Kant Sharma, R. Ghose, Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite spinel powders by homogeneous precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 41, 14684–14691 (2015)
M. Liu, M. Lu, L. Wang, S. Xu, J. Zhao, H. Li, Mössbauer study on the magnetic properties and cation distribution of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 5487–5492 (2016)
K. Pemartin, C. Solans, J. Alvarez-Quintana, M. Sanchez-Dominguez, Synthesis of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles by the oil-in-water microemulsion reaction method. Colloids Surf. A 451, 161–171 (2014)
A.V. Raut, R.S. Barkule, D.R. Shengule, K.M. Jadhav, Synthesis, structural investigation and magnetic properties of Zn2 + substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol–gel auto-combustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 358–359, 87–92 (2014)
J.S. Kounsalye, P.B. Kharat, M.V. Shisode, K. Jadhav, Influence of Ti4 + ion substitution on structural, electrical and dielectric properties of Li0. 5Fe2. 5O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 2017:1–8
C. Cao, A. Xia, S. Liu, L. Tong, Synthesis and magnetic properties of hydrothermal magnesium–zinc spinel ferrite powders. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 4901–4905 (2013)
A. Najafi Birgani, M. Niyaifar, A. Hasanpour, Study of cation distribution of spinel zinc nano-ferrite by X-ray. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 179–181 (2015)
M. Streckova, H. Hadraba, R. Bures, M. Faberova, P. Roupcova, I. Kubena et al., Chemical synthesis of nickel ferrite spinel designed as an insulating bilayer coating on ferromagnetic particles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 270, 66–76 (2015)
Z.V. Mocanu, M. Airimioaei, C.E. Ciomaga, L. Curecheriu, F. Tudorache, S. Tascu et al., Investigation of the functional properties of Mg x Ni1–x Fe2O4 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 3276–3286 (2014)
M. Rahimi, P. Kameli, M. Ranjbar, H. Hajihashemi, H. Salamati, The effect of zinc doping on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni1–x Zn x Fe2O4. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 2969–2976 (2013)
V. Jeseentharani, L. Reginamary, B. Jeyaraj, A. Dayalan, K.S. Nagaraja, Nanocrystalline spinel Ni x Cu0.8–x Zn0.2Fe2O4: a novel material for humidity sensing. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 3529–3534 (2012)
H. Su, H. Zhang, X. Tang, Y. Liu, Effects of nanocrystalline ferrite particles on densification and magnetic properties of the NiCuZn ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 2849–2853 (2007)
V. Tsakaloudi, D. Sakellari, V. Zaspalis, E.K. Polychroniadis, Stress relaxation phenomena in NiCuZn ferrites induced by annealing. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 3692–3699 (2013)
G. Sathishkumar, C. Venkataraju, K. Sivakumar, Effect of nickel on the structural and magnetic properties of nano structured CoZnFe2O4. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22, 1715 (2011)
R. Maleque, M.D. Rahaman, A.K.M. Akther Hossain, Influence of Ca2+ ions substitution on structural, microstructural, electrical and magnetic properties of Mg0.2–xCaxMn0.5Zn0.3Fe2O4 ferrites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 13185–13200 (2017)
K. Modi, Elastic moduli determination through IR spectroscopy for zinc substituted copper ferri chromates. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 2887–2890 (2004)
A. Sutka, G. Mezinskis, Sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis of spinel-type ferrite nanomaterials. Front. Mater. Sci. 6, 128–141 (2012)
I.P. Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ doping in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 767–776 (2010)
G. Luo, W. Zhou, J. Li, G. Jiang, S. Tang, Y-w. Du, Effect of Cu ion substitution on structural and dielectric properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 25, 3678–3684 (2015)
L. Khanna, N.K. Verma, PEG/CaFe2O4 nanocomposite: structural, morphological, magnetic and thermal analyses. Phys. B 427, 68–75 (2013)
G.H. Kale, A.V. Humbe, S.D. Birajdar, A.B. Shinde, K.M. Jadhav, l-Ascorbic acid assisted synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles at different annealing temperatures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 2151–2158 (2016)
K.B. Modi, S.J. Shah, N.B. Pujara, T.K. Pathak, N.H. Vasoya, I.G. Jhala, Infrared spectral evolution, elastic, optical and thermodynamic properties study on mechanically milled Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 spinel ferrite. J. Mol. Struct. 1049, 250–262 (2013)
G. Padmapriya, A. Manikandan, V. Krishnasamy, S.K. Jaganathan, S.A. Antony, Spinel NixZn1–xFe2O4 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) nano-photocatalysts: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J. Mol. Struct. 1119, 39–47 (2016)
S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, Y. Yasukawa, X. Liu, A. Morisako, Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho3+-Mn2+-Fe3+-O2- ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 2347–2357 (2014)
M. Raghasudha, D. Ravinder, P. Veerasomaiah, Electrical resistivity studies of Cr doped Mg nano-ferrites. Mater. Discov. 2, 50–54 (2015)
S.R. Nimbore, D.R. Shengule, S.J. Shukla, G.K. Bichile, K.M. Jadhav, Magnetic and electrical properties of lanthanum substituted yttrium iron garnets. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 6460–6464 (2006)
V.S. Sawant, A.A. Bagade, K.Y. Rajpure, Studies on structural and electrical properties of Li0.5 – 0.5xCoxFe2.5−0.5xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.6) spinel ferrite. Phys. B 474, 47–52 (2015)
V. Vinayak, P.P. Khirade, S.D. Birajdar, R.C. Alange, K.M. Jadhav, Electrical and dielectrical Properties of low-temperature-synthesized nanocrystalline Mg2+-substituted cobalt spinel ferrite. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28, 3351–3356 (2015)
A.M. Abdeen, O.M. Hemeda, E.E. Assem, M.M. El-Sehly, Structural, electrical and transport phenomena of Co ferrite substituted by Cd. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 238 75–83 (2002)
W. Bayoumi, Structural and electrical properties of zinc-substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 8254–8261 (2007)
A.D. Sheikh, V.L. Mathe, Anomalous electrical properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 2018–2025 (2008)
D.R.K.B. Ravinder, Electrical conductivity of cerium substituted Mn–Zn ferrites. Mater. Lett. 57, 1738–1742 (2003)
A.V. Humbe, A.C. Nawle, A.B. Shinde, K.M. Jadhav, Impact of Jahn Teller ion on magnetic and semiconducting behaviour of Ni–Zn spinel ferrite synthesized by nitrate-citrate route. J. Alloy. Compd. 691, 343–354 (2017)
D. Bahadur, O.M. Parkash, D. Kumar, Bull. Mater. Sci. 3, 325–331 (1981)
O.M. Hameda, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256, 63–68 (2003)
E. Ranjith Kumar, P. Siva Prasada Reddy, G. Sarala Devi, S. Sathiyaraj, Structural, dielectric and gas sensing behavior of Mn substituted spinel MFe2O4 (M = Zn, Cu, Ni, and Co) ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 281–288 (2016)
B.P. Rao, K.H. Rao, Effect of sintering conditions on resistivity and dielectric properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 6049–6054 (1997)
J.C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism. Clarendon Press 1873
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951)
K. Iwauchi, Dielectric properties of fine particles of Fe3O4 and some ferrites. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 10, 1520–1528 (1971)
E.J. Verwey, P.W. Haayman, F.C. Romeijn, Physical properties and cation arrangement of oxides with spinel structures II. Electronic conductivity. J. Chem. Phys. 15, 181–187 (1947)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors AVH is thankful to Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai and Indian Institute of Technology Powai, Mumbai for proving XRD and HR-TEM characterizations respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Humbe, A.V., Kharat, P.B., Nawle, A.C. et al. Nanocrystalline Ni0.70−xCuxZn0.30Fe2O4 with 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25 prepared by nitrate-citrate route: structure, morphology and electrical investigations. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 3467–3481 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8281-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8281-8