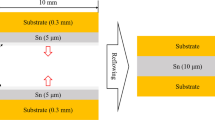
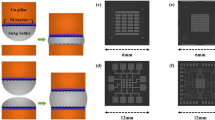
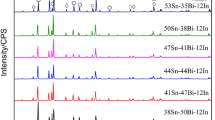
Abstract
Currently, accompanying the development of microelectronic joining and packaging, the integrated level of integrated circuit among the electronic devices has been substantially improved, which means the number of the soldered joints on a device is becoming more and more while the size of the micro-joint turns to be smaller and smaller. Given that soldered joints do play an important role in electronic packaging, serving as both mechanical bridges and electrical interconnections between the components and the bonding pads, to investigate the sensitivity of reliability of lead-free solders to various severe conditions deserves considerable concerns. This paper introduces the recent reliability research of lead-free solders under several specific conditions (e.g., isothermal aging, corrosive environment, drop impact, radiation) comprehensively, producing a fundamental summarization for the further reliability research.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.O. Kim, J.P. Jung, J.H. Lee et al., Effects of laser parameters on the characteristics of a Sn–3.5 wt% Ag solder joint. Met. Mater. Int. 15(1), 119–123 (2009)
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 82, 1–32 (2014)
J.B. Pan, B.J. Toleno, T.C. Chou et al., The effect of reflow profile on SnPb and SnAgCu solder joint shear strength. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 18(4), 48–56 (2006)
Y.L. Gao, C.D. Zou, B. Yang et al., Nanoparticles of SnAgCu lead-free solder alloy with an equivalent melting temperature of SnPb solder alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 484(1–2), 777–781 (2009)
S. Chada, Topics in lead-free solders: interfacial and Sn whisker growth. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 64(10), 1174–1175 (2012)
J. Chen, J. Shen, D. Min et al., Influence of minor Bi additions on the interfacial morphology between Sn–Zn–xBi solders and a Cu layer. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20(11), 1112–1117 (2009)
S.M. Hayes, N. Chawla, D.R. Frear, Interfacial fracture toughness of Pb-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 49(3), 269–287 (2009)
Y. Shi, J. Tian, H. Hao et al., Effects of small amount addition of rare earth Er on microstructure and property of SnAgCu solder. J. Alloys Compd. 453(1), 180–184 (2008)
N. Zhao, X.Y. Liu, M.L. Huang et al., Characters of multicomponent lead-free solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(10), 3925–3931 (2013)
H. Ma, J.C. Suhling, A review of mechanical properties of lead-free solders for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 44(5), 1141–1158 (2009)
X.P. Zhang, L.M. Yin, C.B. Yu, Thermal creep and fracture behaviors of the lead-free Sn–Ag–Cu–Bi solder interconnections under different stress levels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19(4), 393–398 (2008)
L. Zhang, S. Xue, L. Gao et al., Development of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(1), 1–15 (2010)
G. Zeng, S. Xue, L. Zhang et al., Properties and microstructure of Sn–0.7Cu–0.05Ni solder bearing rare earth element Pr. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 22(8), 1101–1108 (2011)
G. Zeng, S. Xue, L. Zhang et al., Recent advances on Sn–Cu solders with alloying elements: review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 22(6), 565–578 (2011)
G. Zeng, S. Xue, L. Zhang et al., A review on the interfacial intermetallic compounds between Sn–Ag–Cu based solders and substrates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(5), 421–440 (2010)
J.W. Yoon, S.B. Jung, Reliability studies of Sn–9Zn/Cu solder joints with aging treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 407(1), 141–149 (2006)
T. Gancarz, P. Fima, J. Pstruś, Thermal expansion, electrical resistivity, and spreading area of Sn–Zn–In alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23(5), 1524–1529 (2014)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J.K. Kivilahti, Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 49(1–2), 1–60 (2005)
M. Abtew, G. Selvaduray, Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 27(5–6), 95–141 (2000)
T.C. Chang, M.C. Wang, M.H. Hon, Growth and morphology of the intermetallic compounds formed at the Sn–9Zn–2.5 Ag/Cu interface. J. Alloys Compd. 402(1–2), 141–148 (2005)
M. Date, K.N. Tu, T. Shoji et al., Interfacial reactions and impact reliability of Sn–Zn solder joints on Cu or electroless Au/Ni (P) bond-pads. J. Mater. Res. 19(10), 2887–2896 (2004)
L. Zhang, J.G. Han, Y.H. Guo et al., Reliability of SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe solder joints with different heights for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(10), 4489–4494 (2014)
Y. Liu, J. Meerwijk, L.L. Luo et al., Formation and evolution of intermetallic layer structures at SAC305/Ag/Cu and SAC0705–Bi–Ni/Ag/Cu solder joint interfaces after reflow and aging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(11), 4954–4959 (2014)
W.X. Chen, S.B. Xue, H. Wang et al., Effects of Ag on microstructures, wettabilities of Sn–9Zn–xAg solders as well as mechanical properties of soldered joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(5), 461–467 (2010)
L. Zhang, S.B. Xue, Y. Chen et al., Effects of cerium on Sn–Ag–Cu alloys based on finite element simulation and experiments. J. Rare Earths 27(1), 138–144 (2009)
K.S. Kim, S.H. Huh, K. Suganuma, Effects of cooling speed on microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–Ag–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 333(1–2), 106–114 (2002)
G.D. Li, Y.W. Shi, H. Hao et al., Effect of rare earth addition on shear strength of SnAgCu lead-free solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20(2), 186–192 (2009)
S. Dunford, S. Canumalla, P. Viswanadham, Intermetallic morphology and damage evolution under thermomechanical fatigue of lead (Pb)-free solder interconnections. 54th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, Feburary, 2004, pp. 726–736
J.H. Lee, A.M. Yu, J.H. Kim et al., Reaction properties and interfacial intermetallics for Sn–xAg–0.5Cu solders as a function of Ag content. Met. Mater. Int. 14(5), 649–654 (2008)
J.M. Song, Y.R. Liu, Y.S. Lai et al., Influence of trace alloying elements on the ball impact test reliability of SnAgCu solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(1), 180–189 (2012)
W. Peng, E. Monlevade, M.E. Marques, Effect of thermal aging on the interfacial structure of SnAgCu solder joints on Cu. Microelectron. Reliab. 47(12), 2161–2168 (2007)
L.L. Gao, S.B. Xue, L. Zhang et al., Effect of alloying elements on properties and microstructures of SnAgCu solders. Microelectron. Eng. 87(11), 2025–2034 (2010)
L.L. Gao, S.B. Xue, L. Zhang et al., Effect of praseodymium on the microstructure and properties of Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(9), 910–916 (2010)
L.L. Gao, Effect of Pr and/or Nd on the Microstructures and Properties of SnAgCu Solder. Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012
L.L. Gao, S.B. Xue, L. Zhang et al., Effects of trace rare earth Nd addition on microstructure and properties of SnAgCu solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(7), 643–648 (2010)
X. Chen, J. Zhou, F. Xue et al., Microstructures and mechanical properties of Sn–0.1Ag–0.7Cu–(Co, Ni, and Nd) lead-free solders. J. Electron. Mater. 44(2), 725–732 (2015)
L. Zhang, S.B. Xue, L.L. Gao et al., Creep behavior of SnAgCu solders with rare earth Ce doping. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 20(3), 412–417 (2010)
L. Zhang, J. Han, Y. Guo et al., Effect of rare earth Ce on the fatigue life of SnAgCu solder joints in WLCSP device using FEM and experiments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 597, 219–224 (2014)
L. Zhang, S.B. Xue, L.L. Gao et al., Microstructure characterization of SnAgCu solder bearing Ce for electronic packaging. Microelectron. Eng. 88(9), 2848–2851 (2011)
H. Hao, J. Tian, Y.W. Shi et al., Properties of Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu solder alloy with trace rare earth element Y additions. J. Electron. Mater. 36(7), 766–774 (2007)
H. Hao, Y. Shi, Z. Xia et al., Microstructure evolution of SnAgCuEr lead-free solders under high temperature aging. J. Electron. Mater. 37(1), 2–8 (2008)
Y. Shi, J. Tian, H. Hao et al., Effects of small amount addition of rare earth Er on microstructure and property of SnAgCu solder. J. Alloys Compd. 453(1–2), 180–184 (2008)
M.A. Dudek, N. Chawla, Effect of rare-earth (La, Ce, and Y) additions on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Sn–3.9Ag–0.7Cu solder alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41A(3), 610–620 (2010)
M.A. Dudek, R. Sidhu, N. Chawla et al., Microstructure and mechanical behavior of novel rare earth-containing Pb-free solders. J. Electron. Mater. 35(12), 2088–2097 (2006)
Y.W. Wang, Y.W. Lin, C.T. Tu et al., Effects of minor Fe Co, and Ni additions on the reaction between SnAgCu solder and Cu. J. Alloys Compd. 478(1–2), 121–127 (2009)
K.J. Zeng, R. Stierman, T.C. Chiu et al., Kirkendall void formation in eutectic SnPb solder joints on bare Cu and its effect on joint reliability. J. Appl. Phys. 97(2), 024508 (2005)
Y.W. Wang, C.C. Chang, C.R. Kao, Minimum effective Ni addition to SnAgCu solders for retarding Cu3Sn growth. J. Alloys Compd. 478(1–2), L1–L4 (2009)
B.L. Chen, G.Y. Li, Influence of Sb on IMC growth in Sn–Ag–Cu–Sb Pb-free solder joints in reflow process. Thin Solid Films 462, 395–401 (2004)
G.Y. Li, X.D. Bi, Q. Chen et al., Influence of dopant on growth of intermetallic layers in Sn–Ag–Cu solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 40(2), 165–175 (2011)
G.Y. Li, B.L. Chen, X.Q. Shi et al., Effects of Sb addition on tensile strength of Sn–3.5Ag–0.7Cu solder alloy and joint. Thin Solid Films 504(1–2), 421–425 (2006)
Y.S. Park, Y.M. Kwon, H.Y. Son, et al., Effect of Sb addition in Sn–Ag–Cu solder balls on the drop test reliability of BGA packages with electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG) surface finish. 2007 9th International Conference on Electronic Materials and Packaging, Daejeon, South Korea, November 2007, pp. 317–321
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, G.S. Al-Ganainy et al., Influence of Zn addition on the microstructure, melt properties and creep behavior of low Ag-content Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 608, 130–138 (2014)
M.G. Cho, S.K. Kang, D.Y. Shih et al., Effects of minor additions of Zn on interfacial reactions of Sn–Ag–Cu and Sn–Cu solders with various cu substrates during thermal aging. J. Electron. Mater. 36(11), 1501–1509 (2007)
M. Ghosh, M.K. Gunjan, S.K. Das et al., Effect of Mn on Sn–Ag–Cu ternary lead free solder alloy-Cu assembly: a comparative study. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26(5), 610–614 (2010)
X.J. Wang, Q.S. Zhu, B. Liu et al., Effect of doping Al on the liquid oxidation of Sn–Bi–Zn solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(5), 2297–2304 (2014)
L. Zhang, L. Sun, Y.H. Guo et al., Reliability of lead-free solder joints in CSP device under thermal cycling. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(3), 1209–1213 (2014)
K.L. Lin, T.P. Liu, High-temperature oxidation of a Sn–Zn–Al solder. Oxid. Met. 50(3–4), 255–267 (1998)
J.X. Jiang, J.E. Lee, K.S. Kim et al., Oxidation behavior of Sn–Zn solders under high-temperature and high-humidity conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 462(1–2), 244–251 (2008)
K.S. Kim, T. Matsuura, K. Suganuma, Effects of Bi and Pb on oxidation in humidity for low-temperature lead-free solder systems. J. Electron. Mater. 35(1), 41–47 (2006)
W.X. Chen, S.B. Xue, H. Wang et al., Investigation on properties of Ga to Sn–9Zn lead-free solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(5), 496–502 (2010)
C.Y. Chou, S.W. Chen, Y.S. Chang, Interfacial reactions in the Sn–9Zn–(xCu)/Cu and Sn–9Zn–(xCu)/Ni couples. J. Mater. Res. 21(7), 1849–1856 (2006)
N. Huang, A. Hu, M. Li et al., Influence of Cr alloying on the oxidation resistance of Sn–8Zn–3Bi solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(8), 2812–2817 (2013)
H. Ye, S.B. Xue, J.D. Luo et al., Properties and interfacial microstructure of Sn–Zn–Ga solder joint with rare earth Pr addition. Mater. Des. 46, 816–823 (2013)
H. Ye, S. Xue, M. Pecht, Evaluation of the microstructure and whisker growth in Sn–Zn–Ga solder with Pr content. J. Mater. Res. 27(14), 1887–1894 (2012)
H. Ye, S. Xue, C. Chen et al., Growth behaviors of tin whisker in RE-doped Sn–Zn–Ga solder. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 25(3), 139–144 (2013)
K. Berent, P. Fima, T. Ganacarz et al., Wetting and microstructure evolution of the Sn–Zn–Ag/Cu interface. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23(5), 1630–1633 (2014)
F.Y. Hung, T.S. Lui, L.H. Chen et al., Resonant characteristics of the microelectronic Sn–Cu solder. J. Alloys Compd. 457(1–2), 171–176 (2008)
N. Zhao, H.T. Ma, L. Wang, Interfacial reactions between Sn–Cu based multicomponent solders and Ni substrates during soldering and aging. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 21(2), 19–23 (2009)
J.W. Yoon, S.W. Kim, J.M. Koo et al., Reliability investigation and interfacial reaction of ball-grid-array packages using the lead-free Sn–Cu solder. J. Electron. Mater. 33(10), 1190–1199 (2004)
J.W. Yoon, S.W. Kim, S.B. Jung, Effect of reflow time on interfacial reaction and shear strength of Sn–0.7Cu solder/Cu and electroless Ni–P BGA joints. J. Alloys Compd. 385(1–2), 192–198 (2004)
M.N. Islam, Y.C. Chan, Interfacial reactions of Sn–Cu solder with Ni/Au surface finish on Cu pad during reflow and aging in ball grid array packages. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 117(3), 246–253 (2005)
J.W. Yoon, Y.H. Lee, D.G. Kim et al., Intermetallic compound layer growth at the interface between Sn–Cu–Ni solder and Cu substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 381(1–2), 151–157 (2004)
L. Hua, C. Yang, Corrosion behavior, whisker growth, and electrochemical migration of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder doping with In and Zn in NaCl solution. Microelectron. Reliab. 51(12), 2274–2283 (2011)
L.R. Garcia, L.C. Peixoto, W.R. Osorio et al., Globular-to-needle Zn-rich phase transition during transient solidification of a eutectic Sn–9 %Zn solder alloy. Mater. Lett. 63(15), 1314–1316 (2009)
T. Fang, M. Osterman, M. Petch, Statistical analysis of tin whisker growth. Microelectron. Reliab. 46(5–6), 846–849 (2006)
M. Liu, A.P. Xian, Tin whisker growth on bulk Sn–Pb eutectic doping with Nd. Microelectron. Reliab. 49(6), 667–672 (2009)
J. Smetana, Theory of tin whisker growth: the end game. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 30(1), 11–22 (2007)
A. Dimitrovska, R. Kovacevic, Mitigation of Sn whisker growth by composite Ni/Sn plating. J. Electron. Mater. 38(12), 2516–2524 (2009)
J.W. Osenbach, J.M. DeLucca, B.D. Potteiger et al., Sn corrosion and its influence on whisker growth. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 30(1), 23–35 (2007)
P. Oberndorff, M. Dittes, P. Crema et al., Humidity effects on Sn whisker formation. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 29(4), 239–245 (2006)
P. Oberndorff, M. Dittes, P. Crema, et al., Whisker formation on matte Sn influencing of high humidity. 55th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Florida, USA, May, 2005, pp. 429–433
B. Liu, T.K. Lee, K.C. Liu, Impact of 5 % NaCl salt spray pretreatment on the long-term reliability of wafer-level packages with Sn–Pb and Sn–Ag–Cu solder interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 40(10), 2111–2118 (2011)
M. Mori, K. Miura, T. Sasaki et al., Corrosion of tin alloys in sulfuric and nitric acids. Corros. Sci. 44(4), 887–898 (2002)
U.S. Mohanty, K.L. Lin, Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Pb-free Sn–8.5Zn–0.05Al–xGa and Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu alloys in chloride containing aqueous solution. Corros. Sci. 50(9), 2437–2443 (2008)
D. Li, P.P. Conway, C. Liu, Corrosion characterization of tin–lead and lead free solders in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 50(4), 995–1004 (2008)
K. Yokoyama, A. Nogami, J. Sakai, Creep corrosion cracking of Sn–3.0Ag and Sn–0.5Cu solder alloys in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 86, 142–148 (2014)
K. Yokoyama, D. Tsuji, J. Sakai, Fracture of sustained tensile-loaded Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 53(10), 3331–3336 (2011)
U.S. Mohanty, K.L. Lin, Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of lead-free Sn–8.5Zn–xAg–0.1Al–0.5 Ga solder in 3.5 % NaCl solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 406(1–2), 34–42 (2005)
U.S. Mohanty, K.L. Lin, The polarization characteristics of Pb-free Sn–8.5Zn–xAg–0.1Al–0.5 Ga alloy in 3.5 % NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 49(7), 2815–2831 (2007)
D. Pavlov, T. Rogachev, Mechanism of the action of Ag and As on the anodic corrosion of lead and oxygen evolution at the Pb/PbO(2 − x)/H2O/O2/H2SO4 electrode system. Electrochim. Acta 31(2), 241–249 (1986). doi:10.1016/0013-4686(86)87115-8
M.F.M. Nazeri, M.G. Affendy, A.A. Mohamad, Corrosion study of Sn–9Zn lead-free solder in alkaline solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7(5), 4182–4191 (2012)
M.F.M. Nazeri, A.A. Mohamad, Corrosion measurement of Sn–Zn lead-free solders in 6M KOH solution. Measurement 47, 820–826 (2014)
U.S. Mohanty, K.L. Lin, Effect of Al on the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Pb free Sn–8.5Zn–0.5Ag–xAl–0.5 Ga solder in 3.5 % NaCl solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252(16), 5907–5916 (2006)
U.S. Mohanty, K.L. Lin, The effect of alloying element gallium on the polarization characteristics of Pb-free Sn–Zn–Ag–Al–XGa solders in NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 48(3), 662–678 (2006)
Y. Gao, C. Cheng, J. Zhao et al., Electrochemical corrosion of Sn–0.75Cu solder joints in NaCl solution. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 22(4), 977–982 (2012)
E.S. Freitas, W.R. Osorio, J.E. Spinelli et al., Mechanical and corrosion resistances of a Sn–0.7 wt%Cu lead-free solder alloy. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(6–7), 1392–1400 (2014)
M. Mostofizadeh, J. Pippola, T. Marttila, et al., Effect of isothermal aging and salt spray tests on reliability and mechanical strength of eutectic Sn–Bi lead-free solder joints. 13th 2012 International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multi-physics Simulation and Experiments in Microelectronics and Microsystems, 2012, pp. 1–8
L. Hua, W. Dai, L.S. Duan, et al., Electrochemical migration and electrochemical corrosion behaviors in 3 wt% NaCI solution of 64Sn–35Bi–lAg solder with In doping for micro-nanoelectronic packagings. 13th 2012 International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology & High Density Packaging, 2012, pp. 1372–1376
D.G. Kim, S.B. Jung, Interfacial reactions and growth kinetics for intermetallic compound layer between In–48Sn solder and bare Cu substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 386(1–2), 151–156 (2005)
J.M. Koo, S.B. Jung, Reliability of In–48Sn solder/Au/Ni/Cu BGA packages during reflow process. J. Electron. Mater. 34(12), 1565–1572 (2005)
X. Zhang, G. Wang, X. Liu et al., Copper dendrites: synthesis, mechanism discussion, and application in determination of l-tyrosine. Cryst. Growth Des. 8(4), 1430–1434 (2008)
G.R. Li, X.H. Lu, D.L. Qu, Electrochemical growth and control of ZnO dendritic structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(18), 6678–6683 (2007)
T. Takemoto, R.M. Latanision, T.W. Eagar et al., Electrochemical migration tests of solder alloys in pure water. Corros. Sci. 39(8), 1415–1430 (1997)
C. Dominkovics, G. Harsanyi, Fractal description of dendrite growth during electrochemical migration. Microelectron. Reliab. 48(10), 1628–1634 (2008)
C.Y. Zhou, T.X. Yu, R.S.W. Lee, Drop/impact tests and analysis of typical portable electronic devices. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 50(5), 905–917 (2008)
D.A. Shnawah, M.F.M. Sabri, I.A. Badruddin, A review on thermal cycling and drop impact reliability of SAC solder joint in portable electronic products. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(1), 90–99 (2012)
H. Tsukamoto, T. Nishimura, S. Suenaga et al., The influence of solder composition on the impact strength of lead-free solder ball grid array joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 51(3), 657–667 (2011)
C.Y. Yu, J. Lee, W.L. Chen et al., Enhancement of the impact toughness in Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu solder joints via modifying the microstructure of solder alloy. Mater. Lett. 119, 20–23 (2014)
Y. Yao, L.M. Keer, Cohesive fracture mechanics based numerical analysis to BGA packaging and lead free solders under drop impact. Microelectron. Reliab. 53(4), 629–637 (2013)
D.Y.R. Chong, F.X. Che, J.H.L. Pang et al., Drop impact reliability testing for lead-free and lead-based soldered IC packages. Microelectron. Reliab. 46(7), 1160–1171 (2006)
K. Mishiro, S. Ishikawa, M. Abe et al., Effect of the drop impact on BGA/CSP package reliability. Microelectron. Reliab. 42(1), 77–82 (2002)
Y.S. Lai, P.C. Yang, C.L. Yeh, Effects of different drop test conditions on board-level reliability of chip-scale packages. Microelectron. Reliab. 48(2), 274–281 (2008)
B. Wang, J. Li, A. Gallagher et al., Drop impact reliability of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu BGA interconnects with different mounting methods. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(7), 1475–1482 (2012)
A. Syed, T.Y. Tee, H.S. Ng et al., Advanced analysis on board trace reliability of WLCSP under drop impact. Microelectron. Reliab. 50(7), 928–936 (2010)
J.W. Elmer, Y. Li, H.D. Barth et al., Synchrotron radiation microtomography for large area 3D imaging of multilevel microelectronic packages. J. Electron. Mater. 43(12), 4421–4427 (2014)
T. Wang, P. Zhou, F. Cao et al., Growth behavior of Cu6Sn5 in Sn–6.5Cu solders under DC considering trace Al: in situ observation. Intermetallics 58, 84–90 (2015)
P. Zhou, H. Kang, F. Cao et al., In situ study on growth behavior of Cu6Sn5 during solidification with an applied DC in RE-doped Sn–Cu solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(10), 4538–4546 (2014)
G. Zeng, S.D. McDonald, C.M. Gourlay et al., Solidification of Sn–0.7Cu–0.15Zn solder: in situ observation. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 45A(2), 918–926 (2014)
W.R. Osorio, D.R. Leiva, L.C. Peixoto et al., Mechanical properties of Sn–Ag lead-free solder alloys based on the dendritic array and Ag3Sn morphology. J. Alloys Compd. 562, 194–204 (2013)
H.T. Chen, J. Han, J. Li et al., Inhomogeneous deformation and microstructure evolution of Sn–Ag-based solder interconnects during thermal cycling and shear testing. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(6), 1112–1120 (2012)
M.N. Wang, J.Q. Wang, H. Feng et al., In-situ observation of fracture behavior of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu lead-free solder during three-point bending tests in ESEM. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 649–655 (2012)
M.L. Huang, F. Yang, N. Zhao et al., Synchrotron radiation real-time in situ study on dissolution and precipitation of Ag3Sn plates in sub-50 μm Sn–Ag–Cu solder bumps. J. Alloys Compd. 602, 281–284 (2014)
M.L. Huang, Z.J. Zhang, N. Zhao et al., A synchrotron radiation real-time in situ imaging study on the reverse polarity effect in Cu/Sn–9Zn/Cu interconnect during liquid solid electromigration. Scr. Mater. 68(11), 853–856 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding Technology of Jiangsu Province, China (JSAWT-14-04). This work was also supported by A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Xue, Sb. Reliability study of lead-free solders under specific conditions. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 9424–9442 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3283-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3283-x