Abstract
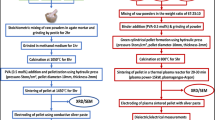
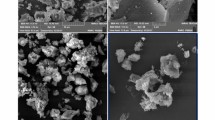
Highly crystallized mullite synthesis with different concentration of tungsten ions has been achieved by sol–gel technique and the effect of tungsten ion doping on mullite was examined at 1,100 and 1,400 °C. Characterizations were done by DTA/TGA, XRD, FTIR, LCR and FESEM instruments at the room temperature. Mullite formation was found to depend on the concentration of the doping ion up to a certain extent. With the addition of tungsten ion, the mullite formation temperature was decreased. The result showed a decrease in mullite phase at higher concentrations of doping ion with respect to undoped mullite. Oxide phases continued to increase with increasing doping concentration, which is mainly responsible for the increment in dielectric value. Dielectric value of the doped mullite was found to decrease with the increase in frequency for all the samples and saturates at higher frequency, which is normal behavior for dielectric ceramics. A.C. conductivity increased with frequency by following Jonscher’s power law. The composite showed maximum dielectric constant of 124.02 sintered at 1,400 °C for 0.05 M at 20 Hz frequency. Highly crystalline mullite whiskers of average dimension 3 μm were obtained at 0.02 tungsten concentration sintered at 1,400 °C. Due to the good dielectric response, comparatively low loss and appropriate nature of the doped mullite it can be used as ceramic capacitors, packaging material for integrated high speed devices. Also, it’s electrical and thermal suitability may prove to be significant as the insulator material of the spark plug.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.S. Mazdiyasni, L.M. Brown, Synthesis and mechanical properties of stoichiometric aluminum silicate (mullite). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 55, 548–552 (1972)
B.L. Metcalfe, J.H. Sant, Synthesis, microstructure, and physical properties of high purity mullite. Trans. J. Br. Ceram. Soc. 74, 193–201 (1975)
S. Kanzaki, H. Tabata, T. Kumazawa, S. Ohta, Sintering and mechanical properties of stoichiometric mullite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 68, C6–C7 (1985)
V.V. Vol’khin, I.L. Kazakova, P. Pongratz, E. Halwax, Mullite formation from highly homogeneous mixtures of Al2O3 and SiO2. Inorg. Mater. 36(4), 375–379 (2000)
H. Schneider, J. Schreuer, B. Hildmann, Structure and properties of mullite: a review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28(4), 329–344 (2008)
S. Rahman, S. Freimann, The Real Structure of Mullite, in Mullite, ed. by H. Schneider, S. Komarneni (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005), pp. 46–70
H. Schneider, S. Komarneni, Mullite, 2nd edn. (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006)
R.J. Angel, C.T. Prewitt, Crystal-structure of mullite: a re-examination of the average structure. Am. Mineral. 71, 1476–1482 (1986)
S. Durovic, P. Fejdi, Synthesis and crystal structure of germanium mullite and crystallochemical parameters of D-mullites. Silikaty 2, 97–112 (1976)
H. Saalfeld, V. Guse, Structure refinement of 3-2-mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2). Neues Jahrbuch Fur Mineralogie-Monatshefte 4, 145–152 (1981)
F. Sahnoune, M. Chegaar, N. Saheb, P. Goeuriot, F. Valdivieso, Algeria kaolinite used for mullite formation. Appl. Clay Sci. 38, 304–310 (2008)
H.F. Chen, M.C. Wang, M.H. Hon, Phase transformation and growth of mullite in kaolin ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 2389–2397 (2004)
V. Viswabaskarana, F.D. Gnanama, M. Balasubramanian, Mullite from clay-reactive alumina for insulating substrate application. Appl. Clay Sci. 25, 29–35 (2004)
V. Viswabaskarana, F.D. Gnanama, M. Balasubramanian, Mullitisation behavior of calcined clay–alumina mixtures. Ceram. Int. 29(5), 561–571 (2003)
D.J. Cassidy, J.L. Woolfrey, B.R. Bartlett, B. Ben-Nissan, The effect of precursor chemistry on the crystallization and densification of sol–gel derived mullite gels and powders. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 10, 19–30 (1997)
A.M.L. Marques Fonseca, J.M.E. Ferreira, I.M. Miranda Salvado, J.L. Baptista, Mullite based compositions prepared by sol–gel techniques. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 8, 403–407 (1997)
Y.X. Huang, A.M.R. Senos, J. Rocha, J.L. Baptista, Gel formation in mullite precursors obtained via tetra ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) pre-hydrolysis. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 105–110 (1997)
F. Mizukami, K. Maeda, M. Toba, T. Sano, S.I. Niwa, Effect of organic ligand used in sol–gel process on the formation of mullite. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 8, 101–106 (1997)
H. Schneider, Transition metal distribution, in Mullite and Mullite Matrix Composites, ed. by S. Somiya, R.F. Davis, J.A. Pask (The American Ceramic Society, Westerville, 1990), p. 135
P. Sarin, W. Yoon, R.P. Haggerty, C. Chiritescu, N.C. Bhorkar, W.M. Kriven, Effect of transition-metal-ion doping on high temperature thermal expansion of 3:2 mullite: an in situ, high temperature, synchrotron diffraction study. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 353–365 (2008)
E.E. Kiss, P.S. Putanov, Influence of transition metal ions on the textural properties of alumina and aluminosilicate. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 75(1), 39–45 (2002)
D. Roy, B. Bagchi, S. Das, P. Nandy, Electrical and dielectric properties of sol–gel derived mullite doped with transition metals. Mater. Chem. Phys. 138(1), 375–383 (2013)
A. Beran, D. Voll, H. Schneider, Dehydration and structural development mullite precursors: an FTIR spectroscopic study. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21(14), 2479–2485 (2001)
S. Shoval, M. Boudeulle, S. Yariv, I. Lapides, G. Panczer, Micro-raman and FT-IR spectroscopy study of thermal transformation of St. Claire dickite. Opt. Mater. 16, 319–327 (2001)
S.P. Chaudhuri, S.K. Patra, A.K. Chakraborty, Electrical resistivity of transition metal ion doped mullite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 2941–2950 (1999)
W.J. Walker, M.E. Saccoccia, Alumina ceramic for spark plug insulator, U.S. Patent No. 20110077141 A1 (2011)
Ph. Colomban, Structure of oxide gels and glasses by infrared and Raman scattering: I. aluminus. J. Mater. Sci. 24, 3002–3010 (1989)
M. Daniele, V. Mario, B. Guido, Mullite type structures in the system Al2O3–Me2O (Me = Na, K) and Al2O3–B2O3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 1929–1934 (1992)
P. Padmaja, G.M. Anilkumar, P. Mukundan, G. Aruldhas, K.G.K. Warrier, Characterisation of stoichiometric sol–gel by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Inorg. Mat. 3, 693–698 (2001)
D.R. Patil, S.A. Lokare, R.S. Devan, S.S. Chougule, C.M. Kanamadi, Y.D. Kolekar, B.K. Chougule, Studies on electrical and dielectric properties of Ba1−xSrxTiO3. Mater. Chem. Phys. 104, 254–257 (2007)
R.A. Abbas, Studing some dielectric properties and effective parameters of composite materials containing of novolak resin. J. Eng. Technol. 8(25), 277–288 (2007)
A. See, J. Hassan, M. Hashim, W.M.D.W. Yusoff, Dielectric variations of barium titanate additions on mullite–kaolinite sample. Solid State Sci. Technol. 16, 197–204 (2008)
G.M. Tsangargi, G.C. Psarras, A.J. Kontopoulos, Dielectric permittivity and loss of an aluminum-filled epoxy resin. J. Compos. Mat. 41, 403–417 (2007)
G.C. Psarras, E. Manolakaki, G.M. Tsangaris, Dielectric dispersion and ac conductivity in—iron particles loaded—polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 34(12), 1187–1198 (2003)
M. Al-Haj Abdallah, Y. Alramadin, M. Ahmad, A. Zihlif, S. Jawad, A. Alnajjar, Electrical characterization of metal fiber-polyester composite. Int. J. Polym. Mat. 37, 33–42 (1997)
S. Sindhu, M.R. Anantharaman, B.P. Thampi, K.A. Malini, P. Kurian, Evaluation of a.c. conductivity of rubber ferrite composites from dielectric measurements. Bull. Mater. Sci. 25(7), 599–607 (2002)
L.H. VanVlack, Elements of Material Science and Engineering, 6th edn. (Addison-Wesley Co, New York, 1989), p. 399
G.C. Psarras, E. Manolakaki, G.M. Tsangaris, Electrical relaxations in polymeric particulate composites of epoxyresin and metal particles. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 33, 375–384 (2002)
Thermal Conductivity, hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/thercond.html. Accessed 28 Sept 2014
F.H. Riddle, Ceramic spark-plug insulator. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 32(11), 333–346 (1949)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to DST and UGC (PURSE program), Government of India, for the financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halder, K., Paul, B.K., Roy, D. et al. High-K tungsten-mullite composite for electronic industrial application: synthesis and study of its microstructure, phase behavior and electrical properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 1172–1180 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2521-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2521-y