Abstract
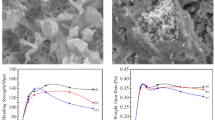
This study focused on the production of mullite ceramic and composites containing HfN reinforcements through spark plasma sintering. Accordingly, 5, 10 and 15wt% HfN powders with calcined Aluminum nitrate nonahydrate (ANN) and colloidal silica mixture were blended through a high-energy mixer mill in ethanol media. Spark plasma sintering of mullite ceramic and composite was performed under almost the same condition consisting of the initial and final applied pressure of 10 and 50 MPa, respectively, vacuum of 15–25 Pa, and the maximum sintering temperature of 1350 °C. The measured relative densities showed the nearly full densification of all prepared samples. The XRD patterns also depicted perfect mullitization for the mullite sample, while in the sintered composites, mullite, HfN and HfO2 peaks were obtained as the crystalline phases. The uniform distribution of HfN and HfO2 as the reaction products of ANN water desorption was recognized in the microstructure of mullite composites with 5 and 10 wt% HfN samples. Meanwhile, the mullite-15wt% HfN composite displayed some agglomerates and porosities. The attained mechanical properties also showed that Vickers hardness was increased by raising HfN contents. However, the maximum bending strength of 424 ± 25 and fracture toughness of 3.74 ± 0.22 MPa m1/2 were achieved for the composite containing 10 wt% HfN.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.E. Lee, Y. Iqbal, Influence of mixing on mullite formation in porcelain. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 2583–2586 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(01)00274-6
K.K. Chawla, Z.R. Xu, J.S. Ha, Processing, Structure, and Properties of Mullite Fiber/Mullite Matrix Composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 16, 293–299 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0955-2219(95)00136-0
N.F. Popovskaya, N.M. Bobkova, Mullite-tialite ceramic materials based on chemically precipitated mixtures (a review). Glas. Ceram. (English Transl. Steklo i Keramika) 59, 234–236 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020979228914
C. Sadik, I.E. El Amrani, A. Albizane, Recent advances in silica-alumina refractory: a review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2, 83–96 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jascer.2014.03.001
D. Pereira, G.R.S. Biasibetti, R.V. Camerini, A.S. Pereira, Sintering of mullite by different methods. Mater. Manuf. Process. 29, 391–396 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2013.864400
J. Anggono, Mullite ceramics: its properties structure and synthesis. Mullite Ceram. Its Prop. Struct. Synth. 7, 1–10 (2005). https://doi.org/10.9744/jtm.7.1.pp.1-10
D.J. Duval, S.H. Risbud, J.F. Shackelford, Mullite, in Ceram. Glass. Mater, (Springer, New York, 2008), pp. 27–39
H. Schneider, R.X. Fischer, J. Schreuer, Mullite: crystal structure and related properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 2948–2967 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.13817
R. Mishra, R.S. Ningthoujam, High-temperature ceramics, in Mater. Under Extrem. Cond., ed. by A.K. Tyagi, S.B.T.-M.U.E.C. Banerjee (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2017), pp. 377–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801300-7.00011-5.
T.F. Choo, M.A.M. Salleh, K.Y. Kok, K.A. Matori, A review on synthesis of mullite ceramics from industrial wastes. Recycling. 4, 39 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4030039
X. Miao, Porous mullite ceramics from natural topaz. Mater. Lett. 38, 167–172 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(98)00153-0
A.I. Abdallah, M. Sayed, M. Awaad, A.H.E. Yousif, S.M. Naga, Characterization of in-situ zirconia/mullite composites prepared by sol–gel technique. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2021.1929738
J. Roy, S. Das, S. Maitra, Solgel-processed mullite coating - A review. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 12, E71–E77 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.12230
H. Ohnishi, T. Kawanami, K. Miyazaki, T. Hiraiwa, Mechanical properties of mullite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 16, 633–641 (1986)
E. Nsiah-Baafi, A. Andrews, Fabrication of mullite from lithomargic clay via spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 43, 14277–14280 (2017)
E. Ghasali, Y. Orooji, A. Faeghi-nia, M. Alizadeh, T. Ebadzadeh, Characterization of mullite-Nd2O3 composite prepared through spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 47, 16200–16207 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.198
K.G.K. Warrier, G.M.A. Kumar, S. Ananthakumar, Densification and mechanical properties of mullite-SiC nanocomposites synthesized through sol–gel coated precursors. Bull. Mater. Sci. 24, 191–195 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02710100
D. Ghahremani, T. Ebadzadeh, A. Maghsodipour, Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of Mullite-TiC composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 41, 1957–1962 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.07.146
E. Ghasali, E.K. Saeidabadi, M. Alizadeh, A. Fazili, H. Rajaei, A. Jam, H. Kazemzadeh, T. Ebadzadeh, Preparation of mullite/B4C composites: a comparative study on the effect of heating methods. Ceram. Int. 44, 18743–18751 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.104
S.M.R. Derakhshandeh, M.S. Gohari, E.K. Saeidabadi, A. Jam, H. Rajaei, A. Fazili, M. Alizadeh, E. Ghasali, A.H. Pakseresht, T. Ebadzadeh, Comparison of spark plasma and microwave sintering of mullite based composite: mullite/Ta2O5 reaction. Ceram. Int. 44, 13176–13181 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.142
E.K. Saeidabadi, E. Salahi, T. Ebadzadeh, Preparation mullite/Si3N4 composites by reaction spark plasma sintering and their characterization. Ceram. Int. 45, 5367–5383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.237
H. Rajaei, M. Farvizi, I. Mobasherpour, M. Zakeri, Effect of spark plasma sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of mullite—WC composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 70, 197–201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.10.012
Y. Orooji, E. Ghasali, M. Moradi, M.R. Derakhshandeh, M. Alizadeh, M.S. Asl, T. Ebadzadeh, Preparation of mullite-TiB2-CNTs hybrid composite through spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 45, 16288–16296 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.154
Y. Orooji, A. Alizadeh, E. Ghasali, M.R. Derakhshandeh, M. Alizadeh, M.S. Asl, T. Ebadzadeh, Co-reinforcing of mullite-TiN-CNT composites with ZrB2 and TiB2 compounds. Ceram. Int. 45, 20844–20854 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.072
Y. Orooji, M.R. Derakhshandeh, E. Ghasali, M. Alizadeh, M. ShahediAsl, T. Ebadzadeh, Effects of ZrB2 reinforcement on microstructure and mechanical properties of a spark plasma sintered mullite-CNT composite. Ceram. Int. 45, 16015–16021 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.113
F. Sahnoune, N. Saheb, M. Chegaar, P. Goeuriot, Microstructure and sintering behavior of mullite-zirconia composites. Mater. Sci. Forum. 638–642, 979–984 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.638-642.979
L.S. Cividanes, T.M.B. Campos, L.A. Rodrigues, D.D. Brunelli, G.P. Thim, Review of mullite synthesis routes by sol–gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 55, 111–125 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2222-9
P.M. Souto, R.R. Menezes, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, Effect of Y2O3 additive on conventional and microwave sintering of mullite. Ceram. Int. 37, 241–248 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2010.08.043
C.Y. Chen, G.S. Lan, W.H. Tuan, Preparation of mullite by the reaction sintering of kaolinite and alumina. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20, 2519–2525 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00125-4
C.A. Harper, B. Esposito, Handbook of ceramics, glasses, and diamonds (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2001)
H.O. Pierson, Handbook of refractory carbides and nitrides: properties, characteristics, processing and applications, William Andrew, 1996.
J. Poetschke, V. Richter, A. Michaelis, Fundamentals of sintering nanoscaled binderless hardmetals. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 49, 124–132 (2015)
O. Guillon, J. Gonzalez-Julian, B. Dargatz, T. Kessel, G. Schierning, J. Räthel, M. Herrmann, Field-assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering: mechanisms, materials, and technology developments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 16, 830–849 (2014)
E. Ghasali, K. Shirvanimoghaddam, M. Alizadeh, T. Ebadzadeh, Ultra-low temperature fabrication of vanadium carbide reinforced aluminum nano composite through spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 753, 433–445 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.239
H. Majidian, E. Ghasali, T. Ebadzadeh, M. Razavi, C. Division, Effect of heating method on microstructure and mechanical properties of zircon reinforced aluminum composites. Mater. Res. 19, 1443–1448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2016-0390
E. Ghasali, M. Alizadeh, K. Shirvanimoghaddam, R. Mirzajany, M. Niazmand, A. Faeghi-Nia, T. Ebadzadeh, Porous and non-porous alumina reinforced magnesium matrix composite through microwave and spark plasma sintering processes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 212, 252–259 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.03.058
E. Ghasali, M. Alizadeh, A.H. Pakseresht, T. Ebadzadeh, Preparation of silicon carbide/carbon fiber composites through high-temperature spark plasma sintering. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jascer.2017.10.004
E. Ghasali, Y. Palizdar, A. Jam, H. Rajaei, T. Ebadzadeh, Effect of Al and Mo addition on phase formation, mechanical and microstructure properties of spark plasma sintered iron alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 13, 221–231 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2017.10.005
E. Ghasali, T. Ebadzadeh, M. Alizadeh, M. Razavi, Spark plasma sintering of WC-based cermets/titanium and vanadium added composites: a comparative study on the microstructure and mechanical properties. Ceram. Int. 44, 10646–10656 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.093
K. Niihara, R. Morena, D.P.H. Hasselman, Evaluation of K Ic of brittle solids by the indentation method with low crack-to-indent ratios. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1, 13–16 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00724706
E. Ghasali, H. Nouranian, A. Rahbari, H. Majidian, M. Alizadeh, T. Ebadzadeh, Low temperature sintering of aluminum-zircon metal matrix composite prepared by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Res. 19, 1189–1192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2016-0395
P. Kang, Q. Zhao, S. Guo, W. Xue, H. Liu, Z. Chao, L. Jiang, G. Wu, Optimisation of the spark plasma sintering process for high volume fraction SiCp/Al composites by orthogonal experimental design. Ceram. Int. 47, 3816–3825 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.240
B. Apak, F.C. Sahin, C-CNT Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 127 (2015) 1029–1031. https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.127.1029.
B. Pacewska, M. Keshr, Thermal transformations of aluminium nitrate hydrate. Thermochim. Acta. 385, 73–80 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00703-1
I.F. Myronyuk, V.I. Mandzyuk, V.M. Sachko, V.M. Gunko, Structural and morphological features of disperse alumina synthesized using aluminum nitrate nonahydrate. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 153 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1366-0
B.C. Schulz, D. Butts, G.B. Thompson, Oxidation behavior of vacuum plasma-sprayed hafnium-tantalum nitrides. J. Mater. Res. 30, 2949–2957 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.191
T. Glechner, O.E. Hudak, T. Wojcik, L. Haager, F. Bohrn, H. Hutter, O. Hunold, J. Ramm, S. Kolozsvári, E. Pitthan, D. Primetzhofer, H. Riedl, Influence of the non-metal species on the oxidation kinetics of Hf, HfN, HfC, and HfB2 coatings. Mater. Des. 211, 110136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110136
R.F. Voitovich, E.A. Pugach, High-temperature oxidation of the nitrides of the group IV transition metals—II. Oxidation of zirconium and hafnium nitrides. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 14, 747–750 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00800246
Y.S. Tishchenko, S.M. Lakiza, V.P. Redko, L.M. Lopato, Isothermal sections of the Al2O3–HfO2–Er2O3 phase diagram at 1250 and 1600 °C. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 51, 594–601 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-013-9473-2
D. Shin, R. Arróyave, Z.K. Liu, Thermodynamic modeling of the Hf–Si–O system. Calphad Comput. Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem. 30, 375–386 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2006.08.006
C. Verdon, O. Szwedek, A. Allemand, S. Jacques, Y. Le Petitcorps, P. David, High temperature oxidation of two- and three-dimensional hafnium carbide and silicon carbide coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 879–887 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.10.019
G. Chen, X. Ge, Y. Wang, W. Xing, Y. Guo, Design and preparation of high permeability porous mullite support for membranes by in-situ reaction. Ceram. Int. 41, 8282–8287 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.02.045
C.H.H. Hsiung, A.J. Pyzik, F. De Carlo, X. Xiao, S.R. Stock, K.T. Faber, Microstructure and mechanical properties of acicular mullite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 503–513 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.09.017
Z. Hou, B. Cui, L. Liu, Q. Liu, Effect of the different additives on the fabrication of porous kaolin-based mullite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 42, 17254–17258 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.020
M. Rashad, G. Logesh, U. Sabu, M. Balasubramanian, A novel monolithic mullite microfiltration membrane for oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Memb. Sci. 620, 118857 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118857
G. Chen, H. Qi, W. Xing, N. Xu, Direct preparation of macroporous mullite supports for membranes by in situ reaction sintering. J. Memb. Sci. 318, 38–44 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2008.01.034
H. Guo, W. Li, F. Ye, Low-cost porous mullite ceramic membrane supports fabricated from kyanite by casting and reaction sintering. Ceram. Int. 42, 4819–4826 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.167
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Islamic Azad University of Shahrood for its support.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moslemi-firoozabadi, H., Manafi, S. & Ghahremani, D. Preparation of mullite-HfN composites through spark plasma sintering: investigation of the microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 775–786 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00252-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00252-7