Abstract
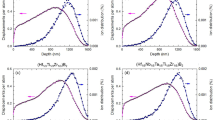
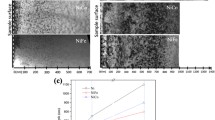
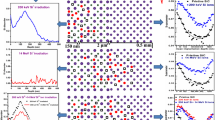
Damage production and amorphization resulting from the interaction of medium-energy (from 40 to 480 keV) noble-gas ions (from He to Kr) with potassium tantalate (KTaO3) are determined using ion channeling measurements. A disorder accumulation model has been fit to the maximum damage concentration versus ion fluence to extract the cross sections for direct-impact and defect-stimulated amorphization, and the results indicate that defect-stimulated amorphization is the dominant mechanism. These cross sections exhibit a strong dependence on the calculated cross sections for displacing lattice atoms, indicating a dominant contribution of nuclear interactions to the defect production and amorphization processes under the irradiation conditions used in this study. These experimental findings, along with the model fits, suggest that the difference in recoil spectra between He and the other heavier ions may be the main driving force for the decreased damage efficiency observed for He ions, which results in a reduced rate of damage accumulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolfram T, Ellialtioglu S (2006) Electronic and optical properties of D-band perovskites. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wemple SH (1965) Some transport properties of oxygen-deficient single-crystal potassium tantalate (KTaO3). Phys Rev 137:A1575–A1582
Harashima S, Bell C, Kim M et al (2013) Coexistence of two-dimensional and three-dimensional Shubnikov–de Haas oscillations in Ar+-irradiated KTaO3. Phys Rev B 88:85102
Wadehra N, Tomar R, Halder S et al (2017) Electronic structure modification of the KTaO 3 single-crystal surface by Ar+ bombardment. Phys Rev B 96:115423
Wong JYC, Zhang L, Kakarantzas G et al (1992) Ion-implanted optical waveguides in KTaO3. J Appl Phys 71:49–52
Ueno K, Inoue IH, Yamada T et al (2004) Field-effect transistor based on KTaO3 perovskite. Appl Phys Lett 84:3726
Ueno K, Nakamura S, Shimotani H et al (2011) Discovery of superconductivity in KTaO3 by electrostatic carrier doping. Nat Nanotechnol 6:408–412
Prassides K (2011) Superconductivity at the double. Nat Nanotechnol 6:400–401
Meldrum A, Boatner LA, Ewing RC (1998) Effects of ionizing and displacive irradiation on several perovskite-structure oxides. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 141:347–352
Meldrum A, Boatner LA, Weber WJ, Ewing RC (2002) Amorphization and recrystallization of the ABO3 oxides. J Nucl Mater 300:242–254
Wendler E, Wendler L (2012) Empirical modeling of the cross section of damage formation in ion implanted III-V semiconductors. Appl Phys Lett 100:192108
Ziegler JF, Biersack JP (1985) The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter. In: Treatise on Heavy-Ion Science. Springer US, Boston, MA, pp 93–129
Zhang Y, Lian J, Zhu Z et al (2009) Response of strontium titanate to ion and electron irradiation. J Nucl Mater 389:303–310
Hecking N, Heidemann KF, Te Kaat E (1986) Model of temperature dependent defect interaction and amorphization in crystalline silicon during ion irradiation. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res B 15:760–764
Weber WJ (2000) Models and mechanisms of irradiation-induced amorphization in ceramics. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 166–167:98–106
Zhang Y, Lian J, Wang CM et al (2005) Ion-induced damage accumulation and electron-beam-enhanced recrystallization in SrTiO3. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys 72:1–8
Zhang Y, Weber WJ, Jiang W et al (2004) Effects of implantation temperature on damage accumulation in Al-implanted 4H–SiC. J Appl Phys 95:4012–4018
Lorenz K, Wendler E, Redondo-Cubero A et al (2017) Implantation damage formation in a-, c- and m-plane GaN. Acta Mater 123:177–187
Wendler E, Bilani O, Gärtner K et al (2009) Radiation damage in ZnO ion implanted at 15 K. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 267:2708–2711
Wendler E, Treiber E, Baldauf J et al (2016) High-level damage saturation below amorphisation in ion implanted β-Ga2O3. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 379:85–90
Zhang Y, Weber WJ, Shutthanandan V et al (2004) Damage evolution on Sm and O sublattices in Au-implanted samarium titanate pyrochlore. J Appl Phys 95:2866–2872
Velişa G, Wendler E, Xue H et al (2018) Revealing ionization-induced dynamic recovery in ion-irradiated SrTiO3. Acta Mater 149:256–264
Gibbons JF (1972) Ion implantation in semiconductors—Part II: damage production and annealing. Proc IEEE 60:1062–1096
Wendler E, Opfermann T, Gaiduk PI (1998) Ion mass and temperature dependence of damage production in ion implanted InP. J Appl Phys 82:5965
Weber WJ, Ewing RC, Wang LM (1994) The radiation-induced crystalline-to-amorphous transition in zircon. J Mater Res 9:688–698
Zhang Y, Xue H, Zarkadoula E et al (2017) Coupled electronic and atomic effects on defect evolution in silicon carbide under ion irradiation. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 21:285–298
Zhang Y, Wang CM, Engelhard MH, Weber WJ (2006) Irradiation behavior of SrTiO3 at temperatures close to the critical temperature for amorphization. J Appl Phys 100:113533
Weber WJ, Wang L, Zhang Y et al (2008) Effects of dynamic recovery on amorphization kinetics in 6H-SiC. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 266:2793–2796
Weber WJ, Zhang Y, Wang L (2012) Review of dynamic recovery effects on ion irradiation damage in ionic-covalent materials. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 277:1–5
Xue H, Zhang Y, Weber WJ (2017) In-cascade ionization effects on defect production in 3C silicon carbide. Mater Res Lett 5:1–7
Thomé L, Fradin J, Jagielski J et al (2003) Radiation damage in ion-irradiated yttria-stabilized cubic zirconia single crystals. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 24:37–48
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences, Materials Sciences and Engineering Division under Contract DE-AC05-00OR22725. The work was also supported by the BMBF of Germany under Contract No. 03SF0478B. The authors gratefully acknowledge the staff of the ion beam center facility at Friedrich-Schiller Universität Jena for their assistance during ion irradiation and ion channeling experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Note of Copyright: This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC, under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velişa, G., Wendler, E., Wang, LL. et al. Ion mass dependence of irradiation-induced damage accumulation in KTaO3. J Mater Sci 54, 149–158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2864-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2864-5