Abstract
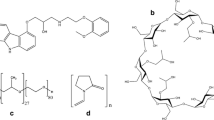
Carvedilol is one of the most effective antihypertensive drugs used in the treatment of congestive heart failure. A major disadvantage of this pharmaceutical active substance is its limited solubility in water, gastric and intestinal fluids. One way to overcome this problem is the preparation of inclusion complexes. The aim of this study was to prepare the inclusion complexes of carvedilol with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) and (2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD) and to investigate their physical properties. The formation of inclusion complexes with β-CD and HP-β-CD was confirmed using FTIR, 1H-NMR and XRD methods. Phase solubility studies indicate the formation of inclusion complexes in 1:2 molar ratio and the increase of carvedilol solubility. The stability constant (β 2) was found to be 3.4 × 104 and 5.1 × 104 M−2 for inclusion complexes of carvedilol:β-CD and carvedilol:HP-β-CD, respectively. Photostability of carvedilol was increased after preparation of inclusion complexes with β-CD and HP-β-CD. Based on the results of this study, it can be concluded that the prepared complexes of carvedilol improve the solubility and stability of carvedilol and give it an advantage to be applied for the design of new pharmaceutical formulations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Packer, M., Lukas, M., Tenero, D., Baidoo, C., Greenberg, B.: Pharmacokinetic profile of controlled-release carvedilol in patients with left ventricular dysfunction associated with chronic heart failure or after myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 98, 39–45 (2006)
Weber, A., Sica, A., Tarka, A., Iyengar, M., Fleck, R., Bakris, L.: Controlled-release carvedilol in the treatment of essential hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 98, 32–38 (2006)
Palazzuoli, A., Calabria, P., Verzuri, M.S., Auteri, A.: Carvedilol: something else than a simple betablocker? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 6, 115–126 (2002)
Ouyang, Y., Chen, Z., Tan, M., Liu, A., Chen, M., Liu, J., Fang, J.: Carvedilol, a third-generation β-blocker prevents oxidative stress-induced neuronal death and activates Nrf2/ARE pathway in HT22 cells. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 441(4), 917–922 (2013)
Lin, C.S., Lin, W.S., Lin, C.L., Kao, C.H.: Carvedilol use is associated with reduced cancer risk: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Int. J. Cardiol. 184, 9–13 (2015)
Takekuma, Y., Yagisawa, K., Sugawara, M.: Mutual inhibition between carvedilol enantiomers during racemate glucuronidation mediated by human liver and intestinal microsomes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35(2), 151–163 (2012)
Shete, A.S., Yadav, A.V., Murthy, S.M.: Chitosan and chitosan chlorhydrate based various approaches for enhancement of dissolution rate of carvedilol. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 20(1), 93–97 (2012)
Kasim, N., Whitehouse, M., Ramchandran, C., Bermejo, M., Lennernas, H., Hussain, A.S., Junginger, H.E., Stavchansky, S.A., Midha, K.K., Shah, V.P., Amidon, G.L.: Molecular properties of WHO essential drugs and provisional biopharmaceutical classification. Mol. Pharm. 1, 85–96 (2004)
Khadra, I., Zhou, Z., Dunn, C., Wilson, C.G., Halbert, G.: Statistical investigation of simulated intestinal fluid composition on the equilibrium solubility of biopharmaceutics classification system class II drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 67, 65–75 (2015)
Möllendorff, E.V., Reiff, K., Neugebauer, G.: Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of carvedilol, a vasodilating beta-blocker. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 33(5), 511–513 (1987)
Savic, I., Marinkovc, V., Savic, I., Sibinovic, P., Cekic, N.: Application of the experimental design method to photostability studies of Karvileks tablet. Ind. J. Pharm. Edu. Res. 46(3), 275–282 (2012)
Yuvaraja, K., Khanam, J.: Enhancement of carvedilol solubility by solid dispersion technique using cyclodextrins, water soluble polymers and hydroxyl acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. 96, 10–20 (2014)
Lee, S.N., Poudel, B.K., Tran, T.H., Marasini, N., Pradhan, R., Im Lee, Y., Kim, J.O.: A novel surface-attached carvedilol solid dispersion with enhanced solubility and dissolution. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36(1), 79–85 (2013)
Planinšek, O., Kovačič, B., Vrečer, F.: Carvedilol dissolution improvement by preparation of solid dispersions with porous silica. Int. J. Pharma. 406(1), 41–48 (2011)
Tapas, A., Kawtikwar, P., Sakarkar, D.: An improvement in physicochemical properties of carvedilol through spherically agglomerated solid dispersions with PVP K30. Acta Pol. Pharm. 69(2), 299–308 (2012)
Sanjula, B., Shah, F.M., Javed, A., Alka, A.: Effect of poloxamer 188 on lymphatic uptake of carvedilol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for bioavailability enhancement. J. Drug Target. 17(3), 249–256 (2009)
Wei, L., Sun, P., Nie, S., Pan, W.: Preparation and evaluation of SEDDS and SMEDDS containing carvedilol. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 31(8), 785–794 (2005)
Salimi, A., Zadeh, B.S.M., Hemati, A., Birgani, S.A.: Design and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) of carvedilol to improve the oral absorption. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 9(3), e16125 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Zhi, Z., Li, X., Gao, J., Song, Y.: Carboxylated mesoporous carbon microparticles as new approach to improve the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble carvedilol. Int. J. Pharm. 454(1), 403–411 (2013)
Nikolic, V., Kapor, A.J., Nikolic, L.B., Savic, I.M., Savic-Gajic, I.M.: The importance of inclusion complexes with cyclodextrins in pharmacy. In: Ramirez, F.G. (ed.) Cyclodextrins: Synthesis, Chemical Applications and Role in Drug Delivery, pp. 225–240. Nova Science Publishers Inc, New York (2015)
Savic, I.M., Nikolic, V.D., Savic-Gajic, I., Nikolic, L.B., Radovanovic, B.C., Mladenovic, J.D.: Investigation of properties and structural characterization of the quercetin inclusion complex with (2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 82(3), 383–394 (2015)
Tačić, A., Savić, I., Nikolić, V., Savić, I., Ilić-Stojanović, S., Ilić, D., Petrović, S., Popsavin, M., Kapor, A.: Inclusion complexes of sulfanilamide with β-cyclodextrin and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 80(1–2), 113–124 (2014)
Dawoud, A.A., Al-Rawashdeh, N.: Spectrofluorometric, thermal, and molecular mechanics studies of the inclusion complexation of selected imidazoline-derived drugs with β-cyclodextrin in aqueous media. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 60(3–4), 293–301 (2008)
Al-Rawashdeh, N.A., Al-Sadeh, K.S., Al-Bitar, M.B.: Physicochemical study on microencapsulation of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in dermal preparations. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 36(6), 688–697 (2010)
Bani-Yaseen, A.D., Al-Rawashdeh, N.F., Al-Momani, I.: Influence of inclusion complexation with β-cyclodextrin on the photostability of selected imidazoline-derived drugs. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 63(1–2), 109–115 (2009)
Al-Rawashdeh, N.A., Al-Sadeh, K.S., Al-Bitar, M.B.: Inclusion complexes of sunscreen agents with β-cyclodextrin: spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 11 (2013)
Al-Rawashdeh, N.A.: Interactions of nabumetone with γ-cyclodextrin studied by fluorescence measurements. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 51(1–2), 27–32 (2005)
Szejtli, J.: Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem. Rev. 98(5), 1743–1754 (1998)
Lombardo, D., Longo, A., Darcy, R., Mazzaglia, A.: Structural properties of nonionic cyclodextrin colloids in water. Langmuir 20(4), 1057–1064 (2004)
Del Valle, E.M.: Cyclodextrins and their uses: a review. Process Biochem. 39(9), 1033–1046 (2004)
Zoghbi, A., Wang, B.: Carvedilol solubility enhancement by inclusion complexation and solid dispersion: review. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 5(2), 1–8 (2015)
Yuvaraja, K., Das, S.K., Khanam, J.: Process optimization and characterization of carvedilol solid dispersion with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and tartaric acid. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32, 1–9 (2015)
Sharma, A., Jain, C.P.: Carvedilol-β-cyclodextrin systems: preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 12(1), 51–58 (2013)
Pamudji, J.S., Mauludin, R., Lestari, V.A.: Improvement of carvedilol dissolution rate through formation of inclusion complex with β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6(4), 228–233 (2014)
Loftsson, T., Vogensen, S.B., Desbos, C., Jansook, P.: Carvedilol: solubilization and cyclodextrin complexation: a technical note. AAPs Pharm. Sci. Tech. 9(2), 425–430 (2008)
Soleymanpour, A., Ghasemian, M.: Chemically modified carbon paste sensor for the potentiometric determination of carvedilol in pharmaceutical and biological media. Measurement 59, 14–20 (2015)
Cappello, B., De Rosa, G., Giannini, L., La Rotonda, M.I., Mensitieri, G., Miro, A., Russo, R.: Cyclodextrin-containing poly (ethyleneoxide) tablets for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: potential as buccal delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 319(1), 63–70 (2006)
Hirlekar, R., Kadam, V.: Preparation and characterization of inclusion complexes of carvedilol with methyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 63(3–4), 219–224 (2009)
Talvani, A., Bahia, M.T., de Sá-Barreto, L.C.L., Lima, E.M., da Cunha-Filho, M.S.S.: Carvedilol: decomposition kinetics and compatibility with pharmaceutical excipients. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 115(3), 2501–2506 (2014)
Wen, X., Tan, F., Jing, Z., Liu, Z.: Preparation and study the 1:2 inclusion complex of carvedilol with β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. 34(3), 517–523 (2004)
Pokharkar, V., Khanna, A., Venkatpurwar, V., Dhar, S., Mandpe, L.: Ternary complexation of carvedilol, β-cyclodextrin and citric acid for mouth-dissolving tablet formulation. Acta Pharm. 59(2), 121–132 (2009)
Shewale, B.D., Sapkal, N.P., Raut, N.A., Gaikwad, N.J., Fursule, R.A.: Effect of hydroxylpropyl-β-cyclodextrin on solubility of carvedilol. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 70(2), 255–257 (2008)
Bhutani, S., Hiremath, S.N., Swamy, P.V., Raju, S.A.: Preparation and evaluation of inclusion complexes of carvedilol. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 66(10), 830–834 (2007)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 7, 117–122 (1965)
Hamidi, H., Abderrahim, R., Meganem, F.: Spectroscopic studies of inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin and benzidine diammonium dipicrate. Spectrochim. Acta A. 75, 32–36 (2010)
Wen, X., Tan, F., Jing, Z., Liu, Z.: Preparation and study the 1:2 inclusion complex of carvedilol with β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. 34(3), 517–523 (2004)
Sambasevam, K.P., Mohamad, S., Sarih, N.M., Ismail, N.A.: Synthesis and characterization of the inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin and azomethine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14(2), 3671–3682 (2013)
Bocanegra-Diaz, A., Mohallem, N.D., Sinisterra, R.D.: Preparation of a ferrofluid using cyclodextrin and magnetite. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 14(6), 936–941 (2003)
Loftsson, T., Magnusdottir, A., Masson, M., Sigurjonsdottir, J.F.: Self-association and cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 91, 2307–2316 (2002)
Loftsson, T., Masson, M., Brewster, M.E.: Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 93(5), 1091–1099 (2004)
Guideline, ICH Harmonised Tripartite.: Stability testing of new drug substances and products. Q1A (R2). Curr. Step 4, 1–22 (2003)
Jouyban, A., Hasanzadeh, M., Shadjou, N.: Non-aqueous electromigration analysis of some degradation products of carvedilol. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 13(2), 471–486 (2014)
http://www.drugfuture.com/pharmacopoeia/usp35/data/v35300/usp35nf30s0_m2730.html
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia under the Project TRp-34012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savic-Gajic, I., Savic, I.M., Nikolic, V.D. et al. Study of the solubility, photostability and structure of inclusion complexes of carvedilol with β-cyclodextrin and (2-hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclodextrin. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 86, 7–17 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-016-0635-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-016-0635-y