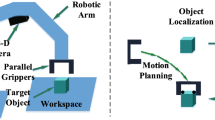
Abstract
Robotic grasping is still challenging due to limitations in perception and control, especially when the CAD models of objects are unknown. Although some grasp planning approaches using computer vision have been proposed, these methods can be seen as open-loop grasp planning methods and are often not robust enough. In this paper, a novel grasp planning method combining CNN-based quality prediction and closed-loop control (CNNB-CL) is proposed for a vacuum gripper. A large-scale dataset is generated for CNN training, which contains more than 2.3 million synthetic grasps and their grasp qualities evaluated by grasp simulations with 3D models. Unlike other neural networks which predict grasp success by assigning a binary value or grasp quality level by assigning an integer value, the proposed CNN predicts the grasp quality via a linear regression architecture. Additionally, the method adjusts the grasp strategies and detects the optimal grasp based on feedback from a force-torque sensor. Various simulations and physical experiments prove that the CNNB-CL method is robust for random noise disturbance in observation and compatible with different depth cameras and vacuum grippers. The proposed method finds the optimal grasp from 2,000 candidates within 300 ms and achieves a 92.18% average success rate for different vacuum grippers, which outperforms the state-of-the-art methods regarding success rate and robustness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data, graphics and video demos generated during the study are uploaded with the source code via the link below: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EKpnjCm_K5GOINCzXvsEWMETdXWucAJ9/view
Code Availability
The code and models in this paper are available via the link below. Please contact the corresponding author for any question about them. https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EKpnjCm_K5GOINCzXvsEWMETdXWucAJ9/view?usp=sharing
References
Pickit: https://www.pickit3d.com/ (2020)
Ackermann, E.: How google wants to solve robotic grasping by letting robots learn for themselves. IEEE Spectrum (2016)
Bohg, J., Johnson-Roberson, M., León, B., Felip, J., Gratal, X., Bergström, N., Kragic, D., Morales, A.: Mind the gap-robotic grasping under incomplete observation. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 686–693. IEEE (2011)
Borst, C., Fischer, M., Hirzinger, G.: Grasp planning: How to choose a suitable task wrench space. In: 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 319–325. IEEE (2004)
Brook, P., Ciocarlie, M., Hsiao, K.: Collaborative grasp planning with multiple object representations. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2851–2858. IEEE (2011)
Calli, B., Walsman, A., Singh, A., Srinivasa, S., Abbeel, P., Dollar, A.M.: Benchmarking in manipulation research: The ycb object and model set and benchmarking protocols. arXiv:1502.03143 (2015)
Chen, D., Dietrich, V., Liu, Z., Von Wichert, G.: A probabilistic framework for uncertainty-aware high-accuracy precision grasping of unknown objects. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 90(1), 19–43 (2018)
Chu, F.J., Vela, P.A.: Deep grasp: Detection and localization of grasps with deep neural networks. arXiv:1802.00520 (2018)
Dasari, S., Ebert, F., Tian, S., Nair, S., Bucher, B., Schmeckpeper, K., Singh, S., Levine, S., Finn, C.: Robonet: Large-scale multi-robot learning. arXiv:1910.11215 (2019)
Della Santina, C., Arapi, V., Averta, G., Damiani, F., Fiore, G., Settimi, A., Catalano, M.G., Bacciu, D., Bicchi, A., Bianchi, M.: Learning from humans how to grasp: a data-driven architecture for autonomous grasping with anthropomorphic soft hands. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 4(2), 1533–1540 (2019)
El-Khoury, S., Sahbani, A.: On computing robust n-finger force-closure grasps of 3d objects. In: 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2480–2486. IEEE (2009)
Ferrari, C., Canny, J.: Planning optimal grasps. In: 1992 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 2290–2295. IEEE (1992)
Fornas, D., Sales, J., Peñalver, A., Pérez, J., Fernández, J. J., Marín, R., Sanz, P.J.: Fitting primitive shapes in point clouds: a practical approach to improve autonomous underwater grasp specification of unknown objects. J. Exper. Theor. Artif. Intell. 28(1-2), 369–384 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778. IEEE (2016)
Herzog, A., Pastor, P., Kalakrishnan, M., Righetti, L., Bohg, J., Asfour, T., Schaal, S.: Learning of grasp selection based on shape-templates. Auton. Robot. 36(1), 51–65 (2014)
Jiang, Y., Moseson, S., Saxena, A.: Efficient grasping from rgbd images: Learning using a new rectangle representation. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3304–3311. IEEE (2011)
Jørgensen, T.B., Jensen, S.H.N., Aanæs, H., Hansen, N.W., Krüger, N.: An adaptive robotic system for doing pick and place operations with deformable objects. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 94(1), 81–100 (2019)
Kao, I., Lynch, K.M., Burdick, J.W.: Contact modeling and manipulation. In: Springer Handbook of Robotics, pp. 931–954. Springer (2016)
Kasper, A., Xue, Z., Dillmann, R.: The kit object models database: An object model database for object recognition, localization and manipulation in service robotics. Int. J. Robot. Res. (IJRR) 31(8), 927–934 (2012)
Kehoe, B., Matsukawa, A., Candido, S., Kuffner, J., Goldberg, K.: Cloud-based robot grasping with the google object recognition engine. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4263–4270. IEEE (2013)
Keselman, L., Iselin Woodfill, J., Grunnet-Jepsen, A., Bhowmik, A.: Intel realsense stereoscopic depth cameras. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 1267–1276. IEEE (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Kumra, S., Joshi, S., Sahin, F.: Antipodal robotic grasping using generative residual convolutional neural network arXiv:1909.04810 (2019)
Kumra, S., Kanan, C.: Robotic grasp detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 769–776. IEEE (2017)
Lenz, I., Lee, H., Saxena, A.: Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. Int. J. Robot. Res. (IJRR) 34(4-5), 705–724 (2015)
Levine, S., Kumar, A., Tucker, G., Fu, J.: Offline reinforcement learning: Tutorial, review, and perspectives on open problems. arXiv:2005.01643 (2020)
Levine, S., Pastor, P., Krizhevsky, A., Ibarz, J., Quillen, D.: Learning hand-eye coordination for robotic grasping with deep learning and large-scale data collection. Int. J. Robot. Res. (IJRR) 37(4-5), 421–436 (2018)
Liang, H., Ma, X., Li, S., Görner, M., Tang, S., Fang, B., Sun, F., Zhang, J.: Pointnetgpd: Detecting grasp configurations from point sets. In: 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3629–3635. IEEE (2019)
Mahler, J., Liang, J., Niyaz, S., Laskey, M., Doan, R., Liu, X., Ojea, J.A., Goldberg, K.: Dex-net 2.0: Deep learning to plan robust grasps with synthetic point clouds and analytic grasp metrics. arXiv:1703.09312 (2017)
Mahler, J., Matl, M., Liu, X., Li, A., Gealy, D., Goldberg, K.: Dex-net 3.0: Computing robust vacuum suction grasp targets in point clouds using a new analytic model and deep learning. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5620–5627. IEEE (2018)
Mahler, J., Matl, M., Satish, V., Danielczuk, M., DeRose, B., McKinley, S., Goldberg, K.: Learning ambidextrous robot grasping policies. Science Robotics 4(26) (2019)
Malvezzi, M., Gioioso, G., Salvietti, G., Prattichizzo, D.: Syngrasp: A matlab toolbox for underactuated and compliant hands. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 22(4), 52–68 (2015)
Miller, A.T., Allen, P.K.: Graspit! a versatile simulator for robotic grasping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 11(4), 110–122 (2004)
Miller, A.T., Knoop, S., Christensen, H.I., Allen, P.K.: Automatic grasp planning using shape primitives. In: 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1824–1829. IEEE (2003)
Morrison, D., Corke, P., Leitner, J.: Learning robust, real-time, reactive robotic grasping. The International Journal of Robotics Research (IJRR) 39(2-3), 183–201 (2020)
Oberlin, J., Tellex, S.: Autonomously acquiring instance-based object models from experience. In: Robotics Research, pp. 73–90. Springer (2018)
ten Pas, A., Gualtieri, M., Saenko, K., Platt, R.: Grasp pose detection in point clouds. Int. J. Robot. Res. (IJRR) 36(13-14), 1455–1473 (2017)
Patten, T., Park, K., Vincze, M.: Dgcm-net: dense geometrical correspondence matching network for incremental experience-based robotic grasping. arXiv:2001.05279 (2020)
Pinto, L., Gupta, A.: Supersizing self-supervision: Learning to grasp from 50k tries and 700 robot hours. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3406–3413. IEEE (2016)
Prattichizzo, D., Trinkle, J.C.: Grasping. In: Springer Handbook of Robotics, pp 955–988. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Qian, K., Jing, X., Duan, Y., Zhou, B., Fang, F., Xia, J., Ma, X.: Grasp pose detection with affordance-based task constraint learning in single-view point clouds. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 100, 145–163 (2020)
Rodriguez, A., Mason, M.T., Ferry, S.: From caging to grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. (IJRR) 31(7), 886–900 (2012)
Singh, A., Yang, L., Hartikainen, K., Finn, C., Levine, S.: End-to-end robotic reinforcement learning without reward engineering. arXiv:1904.07854 (2019)
Song, K.T., Wu, C.H., Jiang, S.Y.: Cad-based pose estimation design for random bin picking using a rgb-d camera. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 87(3), 455–470 (2017)
Swoboda, D.M.: A comprehensive characterization of the asus xtion pro depth sensor. I. In: European Conference on Educational Robotics, p. 3 (2014)
Ulbrich, S., Kappler, D., Asfour, T., Vahrenkamp, N., Bierbaum, A., Przybylski, M., Dillmann, R.: The opengrasp benchmarking suite: An environment for the comparative analysis of grasping and dexterous manipulation. In: 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 1761–1767. IEEE (2011)
Wasenmüller, O., Stricker, D.: Comparison of kinect v1 and v2 depth images in terms of accuracy and precision. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 34–45. Springer (2016)
Wohlkinger, W., Aldoma, A., Rusu, R.B., Vincze, M.: 3dnet: Large-scale object class recognition from cad models. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5384–5391. IEEE (2012)
Yamanobe, N., Nagata, K.: Grasp planning for everyday objects based on primitive shape representation for parallel jaw grippers. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp. 1565–1570. IEEE (2010)
Funding
This work is partially supported by the China Scholarship Council (Grant NO. CSC201806090290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
• Mr. Hui Zhang (main contributor and first author): concept, method and software development, design and implementation of experiments, data analysis and original draft writing, etc.
• Prof. Dr. Ing. Jef Peeters: follow up, review and iteration of method, experiments, data analysis and manuscript.
• Prof. Dr. Ir. Eric Demeester: follow up, review and iteration of method, experiments, data analysis and manuscript.
• Prof. Dr. Ing. Karel Kellens (project promotor): concept and method optimization, data analysis, review and editing of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Peeters, J., Demeester, E. et al. A CNN-Based Grasp Planning Method for Random Picking of Unknown Objects with a Vacuum Gripper. J Intell Robot Syst 103, 64 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-021-01518-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-021-01518-8