Abstract
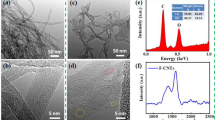
Carbon nanotubes have been the focus of intensive study due to their unique structure-dependent electronic and mechanical properties. They are thought to have potential applications as catalyst supports in heterogeneous catalysis, high engineering reinforcements, and molecular wires for the next generation of electronic devices. Good dispersion of carbon nanotubes in a matrix of composite materials, especially in inorganic materials, indeed is a significant problem due to the strong Van der Walls force between CNTs and the poor compatibility between the two phases. It is the intention of our research work to overcome the difficulties regarding incorporation of carbon nanotubes in structural and functional ceramics. The initial step toward this goal involves coating CNTs with materials that will eliminate the undesirable attractive interactions between the nanotubes and facilitate their incorporation into composites. In the present study, two new and simple methods named as heterogeneous coagulation and direct hydrolysis have been developed to attach various inorganic nano particles such as alumina, zirconia and titania to the surface of carbon nanotubes. These functionalization methods might be new strategies to altering the electronic properties of nanotubes. We expected that the attachment of metal oxides to nanotube surfaces will promote better ceramic or other inorganic matrix-CNT adhesion and may lead to the development of homogeneous composites, thereafter improving mechanical and/or electrical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Iijima, Nature, 354, 56 (1991).
R.Z. Ma, J. Wu, B.Q. Wei, J. Liang, and D.H. Wu, J. Mater. Sci., 33(21), 5243 (1998).
E. Flahaut, A. Peigney, Ch. Laurent, Ch. Marliere, F. Chastel, and A. Rousset, Acta Materialia, 48(14), 3803 (2000).
A. Peigney, Ch. Laurent, E. Flahaut, and A. Rousset, Ceram. Inter., 26(6), 667 (2000).
A. Peigney, Ch. Laurent, E. Flahaut, and A. Rousset, Key Eng. Mater., 132 – 136, 743 (1997).
J. Sun, L. Gao, and W. Li, Chem. Mater., 14, 5169 (2002).
J. Sun, L. Gao, and Q.H. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 86(10), 1677 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Gao, L. Attachment of inorganic nanoparticles onto carbon nanotubes. J Electroceram 17, 91–94 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-006-9944-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-006-9944-7