Abstract
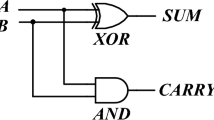
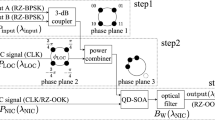
All-optical logic and arithmetic operations are expected to play an important role in high-speed communication systems. In this paper, we have presented a model to perform two basic arithmetic operations (addition/subtraction) on two binary digits based on a quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifier (QD-SOA)-assisted Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Using two QD-SOA-based switches, we have designed a half adder/subtractor circuit. The main advantage of this circuit is that simultaneous addition and subtraction operations are realized at the outputs. This circuit is designed theoretically and verified through numerical simulations. The theoretical study is carried out by taking into account the effect of amplified spontaneous emission. The dependence of the peak data power and that of the QD-SOA current density and length on the ER and Q factor of the switching outcome are explored and assessed by means of numerical simulations. The desirable device parameters has been examined in order to obtain the optimum best performance.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Politi, C., Klonidis, D., O’Mahony, M.J.: Dynamic behavior of wavelength converters based on FWM in SOAs. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 42, 108–125 (2006)
Igarashi, K., Kikuchi, K.: Optical signal processing by phase modulation and subsequent spectral filtering aiming at applications to ultrafast optical communication systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 14, 551–565 (2008)
Kim, S.H., Kim, J.H., Choi, J.W., Son, C.W., Byun, Y.T., Jhon, Y.M., Lee, S., Woo, D.H., Kim, S.H.: All-optical half-adder using cross-gain modulation in semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Express 14(22), 10693–10698 (2006)
Kim, J.H., Byun, Y.T., Jhon, Y.M., Lee, S., Woo, D.H., Kim, S.H.: All-optical half-adder using semiconductor optical amplifier based devices. Opt. Commun. 218(4–6), 345–349 (2003)
Chen, Z.: Simple novel all-optical half-adder. Opt. Eng. 49(4), 4320–4326 (2010)
Singh, K., Kaur, G.: All-optical half adder and half subtractor based on semiconductor optical amplifier. J. Commun. Softw. 1(1), 42–51 (2014)
Ghadrdan, M., Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A.: Concurrent implementation of all-optical half adder and AND & XOR logic gates based on nonlinear photonic crystal. Opt. Quantum Electron. 45(10), 1027–1036 (2013)
Bakhtiar, L.A., Yaghoubi, E., Adami, A., Hamidi, S.M., Hosseinzadeh, M.: The design of half subtractor logic function based on nonlinear directional coupler. J. Adv. Comput. Res. 2(2), 13–20 (2011)
Thongmee, S., Yupapin, P.P.: All-optical half adder/subtractor using dark-bright soliton conversion control. Procedia Eng. 8, 217–222 (2011)
Lei, L., Dong, J., Zhang, Y., He, H., Yu, Y., Zhang, X.: Reconfigurable photonic full adder and full subtractor based on three-input XOR gate and logic minterms. Electron. Lett. 48(7), 399–400 (2012)
Kumar, A., Kumar, S., Raghuwanshi, S.K.: Implementation of full adder and full subtractor based on electro-optic effect in Mach-Zehnder interferometers. Opt. Commun. 324, 93–107 (2014)
Luangxaysana, K., Phongsanam, P., Mitatha, S., Yoshida, M., Komine, N., Yupapin, P.P.: All-optical logic and arithmetic operation using soliton control for tree architecture use. Inf. Technol. J. 11, 1227–1234 (2012)
Gayen, D.K., Bhattachryya, A., Chattopadhyay, T., Roy, J.N.: Ultrafast all-optical half adder using quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. J. Lightwave Technol. 30(21), 3387–3393 (2012)
Gayen, D.K., Chattopadhyay, T.: Designing of optimized all-optical half adder circuit using single quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier assisted Mach-Zehnder interferometer. J. Lightwave Technol. 31(12), 2029–2035 (2013)
Gayen, D.K., Chattopadhyay, T., Bhattacharyya, A., Basak, S., Dey, D.: All-optical half-adder/half-subtractor using terahertz optical asymmetric demultiplexer. Appl. Opt. 53(36), 8401–8409 (2014)
Kotb, A., Zoiros, K.E.: 1 Tb/s high quality factor NAND gate quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers in Mach-Zehnder interferometers. J. Comput. Electron. 13, 555–561 (2014)
Wegert, M., Schwochert, D., Scholl, E., Ludge, K.: Integrated quantum-dot laser devices: modulation stability with electro-optic modulator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 46, 1337–1344 (2014)
Kotb, A., Zoiros, K.E.: Simulation of all-optical logic XNOR gate based on quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers with amplified spontaneous emission. Opt. Quantum Electron. 45, 1213–1221 (2013)
Ezra, Y.B., Lembrikov, B.I.: Semiconductor optical amplifier based on a quantum dot-in-a-well (QDWELL) structure under optical pumping. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 50(5), 340–347 (2014)
Taleb, H., Abedi, K.: Optical gain, phase, and refractive index dynamics in photonic crystal quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 50(8), 605–612 (2014)
Trapala, K.S., Dorren, H.J.S.: Dynamic and static gain characteristics of quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers operating at 1.55 \(\mu \) m. Opt. Commun. 298–299, 106–113 (2013)
Hakimiyan, F., Derhami, V.: Design of quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifier by intelligence methods. Procedia Comput. Sci. 3, 449–452 (2011)
Ma, S., Sun, H., Chen, Z., Dutta, N.K.: High speed all-optical PRBS generation based on quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Express 17(21), 18469–18477 (2009)
Dimitriadou, E., Zoiros, K.E.: All-optical XOR gate using single quantum-dot SOA and optical filter. J. Lightwave Technol. 31(23), 3813–3821 (2013)
Taleb, H., Abedi, K.: Design of a low-power all-optical NOR gate using photonic crystal quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Lett. 39(21), 6237–6240 (2014)
Li, W., Hu, H., Dutta, N.K.: High speed all-optical encryption and decryption using quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. J. Mod. Opt. 60(20), 1741–1749 (2013)
Meuer, C., Kim, J., Laemmlin, M., Liebich, S., Capua, A., Eisenstein, G., Kovsh, A.R., Mikhrin, S.S., Krestnikov, I.L., Bimberg, D.: Static gain saturation in quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Express 16(11), 8269–8279 (2008)
Kotb, A., Ma, S., Chen, Z., Dutta, N.K., Said, G.: All optical logic NAND gate based on two-photon absorption in semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Commun. 283, 4707–4712 (2010)
Dimitriadou, E., Zoiros, K.E.: On the feasibility of 320 Gb/s all-optical and gate using quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach-Zehnder Interferometer. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 50, 113–140 (2013)
Ma, S., Chen, Z., Sun, H., Dutta, N.K.: High speed all optical logic gates based on InAs/GaAs quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. In: Osinski, M. (ed.) Physics and Simulation of optoelectronic devices XVII, vol. 7211, p. 721190-1-9. Proc. of SPIE. doi:10.1117/12.802589
Rostami, A., Nejad, H.B.A., Qartavol, R.M., Saghai, H.R.: Tb/s optical logic gates based on quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 46, 354–360 (2010)
Mork, J., Nielsen, M.L., Berg, T.W.: The dynamics of semiconductor optical amplifiers: modeling and applications. Opt. Photonics News 14(7), 42–48 (2003)
Ben-Ezra, Y., Lembrikov, B.I., Haridim, M.: Specific features of XGM in QD-SOA. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 43(8), 730–737 (2007)
Borri, A., Langbein, W., Heinrichsdorff, F., Mao, M.-H.: Spectral hole-burning and carrier-heating dynamics in InGaAs quantum-dot amplifiers. IEEE Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 6(3), 544–551 (2000)
Schneider, S., Borri, P., Langbein, W., Woggon, U., Sellin, R.L., Ouyang, D., Bimberg, D.: Line-width enhancement factor in InGaAs quantum dot amplifiers. IEEE Quantum Electron. 40(10), 1423–1429 (2004)
Lin, W., Ma, S., Hu, H., Dutta, N.K.: All optical latches using quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier. Opt. Commun. 285, 5138–5143 (2012)
Girardin, F., Guekos, G., Houbavlis, A.: Gain recovery of bulk semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE Photon. Techol. Lett. 10(6), 784–786 (1998)
Kim, J., Meuer, C., Bimberg, D., Eisenstein, G.: Effect of inhomogeneous broadening on gain and phase recovery of quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 46(11), 1670–1680 (2010)
Akiyama, T., Kuwatsuka, H., Simoyama, T., Nakata, Y., Mukai, K., Sugawara, M., Wada, O., Ishikawa, H.: Application of spectral-hole burning in the inhomogeneously broadened gain of self-assembled quantum dots to a multiwavelength-channel nonlinear optical device. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 12, 1301–1303 (2000)
Sugawara, M., Akiyama, T., Hatori, N., Nakata, Y., Otsubo, K., Ebe, H.: Quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier, materials and devices for optics and wireless communications. Proc. SPIE 4905, 259–275 (2002)
Dimitriadou, E., Zoiros, K.E.: On the feasibility of ultrafast all-optical NAND gate using single quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Laser Technol. 44(6), 1971–1981 (2012)
Dimitriadou, E., Zoiros, K.E.: Proposal for all-optical NOR gate using single quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Commun. 285, 1710–1716 (2012)
Bogoni, A., Poti, L., Ghelfi, P., Scaffardi, M., Porzi, C., Ponzini, F., Meloni, G., Berrettini, G., Malacarne, A., Prati, G.: OTDM-based optical communications networks at 160 Gbit/s and beyond. Opt. Fiber Technol. 13(1), 1–12 (2007)
Weber, H.-G., Ludwig, R., Ferber, S., Langhorst, C.S., Kroh, M., Marembert, V., Boerner, C., Schubert, C.: Ultrahigh-speed OTDM-transmission technology. J. Lightwave Technol. 24(12), 4616–4627 (2006)
Zoiros, K.E., Houbavlis, T., Moyssidis, M.: Complete theoretical analysis of actively mode-locked fiber ring laser with external optical modulation of a semiconductor optical amplifier. Opt. Commun. 254(4–6), 310–329 (2005)
Yao, X.S., Yan, L.-S., Zhang, B., Willner, A.E., Jiang, J.: All-optical scheme for automatic polarization division demultiplexing. Opt. Express. 15(12), 7407–7414 (2007)
Goodman, J.W.: Fan-in and Fan-out with optical interconnections. OpticaActa 32(12), 1489–1496 (1985)
Ueno, Y., Nakamura, S., Tajina, K.: Nonlinear phase shifts induced by semiconductor optical amplifiers with control pulses at repetition frequencies in the 40–160-GHz range for use in ultrahigh-speed all-optical signal processing. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19(11), 2573–2589 (2002)
Gayen, D.K., Chattopadhyay, T., Zoiros, K.E.: All-optical D flip-flop using single quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier assisted Mach-Zehnder interferometer. J. Comput. Electron. 14, 129–138 (2015)
Qasaimeh, O.: Characteristics of cross-gain(XG) wavelength conversion in quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16(2), 542–544 (2004)
Han, H., Zhang, M., Ye, P., Zhang, F.: Parameter design and performance analysis of a ultrafast all-optical XOR gate based on quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers in nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Commun. 281, 5140–5145 (2008)
Xiao, J.-L., Huang, Y.-Z.: Numerical analysis of gain saturation, noise figure and carrier distribution for quantum-dot semiconductor-optical amplifiers. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 44(5), 448–455 (2008)
Hinton, K., Raskutti, G., Farrell, P.M., Tucker, R.S.: Switching energy and device size limits on digital photonic signal processing technologies. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Quant. Electron. 14, 938–945 (2008)
Dimitriadou, E., Zoiros, K.E.: On the design of ultrafast all-optical NOT gate using quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Laser Technol. 44(3), 600–607 (2012)
Li, G., Qian, F.: Code conversion from signed-digit to complement representation based on look-ahead optical logic operations. Opt. Eng. 40(11), 2446–2451 (2001)
Zoiros, K.E., Avramidis, P., Koukourlis, C.S.: Performance investigation of semiconductor optical amplifier-based ultrafast nonlinear interferometer in nontrivial switching mode. Opt. Eng. 47(11), Art. No. 115006 (2008)
Sun, H., Wang, Q., Dong, H., Dutta, N.K.: XOR performance of a quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifier based Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Express 13(6), 1892–1899 (2005)
Ma, S., Chen, Z., Sun, H., Dutta, N.K.: High speed all optical logic gates based on quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Opt. Express 18(7), 6417–6422 (2010)
Nady, M., Hussein, K.F.A., Ammar, A.A.: Ultrafast all-optical full adder using quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 54, 69–88 (2013)
Jung, Y.J., Wan Son, C., Min Jhon, Y., Lee, S., Park, N.: One-level simplification method for all—optical combinational logic circuits. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 20(10), 800–802 (2008)
Dong, J., Zhang, X., Huang, D.: A proposal for two-input arbitrary Boolean logic gates using single semiconductor optical amplifier by picosecond pulse injection. Opt. Express 17(10), 7725–7730 (2009)
Ezra, Y.B., Lembrikov, B.I., Haridim, M.: Improvement of gain recovery in QD-VCSOA at 1-Tb/s cross gain modulation using an additional light beam. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 45(1), 34–41 (2009)
Wu, X., Qiu, K., Ling, Y.: Novel optical power equalizer and optical hard limiter based on quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifiers. Optoelectronic materials and devices III, Luo,Y., Buus, J., Koyama, F., Lo, Y.-H. (eds) Proc. Of SPIE, vol. 7135, 71353N-1-8
Kotb, A., Ma, S., Chen, Z., Dutta, N.K., Said, G.: Effect of amplified spontaneous emission on semiconductor optical amplifier based all-optical logic. Opt. Commun. 284, 5798 (2011)
Agrawal, G.P.: Fiber-Optic Communication System, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York (2002)
Acknowledgments
One of the author (D.K.Gayen) is grateful to Technical Education Quality Improvement Program (TEQIP) phase II by National Project Implementation Unit (A Unit of Ministry of Human Resource Development, Govt. of India for Implementation of World Bank-Assisted Project in Technical Education) for providing the grant for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gayen, D.K., Chattopadhyay, T. Simultaneous all-optical basic arithmetic operations using QD-SOA-assisted Mach–Zehnder interferometer. J Comput Electron 15, 982–992 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0854-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0854-x