Abstract
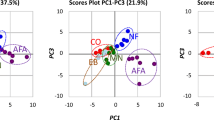
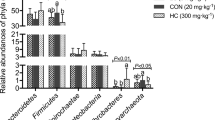
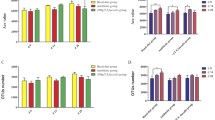
Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, a freshwater cyanobacterium harvested from Upper Klamath Lake, Oregon, USA, is employed as a functional food material. Aphanizomenon flos-aquae can be fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Here, to determine the dietary effects of A. flos-aquae (AFA) and fermented A. flos-aquae (F-AFA) on the mouse gut microbiome, high-sucrose diet containing no dietary fibre (NF), 5% AFA or 5% F-AFA was administered to ICR mice for 14 days. Compared with those in mice fed the NF, lower body weight gains and epididymal fat pad tissue weights were observed in mice fed the diet containing F-AFA. After feeding, the caecal microbiome was analysed by 16S rRNA (V4) gene amplicon sequencing using the Illumina MiSeq system. Sequences were clustered into operational taxonomic units, with a 97% identity cutoff, using the QIIME2 workflow script and SILVA database. The caecal microbiome alpha diversity was high in mice fed the F-AFA diet. The abundances of Muribaculum- and Alistipes inops-like bacteria belonging to the phylum Bacteroidetes and Ruminococcaceae UCG-014-like bacteria belonging to phylum Firmicutes were higher in the F-AFA group than in the AFA group. Isolation of typical F-AFA-susceptible gut indigenous bacteria and functional studies of the isolates in the presence of F-AFA are warranted to validate the current findings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Qadiri HM, Al-Holy AA, Cavinnato AG, Rasco BA (2008) Detection of sublethal thermal injury in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium and Listeria monocytogenes using fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. J Food Sci 73:M54–M61
Barouei J, Bendiks Z, Martinic A, Mishchuk D, Heeney D, Hsieh Y, Kieffer D, Zaragoza J, Martin R, Slupsky C, Marco M (2017) Microbiota, metabolome, and immune alterations in obese mice fed a high-fat diet containing type 2 resistant starch. Mol Nutr Food Res 61:20170084
Benedetti S, Benvenuti F, Pagliarani S, Francogli S, Scoglio S, Canestrati F (2004) Antioxidant properties of a novel phycocyanin extract from the blue-green alga Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Life Sci 75:2353–2362
Bo T, Wen J, Zhao Y, Tian S, Zhang X, Wang D (2020) Bifidobacterium pseudolongum reduces triglycerides by modulating gut microbiota in mice fed high-fat food. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 198:105602
Bunyavanich S, Shen N, Grishin A, Wood R, Burks W, Dawson P (2016) Early-life gut microbiome composition and milk allergy resolution. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138:1122–1130
Campana R, Martinelli V, Scoglio S, Colombo E, Benedetti S, Baffone W (2017) Influence of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and two of its extracts on growth ability and antimicrobial properties of Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1. LWT-Food Sci Technol 81:291–298
Carmichael WW, Drapeau C, Anderson DM (2000) Harvesting of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Ralfs ex Born. & Flah. var. flos-aquae (Cyanobacteria) from Klamath Lake for human dietary use. J Appl Phycol 12:585–595
Chang S, Cui X, Guo M, Tian Y, Xu W, Huang K, Zhang Y (2017) Insoluble dietary fiber from pear pomace can prevent high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats mainly by improving the structure of the gut microbiota. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:856–867
Cirés S, Ballot A (2016) A review of the phylogeny, ecology and toxin production of bloom-forming Aphanizomenon spp. and related species within the Nostocales (cyanobacteria). Harmful Algae 54:21–23
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Vama Y, Fishbach MA, Biddinger SB, Dutton RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505:559–563
Frazier K, Chang EB (2020) Intersection of the gut microbiome and circadian rhythms in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 31:25–36
Gao R, Zhu C, Li H, Yin M, Pan C, Huang L, Kong C, Wang X, Zhang Y, Qu S, Qin SH (2018) Dysbiosis signatures of gut microbiota along the sequence from healthy, young patients to those with overweight and obesity. Obesity 26:351–361
Genda T, Kondo T, Sugiura S, Hino S, Shimamoto S, Nakamura T, Ukita S, Morita T (2018) Bacterial fermentation of water-soluble cellulose acetate raises large-bowel acetate and propionate and decreases plasma cholesterol concentrations in rats. J Agric Food Chem 66:11909–11916
Hirota K, Inagaki R, Hamada R, Ishida K, Miyatake Y (2014) Evaluation of a rapid oral bacteria quantification system using dielectrophoresis and the impedance measurement. Biocontrol Sci 19:45–49
Hussain M, Bonilla-Rosso G, Chung CK, Bariswyl L, Rodriguez MP, Kim BS, Emgel P, Noti M (2019) High dietary fat intake induces a microbiota signature that promotes food allergy. J Clin Immunol 144:157–170
Kim B, Shin J, Guevarra RB, Lee JH, Kim DW, Seol K, Lee JH, Kim HB, Isaacson R (2017) Deciphering diversity indices for a better understanding of microbial communities. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:2089–2093
Koliada A, Syzenko G, Moseiko V, Puchkov L, Budovska K, Perederiy V, Gavalko Y, Dorofeyev A, Romanenko M, Tkach S, Sineok L, Lushchak O, Vaiserman A (2017) Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol 17:120
Kuda T, Yazaki T, Ono M, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2013) In vitro cholesterol-lowering properties of Lactobacillus plantarum AN6 isolated from aji-narezushi. Lett Appl Microbiol 57:187–192
Kuda T, Masuko Y, Kawahara M, Kondo S, Nemoto M, Nakata T, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2016) Bile acid-lowering properties of Lactobacillus plantarum Sanriku–SU3 isolated from Japanese surfperch fish. Food Biosci 14:41–46
Kuda T, Yokota Y, Shikano A, Takei M, Takhashi H, Kimura B (2017) Dietary and lifestyle disease indices and caecal microbiota in high fat diet, dietary fibre free diet, or DSS induced IBD models in ICR mice. J Funct Foods 35:605–614
Kushak PI, Drapeau C, Van Cott EM, Winter HH (2000) Favorable effects of blue-green algae Aphanizomenon flos-aquae on rat plasma lipids. J Am Nutraceut Assoc 2:59–65
Lagkouvardos I, Lesker TR, Hitch TC, Gálvez EJC, Smit N, Neuhaus K, Wang J, Baines JF, Abt B, Stecher B, Overmann J, Strowig T, Clavel T (2019) Sequence and cultivation study of Muribaculaceae reveals novel species, host preference, and functional potential of this yet undescribed family. Microbiome 7:28
Li L, Wang Y, Zhu L, Liu Z, Ye C, Qin S (2020) Inulin with different degrees of polymerization protects against diet-induced endotoxemia and inflammation in association with gut microbiota regulation in mice. Sci Rep 10:978
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235
Lu Y, Fan C, Li P, Lu Y, Chang X, Qi K (2016) Short chain fatty acids prevent high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice by regulating G protein coupled receptors and gut microbiota. Sci Rep 6:37589
Mangin I, Dossou-Yovo F, Lévêque C, Dessoy M, Sawoo O, Suau A, Pochart P (2018) Oral administration of viable Bifidobacterium pseudolongum strain Patronus modified colonic microbiota and increased mucus layer thickness in rat. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94: fiy177
Mitsuoka T (2014) Establishment of intestinal bacteriology. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 33:99–116
Nagpal R, Wang S, Ahmadi S, Hayes J, Gagliano J, Subashchandrabose S, Kitzman DW, Becton T, Read R, Yadov H (2018) Human-origin probiotic cocktail increases short-chain fatty acid production via modulation of mice and human gut microbiome. Sci Rep 8:12649
Ni Y, Yang X, Zheng L, Wang Z, Wu L, Jiang J, Yang T, Ma L, Fu Z (2019) Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium improves physiological function and cognitive ability in aged mice by the regulation of gut microbiota. Mol Nutr Food Res 63:1900603
Patterson E, Ryan PM, Wiley N, Carafa I, Sherwin E, Moloney G, Franciosi E, Mandal R, Wishart DS, Tuohy K, Ross RP, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Stanton C (2019) Gamma-aminobutyric acid producing lactobacilli positively affect metabolism and depressive like behaviour in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Sci Rep 9:16323
Payling L, Fraser K, Loveday SM, Sims I, Roy N, McNabb W (2020) The effects of carbohydrate structure on the composition and functionality of the human gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci Technol 97:233–248
Pereira P, Onodera H, Andorinolo D, Franca S, Araújo F, Lagos N, Oshima Y (2000) Paralytic shellfish toxins in the freshwater cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, isolated from Montargil reservoir. Portugal Toxicon 38:1689–1702
Pugh N, Pasco DS (2001) Characterization of human monocyte activation by a water soluble preparation of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Phytomedicine 8:445–453
Sharma NK, Tiwari SP, Tripathi K, Rai AK (2011) Sustainability and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae): facts and challenges. J Appl Phycol 23:105–1081
Shikano A, Kuda T, Shinayama J, Toyama A, Ishida Y, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2019) Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Uruma-SU4 fermented green loofah on plasma lipid levels and gut microbiome of high-fat diet fed mice. Food Res Int 121:817–824
Shkoporov AN, Chaplin AV, Khokholova EK, Shcheribakova VA, Motuzova OV, Bozhenko VK, Kafarskaia LI, Efimov BA (2015) Alistipes inops sp. nov. and Coprobacter secundus sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4580–4588
Sinclair L, Osman OA, Bertilsson S, Eiler A (2015) Microbial community composition and diversity via 16S rRNA gene amplicons: evaluating the Illumina platform. PLoS One 10:e0116955
Takei M, Kuda T, Fukunaga M, Toyama A, Goto M, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2019) Effects of edible algae on caecal microbiomes of ICR mice fed a high-sucrose and low–dietary fibre diet. J Appl Phycol 31:3969–3978
Takei NM, Kuda T, Taniguchi M, Nakamura S, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2020) Detection and isolation of low molecular weight alginate- and laminaran susceptible gut indigenous bacteria from ICR mice. Carbohydr Polyomers 238:116205
Taniguchi M, Kuda T, Shibayama J, Sasaki T, Michihata T, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2019) In vitro antioxidant, anti-glycation and immunomodulation activities of fermented blue-green algae Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Mol Biol Rep 46:1775–1786
Wang CS, Li WB, Wang HY, Ma YM, Zhao XH, Yang H, Qian JM, Li JN (2018) VSL#3 can prevent ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 24:4254–4262
Williams BA, Mikkeisen D, Flanagan BM, Gidley MJ (2019) “Dietary fibre”: moving beyond the “soluble/insoluble” classification for monogastric nutrition, with an emphasis on humans and pigs. J Animal Sci Biotechnol 10:45
Xia Y, Kuda T, Toyama A, Goto M, Fukunaga M, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2019) Detection and isolation of bacteria affected by dietary cumin, coriander, turmeric, and red chili pepper in the caecum of ICR mice. J Funct Foods 61:103467
Xia Y, Fukunaga M, Kuda T, Goto M, Chiaraluce G, Hoshiba H, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2020) Detection and isolation of protein susceptible indigenous bacteria affected by dietary milk-casein, albumen and soy-protein in the caecum of ICR mice. J Biol Macromol 144:813–820
Yokota Y, Haraguchi Y, Shikano A, Kuda T, Takahashi H, Kimura B (2018) Induction of gut Lactobacillus reuteri in normal ICR mice by oral administration of L. plantarum AN1. J Food Biochem 42:e12589
Zhang L, Liu SY, Zhang J, Zhang JK, Hu C, Liu CX (2016) Respiratory toxicity of cyanobacterial aphantoxins from Aphanizomenon flos-aquae DC-1 in the zebrafish gill. Aquat Toxicol 176:106–115
Zhang C, Wu W, Li X, Xin X, Liu D (2019) Daily supplementation with fresh Angelica keiskei juice alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice by modulating gut microbiota composition. Mol Nutr Food Res 63:19000248
Zhao L, Lou H, Peng Y, Chen S, Zhang Y, Li X (2019) Comprehensive relationships between gut microbiome and faecal metabolome in individuals with type 2 diabetes and its complications. Endocrine 66:526–537
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for the English language editing.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Towa Foundation for Food Science & Research, Tokyo, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statements of animal rights
Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the Fundamental Guidelines for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiments and Related Activities in Academic Research Institutions, under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. The study protocol was approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of the Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology (Approval No. H31-5).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniguchi, M., Kuda, T., Takei, M. et al. Effects of fermented Aphanizomenon flos-aquae on the caecal microbiome of mice fed a high-sucrose and low-dietary fibre diet. J Appl Phycol 33, 397–407 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02306-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02306-x