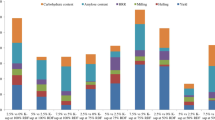
Abstract
The present study aimed to assess not only the efficacy of sap from two seaweeds Kappaphycus alvarezii (K-sap) and Gracilaria edulis (G-sap) on productivity and quality of Zea mays under rain-fed condition, but also to quantify whether sap application is beneficial in terms of lowering the carbon and phosphate footprint of mineral fertilizers per unit of produce. Field experiment was carried out to test 18 treatments, viz., 5 concentrations (2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10 and 15 %) each of K-sap and G-sap applied along with recommended rate of fertilizers (RRF); 3 concentrations (7.5, 10 and 15 %) of each of the two types of sap applied along with 50 % RRF; alongside 2 control treatments T1 (water spray along with 100 % RRF) and T18 (water spray along with 50 % RRF). The optimal treatments that enhanced the grain productivity of maize were 5 % G-sap or 7.5 % K-sap applied in conjunction with 100 % RRF and the grain yield enhancements ranged from 21.4 to 29.8 % as compared to T1. Significant increase in P (35.5 %) and K (14.4 %) content in grains was observed through G-sap application, suggesting bio-stimulation in absorption of these elements. Notably, stover yield production at reduced RRF in certain combinations with sap was at par with T1 suggesting a possible saving on fertilizer requirement for fodder production under rain-fed conditions. Compared to T1, there was marked reduction of 17.5 and 23.1 % in global warming potential per unit of produce when 7.5 % K-sap and 5 % G-sap were used respectively in conjunction with 100 % RRF.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvim PDT (1960) Net assimilation rate and growth behavior of beans as affected by gibberellic acid urea and sugar sprays. Plant Physiol 35:285--288
Anantharaj M, Venkatesalu V (2002) Studies on the effect of seaweed extracts on Dolichos biflorus. Seaweed Res Util 24:129–137
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Beckett RP, Van Staden J (1990) The effect of seaweed concentrate on the yield of nutrient stressed wheat. Bot Mar 33:147–152
Blunden G, Cripps AL, Gordon SM, Mason TG, Turner CH (1986) The characterization and quantitative estimation of betaines in commercial seaweed extracts. Bot Mar 24:155–160
Blunden G, Jenkins T, Liu YW (1996) Enhanced leaf chlorophyll levels in plants treated with seaweed extract. J Appl Phycol 8:535–543
Blunden G, Wildgoose PB, Necholson FE (1979) The effect of aqueous seaweed extract on sugar beet. Bot Mar 22:539–541
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Briceño-Domínguez D, Hernández-Carmona G, Moyo M, Stirk W, van Staden J (2014) Plant growth promoting of seaweeds liquid extract produced from Macrocystis pyrifera under different pH and temperature conditions. J Appl Phycol 26:2203–2210
Chaudhary DP, Jat SL, Kumar R, Kumar A, Kumar B (2014) In: Chaudhary DP, Kumar S, Singh S (eds) Maize: nutrition dynamics and novel uses. Springer, India, pp 153–156
Crouch IJ, Beckett RP, Van Staden J (1990) Effect of seaweed concentrate on the growth and mineral nutrition of nutrient-stressed lettuce. J Appl Phycol 2:269–272
Crouch IJ, Van Staden J (1993) Evidence for the presence of plant growth regulators in commercial seaweed products. Plant Growth Regul 13:21–29
Dass S, Jat ML, Singh KP, Rai HK (2008) Agro-economic analysis of maize-based cropping systems in India. Ind J Fertil 4:53–62
Dobermann AR (2005) “Nitrogen use efficiency—state of the art”. Agronomy and Horticulture, Faculty publications. Paper 316. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/agronomyfacpub/316
Dwivedi SK, Pal A, Meshram MR (2014) Effects of seaweed saps on soil health and productivity of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Curr Adv Agric Sci 6:133–137
Eswaran K, Ghosh PK, Siddhanta AK, Patolia JS, Periyasamy C, Mehta AS, Mody KH, Ramavat BK, Prasad K, Rajyaguru MR, Kulandaivel S, Reddy CRK, Pandya JB, Tewari A (2005) Integrated method for production of carrageenan and liquid fertilizer from fresh seaweeds, U.S. Patent No. 6,893,479
FAO (2014) The state of food and agriculture—innovation in family farming. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Ganesan M, Sahu N, Eswaran K (2011) Raft culture of Gracilaria edulis in open sea along the south-eastern coast of India. Aquaculture 321:145–151
Greenboim-Wainberg Y, Maymon I, Borochov R, Alvarez J, Olszewski N, Ori N, Esed Y, Weiss D (2005) Cross talk between gibberellin and cytokinin: the Arabidopsis GA response inhibitor SPINDLY plays a positive role in cytokinin signalling. Plant Cell 17:92–102
Guinn EJ, Pegram LM, Capp MW, Pollock MN, Record MT (2011) Quantifying why urea is a protein denaturant, whereas glycine betaine is a protein stabilizer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:16932–16937
Hanway JJ, Heidel H (1952) Soil analysis method as used in Iowa state college soil testing Laboratory. Iowa Agriculture 57:1–31
Hernández-Herrera RM, Santacruz-Ruvalcaba F, Ruiz-López MA, Norrie J, Hernández-Carmona G (2014) Effect of liquid seaweed extracts on growth of tomato seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J Appl Phycol 26:619–628
Hillier J, Hawes C, Squire G, Hilton A, Wale S, Smith P (2009) The carbon foot prints of food crop production. Int J Agric Sust 7:107–118
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall, New Delhi
Khan SA, Mulvaney RL, Ellsworth TR, Boast CW (2007) The myth of nitrogen fertilization for soil carbon sequestration. J Environ Qual 36:1821–1832
Khan W, Rayirath UP, Subramanian S, Jithesh MN, Rayorath P, Hodges DM, Critchley AT, Cragie JS, Norrie J, Prithiviraj B (2009) Seaweed extracts as biostimulants of plant growth and development. J Plant Growth Regul 28:386–399
Layek J, Ramkrushna GI, Das A, Ghosh A, Krishnappa R, Panwar AS, Azad Thakur NS, Ngachan SV, Zodape ST, Buragohain J, Mawlong B (2014). Seaweed sap as organic bio-stimulant for rice and maize production. Research Bulletin no.82. ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Umiam, Meghalaya, India
Layek J, Das A, Ramkrushna GI, Trivedi K, Yesuraj D, Chandramohan M, Kubavat D, Agarwal PK, Ghosh A (2015) Seaweed sap potential towards sustainable improvement of maize productivity: a dominant staple food crop of the North-east India. Int J Environ Stud 72:305–315
Mondal D, Ghosh A, Prasad K, Singh S, Bhatt N, Zodape ST, Chaudhary JP, Chaudhari J, Chatterjee PB, Seth A, Ghosh PK (2015) Elimination of gibberellin from Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed sap foliar spray enhances corn stover production without compromising the grain yield advantage. Plant Growth Regul 75:657–666
Mondal D, Sharma M, Maiti P, Prasad K, Meena R, Siddhanta AK, Bhatt P, Ijardar S, Mohandas VP, Ghosh A, Eswaran K, Shah BG, Ghosh PK (2013) Fuel intermediates, agricultural nutrients and pure water from Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed. RSC Adv 3:17989–17997
Fleishon S, Shani E, Ori N, Weiss D (2011) Negative reciprocal interactions between gibberellin and cytokinin in tomato. New Phytol 190:609–617
Murphy RP (1958) Extraction of plant samples and the determination of total soluble carbohydrates. J Sci Food Agri 9:714–717
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2: Chemical and microbial properties—agronomy. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 570–571
Patidar R, Ghosh A, Paul P (2013) WD-XRF method for rapid analysis of macro and micronutrient uptake in maize grain upon foliar application of seaweed sap formulations. J Indian Chem Soc 90:2023–2028
Patra AK, Tripathy SK, Samui RC (1995) Physiological basis of yield variation in rain-fed groundnut. Indian J Plant Physiol 38:131–134
Pise NM, Sabale AB (2010) Effect of seaweed concentrates on the growth and biochemical constituents of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. J Phytol 2:50–56
Pramanick B, Brahmachari K, Ghosh A (2013) Effect of seaweed sap on growth and yield improvement of green gram. Afr J Ag Res 8:1180–1186
Prasad K, Das AK, Oza MD, Brahmbhatt H, Siddhanta AK, Meena R, Eswaran K, Rajyaguru MR, Ghosh PK (2010) Detection and quantification of some plant growth regulators in a seaweed-based foliar spray employing a mass spectrometric technique sans chromatographic separation. J Agr Food Chem 58:4594–4601
Radford PJ (1967) Growth analysis formula—their use and abuse. Crop Sci 7:171–175
Ranatunga MAB, Meenakshisundaram P, Arumugachamy S, Maheswaran M (2009) Genetic diversity analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) inbreds determined with morphometric traits and simple sequence repeat markers. Maydica 54:113–123
Rathore SS, Chaudhary DR, Boricha GN, Ghosh A, Bhatt BP, Zodape ST, Patolia JS (2009) Effect of seaweed extract on the growth, yield and nutrient uptake of soybean (Glycine max) under rain-fed conditions. S Afr J Bot 75:351–355
Shah MT, Zodape ST, Chaudhary DR, Eswaran K, Chikara J (2013) Seaweed sap as an alternative liquid fertilizer for yield and quality improvement of wheat. J Plant Nutr 36:192–200
Sharma HSS, Fleming C, Selby C, Rao JR, Martin T (2014) Plant biostimulants: a review on the processing of macroalgae and use of extracts for crop management to reduce abiotic and biotic stresses. J Appl Phycol 26:465–490
Shibles RM, Weber CR (1965) Interception of solar radiation and dry matter production by various soybean planting pattern. Crop Sci 6:49–52
Sivasankari S, Venkatesalu V, Anantharaj M, Chandrasekaran M (2006) Effect of seaweed extracts on the growth and biochemical constituents of Vigna sinensis. Bioresour Technol 97:1745–1751
Smith D, Paulsen GM, Raguse CA (1964) Comparative accuracy and efficiency in determination of carbohydrate from grasses and legume tissue. Plant Physiol 39:960–962
Stevens GA, Westwood MN (1984) Fruit set and cytokinines like activity in the xylem sap of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium) as affected by root stock. Physiol Plantarum 61:464–468
Subbiah BV, Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for the determination of available N in soils. Current Sci 25:259–260
Thirumaran G, Arumugam M, Arumugam R, Anantharaman P (2009) Effect of seaweed liquid fertilizer on growth and pigment concentration of Abelmoschus esculentus (L) Medikus. Amer-Euras J Agronomy 2:57–66
Weiss D, Ori N (2007) Mechanisms of cross talk between gibberellin and other hormones. Plant Physiol 144:1240–1246
Whigham DK (1983) Soybean. In: Smith WH (ed) Symposium on potential productivity of field crops under different environment. IRRI, Los Banos, pp 205–225
Zodape ST, Mukherjee S, Reddy MP, Chaudhary DR (2009) Effect of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty ex silva. Extract on grain quality, yield and some yield components of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Int J Plant Prod 3:97–101
Zodape ST, Mukhopadhyay S, Eswaran S, Reddy MP, Chikara J (2010) Enhanced yield and nutritional quality in greengram (Phaseolus radiata L.) treated with seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) extract. J Sci Ind Res 69:468–471
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, for this project (MLP 0016). We also thank Dr. PK Ghosh for helping conceive this Pan-India multi-institutional multi-crop project and for all his personal encouragement. We also thank sincerely the following: M/s Aquagri Processing Pvt. Ltd. (the licensee of CSIR-Central Salt & Marine Chemicals Research Institute’s sap technology) and CSIR-CSMCRI for providing Kappaphycus sap; the Marine Biotechnology and Ecology discipline, especially Dr. CRK Reddy, Dr. K. Eswaran and Dr. V Mantri for their help in providing Gracilaria sap from Mandapam field station, Tamilnadu, India. Dr. K Prasad is acknowledged for analyzing the sap constituents and Dr. PK Agarwal for all his support. This manuscript bears CSIR-CSMCRI communication No. 052/2015.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Singh, M.K., Pal, S.K. et al. Sustainable enhancement in yield and quality of rain-fed maize through Gracilaria edulis and Kappaphycus alvarezii seaweed sap. J Appl Phycol 28, 2099–2112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0680-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0680-8