Abstract
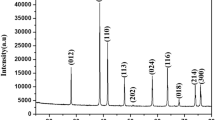
Ferromagnetic Ni–Cr and Co–Cr alloy thin films were electrodeposited from aqueous solution containing trivalent chromium (Cr3+) ions and glycine. According to the Tafel slopes obtained from the cathode polarization curves for Ni–Cr and Co–Cr alloy deposition, it was estimated that Cr3+ ions inhibited Ni2+ and Co2+ ions from electrodepositing. Ni and Co preferentially electrodeposited rather than Cr and the electrodeposition process of Ni–Cr and Co–Cr was categorized to “normal co-deposition type.” At the cathode potential of −1.8 V versus Ag/AgCl/KCl sat., Ni—9.5 %Cr and Co—8.4 %Cr alloy deposits were obtained. X-ray diffraction patterns of the electrodeposits revealed that pure Ni and pure Co consist of large crystal grains, while Ni—9.5 %Cr and Co—8.4 %Cr alloys were composed of a solid solution phase with fine crystal grains. Magnetization of Ni—9.5 %Cr and Co—8.4 %Cr alloy thin films with fine crystalline phase reached to saturation at ca. 2.5 kOe in perpendicular direction to the film plane, while pure Ni and pure Co thin film with large crystal grains were hardly magnetized in the perpendicular direction. Soft magnetic properties were improved with increasing Cr content in the deposits.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoare JP (1979) On the mechanisms of chromium electrodeposition. J Electrochem Soc 126:190–199
Rosas WR, Robin A (2001) Cathodic film formation during chromium electrolysis on low-carbon steel using short duration current steps. J Appl Electrochem 31:531–536
Fontanesi C, Giovanardi R, Cannio M, Soragni E (2008) Chromium electrodeposition from Cr(VI) low concentration solutions. J Appl Electrochem 38:425–436
Drela I, Szynkarczuk J, Kubicki J (1989) Electrodeposition of chromium from Cr(III) electrolytes in the presence of formic acid. J Appl Electrochem 19:933–936
Giovanardi R, Orlando G (2011) Chromium electrodeposition from Cr(III) aqueous solutions. Surf Coat Technol 205:3947–3955
Kang JC, Lalvani SB, Melendres CA (1995) Electrodeposition and characterization of amorphous Fe–Ni–Cr-based alloys. J Appl Electrochem 25:376–383
Song YB, Chin DT (2002) Current efficiency and polarization behavior of trivalent chromium electrodeposition process. Electrochim Acta 48:349–356
Dolati AG, Ghorbani M, Afshar A (2003) The electrodeposition of quaternary Fe–Cr–Ni–Mo alloys from the chloride-complexing agents electrolyte. Part I. Processing. Surf Coat Technol 166:105–110
Protsenko V, Danilov F (2009) Kinetics and mechanism of chromium electrodeposition from formate and oxalate solutions of Cr(III) compounds. Electrochim Acta 54:5666–5672
McDougall J, El-Sharif M, Ma S (1998) Chromium electrodeposition using a chromium(III) glycine complex. J Appl Electrochem 28:929–934
Survilienė S, Nivinskienė O, Češunienė A, Selskis A (2006) Effect of Cr(III) solution chemistry on electrodeposition of chromium. J Appl Electrochem 36:649–654
Danilov FI, Protsenko VS, Gordiienko VO, Kwon SC, Lee JY, Kim M (2011) Nanocrystalline hard chromium electrodeposition from trivalent chromium bath containing carbamide and formic acid: structure, composition, electrochemical corrosion behavior, hardness and wear characteristics of deposits. Appl Surf Sci 257:8048–8053
Protsenko VS, Danilov FI, Gordiienko VO, Kwon SC, Kim M, Lee JY (2011) Electrodeposition of hard nanocrystalline chrome from aqueous sulfate trivalent chromium bath. Thin Solid Films 520:380–383
Howarth JN, Pletcher D (1988) The electrodeposition of chromium from chromium(III) solutions—a study using microelectrodes. J Appl Electrochem 18:644–652
Souza CAC, May JE, Machado AT, Tachard ALR, Bidoia ED (2005) Preparation of Fe–Cr–P–Co amorphous alloys by electrodeposition. Surf Coat Tech 190:75–82
Harris TM, Whitney GM, Croll IM (1995) The electrodeposition of Ni–Fe–Cr alloys for magnetic thin film applications. J Electrochem Soc 142:1031–1034
Stokłosa Z, Kwapuliński P, Rasek J, Badura G, Haneczok G, Pająk L, Lelątko L (2008) Structural relaxation, crystallization and improvement of magnetic properties in FeXSiB (X = Cr, Nb)-type amorphous alloys. J Magn Magn Mater 320:e762–e765
Bas JA, Calero JA, Dougan MJ (2003) Sintered soft magnetic materials: properties and applications. J Magn Magn Mater 254–255:391–398
Brenner A (1963) Electrodeposition of alloys. Academic Press, New York
Hansen M, Anderko K (1958) Constitution of binary alloys. McGraw-Hill, New York
Lin KL, Ho JK (1992) Electrodeposited Ni–Cr and Ni–Cr–P alloys. J Electrochem Soc 139:1305–1310
Li B, Lin A, Wu X, Zhang Y, Gan F (2008) Electrodeposition and characterization of Fe–Cr–P amorphous alloys from trivalent chromium sulfate electrolyte. J Alloys Compd 453:93–101
Pommier J, Meyer P, Penissard G, Ferre J, Bruno P, Renard D (1990) Magnetization reversal in ultrathin ferromagnetic films with perpendicular anisotropy: domain observations. Phys Rev Lett 65:2054–2057
Ohgai T, Enculescu I, Zet C, Westerberg L, Hjort K, Spohr R, Neumann R (2006) Magneto-sensitive nickel nanowires fabricated by electrodeposition into multi- and single-ion track templates. J Appl Electrochem 36:1157–1162
Ohgai T, Hjort K, Spohr R, Neumann R (2008) Electrodeposition of cobalt based ferro-magnetic metal nanowires in polycarbonate films with cylindrical nanochannels fabricated by heavy-ion-track etching. J Appl Electrochem 38:713–719
Spohr R, Zet C, Fischer BE, Kiesewetter H, Apel P, Gunko I, Ohgai T, Westerberg L (2010) Controlled fabrication of ion track nanowires and channels. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res B 268:676–686
Krimpalis S, Dragos OG, Moga AE, Lupu N, Chiriac H (2011) Magnetization processes in electrodeposited NiFe/Cu multilayered nanowires. J Mater Res 26:1081–1090
Kim DJ, Seol JK, Lee MR, Hyung JH, Kim GS, Ohgai T, Lee SK (2012) Ferromagnetic nickel silicide nanowires for isolating primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. Appl Phys Lett 100:163703
Sulitanu N (2001) Structural origin of perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in Ni–W thin films. J Magn Magn Mater 231:85–93
Hernando A, Marin P, Vazquez M, Barandiaran JM, Herzer G (1998) Thermal dependence of coercivity in soft magnetic nanocrystals. Phys Rev B 58:366–370
Lodder JC (1996) Magnetic structures in Co–Cr media for perpendicular magnetic recording. J Magn Magn Mater 159:238–248
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the TDK Corporation, Mitutoyo Association for Science & Technology, Yazaki Memorial Foundation for Science & Technology, Research Foundation for Materials Science, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research C: No. 19560734).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohgai, T., Tanaka, Y. & Fujimaru, T. Soft magnetic properties of Ni–Cr and Co–Cr alloy thin films electrodeposited from aqueous solutions containing trivalent chromium ions and glycine. J Appl Electrochem 42, 893–899 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-012-0472-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-012-0472-7