Abstract
Purpose
This study investigated the levels of interleukin (IL)-8, IL-10, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the aqueous humor (AqH) of patients with Behçet’s uveitis (BU) and Fuchs’ uveitis syndrome (FUS) during an inactive period and compared these levels with those in the AqH of noninflammatory healthy control subjects.
Methods
This prospective and case–control study included 33 patients (16 patients with BU and 17 patients with FUS) and 35 control subjects. IL-8, IL-10, and VEGF levels in the AqH were quantified by performing sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare the cytokine levels in the different groups, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
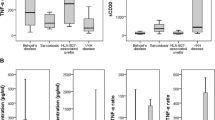
IL-8 levels were significantly higher in the AqH of patients with BU and FUS than in the AqH of control subjects (p < 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively). IL-10 levels were significantly lower in the AqH of patients with BU than in the AqH of patients with FUS and of control subjects (p = 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively). Although VEGF levels were higher in the AqH of patients with FUS than in the AqH of patients with BU and of control subjects, the difference was significant only between patients with FUS and control subjects (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
We observed a significant decrease in IL-10 levels in the AqH of patients with BU and a significant increase in VEGF levels in the AqH of patients with FUS compared to controls. IL-8 and VEGF levels showed no significant difference among uveitis patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oppenheim JJ, Ruscetti FW, Faltynek C (1994) Cytokines. In: Stites DP, Terr AI, Parslow TG (eds) Basic and clinical immunology, 8th edn. Norwalk, Connecticut, pp 105–123
Brocker C, Thompson D, Matsumoto A, Nebert DW, Vasiliou V (2010) Evolutionary divergence and functions of the human interleukin (IL) gene family. Hum Genom 5:30–55
Akdis M, Burgler S, Crameri R, Eiwegger T, Fujita H, Gomez E et al (2011) Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferon-γ: receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127:701–721
Gu C, Wu L, Li X (2013) IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine 64:477–485
Ivashkiv LB, Donlin LT (2014) Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol 14:36–49
Rizzo LV, Xu H, Chan CC, Wiggert B, Caspi RR (1998) IL-10 has a protective role in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Int Immunol 10:807–814
Rosenbaum JT, Angell E (1995) Paradoxical effects of IL-10 in endotoxin-induced uveitis. J Immunol 155:4090–4094
Deschenes J, Char DH, Kaleta S (1988) Activated T lymphocytes in uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 72:83–87
Wang XC, Norose K, Yano A, Ohta K, Segawa K (1995) Two-color flow cytometric analysis of activated T lymphocytes in aqueous humor of patients with endogenous versus exogenous uveitis. Curr Eye Res 14:425–433
Murphy PM (1997) Neutrophil receptors for interleukin-8 and related CXC chemokines. Semin Hematol 34:311–318
Baggiolini M, Walz A, Kunkel SL (1989) Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest 84:1045–1049
Ferrick MR, Thurau SR, Oppenheim MH, Herbort CP, Ni M, Zachariae CO et al (1991) Ocular inflammation stimulated by intravitreal interleukin-8 and interleukin-1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 32:1534–1539
Curnow SJ, Falciani F, Durrani OM, Cheung CM, Ross EJ, Wloka K et al (2005) Multiplex bead immunoassay analysis of aqueous humor reveals distinct cytokine profiles in uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:4251–4259
Sakaguchi M, Sugita S, Sagawa K, Itoh K, Mochizuki M (1998) Cytokine production by T cells infiltrating in the eye of uveitis patients. Jpn J Ophthalmol 42:262–268
Calder VL, Shaer B, Muhaya M, Mclauchlan M, Pearson RV, Jolly G et al (1999) Increased CD4+ expression and decreased IL-10 in the anterior chamber in idiopathic uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:2019–2024
Muhaya M, Calder V, Towler HM, Shaer B, McLauchlan M, Lightman S (1998) Characterization of T cells and cytokines in the aqueous humour (AH) in patients with Fuchs’ heterochromic cyclitis (FHC) and idiopathic anterior uveitis (IAU). Clin Exp Immunol 111:123–128
Ongkosuwito JV, Feron EJ, van Doornik CE, Van der Lelij A, Hoyng CB, La Heij EC et al (1998) Analysis of immunoregulatory cytokines in ocular fluid samples from patients with uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 39:2659–2665
Pepper MS, Ferrara N, Orci L, Montesano R (1991) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in microvascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:902–906
Vinores SA, Chan CC, Vinores MA, Matteson DM, Chen YS, Klein DA et al (1998) Increased vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis: upregulation of VEGF without neovascularization. J Neuroimmunol 89:43–50
Paroli MP, Teodori C, D’Alessandro M, Mariani P, Iannucci G, Paroli M (2007) Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in aqueous humor and serum of patients with quiescent uveitis. Eur J Ophthalmol 17:938–942
International Study Group for Behçet’s Disease (1990) Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet’s disease. Lancet 335:1078–1080
Kimura SJ, Hogan MJ, Thygeson P (1955) Fuchs’ syndrome of heterochromic cyclitis. AMA Arch Ophthalmol 54:179–186
Takase H, Futagami Y, Yoshida T, Kamoi K, Sugita S, Imai Y et al (2006) Cytokine profile in aqueous humor and sera of patients with infectious or noninfectious uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:1557–1561
Sijssens KM, Rijkers GT, Rothova A, Stilma JS, Schellekens PA, de Boer JH (2007) Cytokines, chemokines and soluble adhesion molecules in aqueous humor of children with uveitis. Exp Eye Res 85:443–449
Lacomba MS, Martin CM, Chamond RR, Galera JM, Omar M, Estevez EC (2000) Aqueous and serum interferon gamma, interleukin (IL) 2, IL-4, and IL-10 in patients with uveitis. Arch Ophthalmol 118:768–772
van Kooij B, Rothova A, Rijkers GT, de Groot-Mijnes JD (2006) Distinct cytokine and chemokine profiles in the aqueous of patients with uveitis and cystoid macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol 142:192–194
El-Asrar AM, Struyf S, Kangave D, Al-Obeidan SS, Opdenakker G, Geboes K et al (2011) Cytokine profiles in aqueous humor of patients with different clinical entities of endogenous uveitis. Clin Immunol 139:177–184
Chavis PS, Tabbara KF (1995) Behçet’s disease. Int Ophthalmol Clin 35:43–67
Charteris DG, Barton K, McCartney AC, Lightman SL (1992) CD4+ lymphocyte involvement in ocular Behçet’s disease. Autoimmunity 12:201–206
Ahn JK, Yu HG, Chung H, Park YG (2006) Intraocular cytokine environment in active Behçet uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol 142:429–434
Wallace GR, Kondeatis E, Vaughan RW, Verity DH, Chen Y, Fortune F et al (2007) IL-10 genotype analysis in patients with Behçet’s disease. Hum Immunol 68:122–127
Mizuki N, Meguro A, Ota M, Ohno S, Shiota T, Kawagoe T et al (2010) Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behçet’s disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42:703–706
Remmers EF, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello MJ, Abaci N, Satorius C et al (2010) Genome-wide association study identifies variants in the MCH class I, IL10, and IL23R-IL12RB2 regions associated with Behçet’s disease. Nat Genet 42:698–702
Hill T, Galatowicz G, Akerele T, Lau CH, Calder V, Lightman S (2005) Intracellular T lymphocyte cytokine profiles in the aqueous humour of patients with uveitis and correlation with clinical phenotype. Clin Exp Immunol 139:132–137
Zeilhofer HU, Schorr W (2000) Role of interleukin-8 in neutrophil signaling. Curr Opin Hematol 7:178–182
Valentincic NV, de Groot-Mijnes JD, Kraut A, Korosec P, Hawlina M, Rothova A (2011) Intraocular and serum cytokine profiles in patients with intermediate uveitis. Mol Vis 17:2003–2010
Bae JH, Lee SC (2012) Effect of intravitreal methotrexate and aqueous humor cytokine levels in refractory retinal vasculitis in Behcet disease. Retina 32:1395–1402
El-Asrar AM, Struyf S, Descamps FJ, Al-Obeidan SA, Proost P, Van Damme J et al (2004) Chemokines and gelatinases in the aqueous humor of patients with active uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol 138:401–411
El-Asrar AM, Al-Obeidan SS, Kangave D, Geboes K, Opdenakker G, Van Damme J et al (2011) CXC chemokine expression profiles in aqueous humor of patients with different clinical entities of endogenous uveitis. Immunobiology 216:1004–1009
Bates DO, Hillman NJ, Williams B, Neal CR, Pocock TM (2002) Regulation of microvascular permeability by vascular endothelial growth factors. J Anat 200:581–597
Clavel G, Bessis N, Lemeiter D, Fardellone P, Mejjad O, Ménard JF et al (2007) Angiogenesis markers (VEGF, soluble receptor of VEGF and angiopoietin-1) in very early arthritis and their association with inflammation and joint destruction. Clin Immunol 124:158–164
Erdem F, Gündoğdu M, Kiki I, Ali Sari R, Kiziltunc A (2005) Vascular endothelial and basic fibroblast growth factor serum levels in patients with Behçet’s disease. Rheumatol Int 25:599–603
Fine HF, Baffi J, Reed GF, Csaky KG, Nussenblatt RB (2001) Aqueous humor and plasma vascular endothelial growth factor in uveitis-associated cystoid macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol 132:794–796
Brooks AM, Grant G, Gillies WE (1986) Changes in the iris vasculature and corneal endothelium in chronic cyclitis. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol 14:189–197
Verma LV, Arora R (1990) Clinico-pathologic correlates in Fuchs’ heterochromic iridocyclitis: an iris angiographic study. Indian J Ophthalmol 38:159–161
Acknowledgements
The authors have no financial interest in any materials used in the study.
Funding
The authors have indicated that they have no financial relationships with any company/corporation. This work was supported by Ankara Department of Turkish Ophthalmological Association [Grant Number 2015-144].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simsek, M., Cakar Ozdal, P., Akbiyik, F. et al. Aqueous humor IL-8, IL-10, and VEGF levels in Fuchs’ uveitis syndrome and Behçet’s uveitis. Int Ophthalmol 39, 2629–2636 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-019-01112-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-019-01112-w