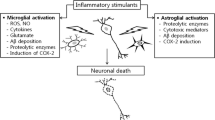
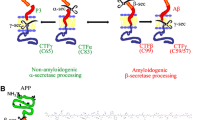
Abstract
It has become increasingly clear that inflammatory processes play a significant role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Neuroinflammation is characterized by the activation of astrocytes and microglia and the release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Vascular inflammation, mediated largely by the products of endothelial activation, is accompanied by the production and the release of a host of inflammatory factors which contribute to vascular, immune, and neuronal dysfunction. The complex interaction of these processes is still only imperfectly understood, yet as the mechanisms continue to be elucidated, targets for intervention are revealed. Although many of the studies to date on therapeutic or preventative strategies for AD have been narrowly focused on single target therapies, there is accumulating evidence to suggest that the most successful treatment strategy will likely incorporate a sequential, multifactorial approach, addressing direct neuronal support, general cardiovascular health, and interruption of deleterious inflammatory pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- AChE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- AChEI:
-
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- AGE:
-
Advanced glycation end product
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- AICD:
-
Amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain
- BACE-1:
-
β-Site APP cleaving enzyme 1
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CD14:
-
Cluster of differentiation 14
- COX:
-
Cyclooxygenase
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- GLUT-1:
-
Glucose tansporter-1
- GLT-1:
-
Glutamate transporter-1
- GSK:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase
- HPC:
-
Hippocampal progenitor cell
- Hcy:
-
Homocysteine
- 4-HNE:
-
4-Hydroxynonenal
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IFNγ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IP-10:
-
Interferon-γ induced protein-10
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- KO:
-
Knockout
- LRP-1:
-
LDL-receptor related protein-1
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- MCSF:
-
Macrophage colony stimulating factor
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MAP:
-
Microtubule-associated protein
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- MLK-3:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemotactic protein-1
- NFT:
-
Neurofibrillary tangle
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartic acid
- NALP3:
-
NACHT/LRR/PYD domains-containing protein 3
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- nNOS:
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NSAID:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ
- PS-1:
-
Presenilin-1
- PGE2:
-
Prostaglandin E2
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RAGE:
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end product
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TSP:
-
Thrombospondin
- TIMP-1:
-
Tissue inhibitor of MMP
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell-adhesion molecule
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Abbott NJ, Revest PA, Romero IA (1992) Astrocyte-endothelial interaction: physiology and pathology. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18(5):424–433
Abramov AY, Canevari L, Duchen MR (2004) Calcium signals induced by amyloid beta peptide and their consequences in neurons and astrocytes in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta 1742(1–3):81–87
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16(25):2766–2778
Akiyama H, Arai T, Kondo H, Tanno E, Haga C, Ikeda K (2000) Cell mediators of inflammation in the Alzheimer disease brain. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 14(Suppl 1):S47–S53
Alexander CL, Fitzgerald UF, Barnett SC (2002) Identification of growth factors that promote long-term proliferation of olfactory ensheathing cells and modulate their antigenic phenotype. Glia 37(4):349–364
Aliev G, Smith MA, Obrenovich ME, de la Torre JC, Perry G (2003) Role of vascular hypoperfusion-induced oxidative stress and mitochondria failure in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Neurotox Res 5(7):491–504
Aliyev A, Seyidova D, Rzayev N, Obrenovich ME, Lamb BT, Chen SG, Smith MA, Perry G, de la Torre JC, Aliev G (2004) Is nitric oxide a key target in the pathogenesis of brain lesions during the development of Alzheimer’s disease? Neurol Res 26(5):547–553
Altman R, Rutledge JC (2010) The vascular contribution to Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 119(10):407–421
Alzheimer A (1991) A contribution concerning the pathological anatomy of mental disturbances in old age, 1899. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 5(2):69–70
Anisman H (2009) Cascading effects of stressors and inflammatory immune system activation: implications for major depressive disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 34(1):4–20
Arbour NC, Lorenz E, Schutte BC, Zabner J, Kline JN, Jones M, Frees K, Watt JL, Schwartz DA (2000) TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet 25(2):187–191
Ard MD, Cole GM, Wei J, Mehrle AP, Fratkin JD (1996) Scavenging of Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-protein by microglia in culture. J Neurosci Res 43(2):190–202
Attwell D, Laughlin SB (2001) An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21(10):1133–1145
Avila J, Wandosell F, Hernandez F (2010) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors. Expert Rev Neurother 10(5):703–710
Bading JR, Yamada S, Mackic JB, Kirkman L, Miller C, Calero M, Ghiso J, Frangione B, Zlokovic BV (2002) Brain clearance of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta40 in the squirrel monkey: a SPECT study in a primate model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Drug Target 10(4):359–368
Bales KR, Tzavara ET, Wu S, Wade MR, Bymaster FP, Paul SM, Nomikos GG (2006) Cholinergic dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease is reversed by an anti-A beta antibody. J Clin Invest 116(3):825–832
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(9):663–672
Banati RB, Gehrmann J, Schubert P, Kreutzberg GW (1993) Cytotoxicity of microglia. Glia 7(1):111–118
Barbagallo AP, Weldon R, Tamayev R, Zhou D, Giliberto L, Foreman O, D’Adamio L (2010) Tyr(682) in the intracellular domain of APP regulates amyloidogenic APP processing in vivo. PLoS One 5(11):e15503
Barger SW, Harmon AD (1997) Microglial activation by Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein and modulation by apolipoprotein E. Nature 388(6645):878–881
Bate C, Veerhuis R, Eikelenboom P, Williams A (2004) Microglia kill amyloid-beta1-42 damaged neurons by a CD14-dependent process. Neuroreport 15(9):1427–1430
Bate C, Kempster S, Williams A (2006) Prostaglandin D2 mediates neuronal damage by amyloid-beta or prions which activates microglial cells. Neuropharmacology 50(2):229–237
Baum L, Lam CW, Cheung SK, Kwok T, Lui V, Tsoh J, Lam L, Leung V, Hui E, Ng C, Woo J, Chiu HF, Goggins WB, Zee BC, Cheng KF, Fong CY, Wong A, Mok H, Chow MS, Ho PC, Ip SP, Ho CS, Yu XW, Lai CY, Chan MH, Szeto S, Chan IH, Mok V (2008) Six-month randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, pilot clinical trial of curcumin in patients with Alzheimer disease. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28(1):110–113
Bell RD, Zlokovic BV (2009) Neurovascular mechanisms and blood-brain barrier disorder in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 118(1):103–113
Bell RD, Sagare AP, Friedman AE, Bedi GS, Holtzman DM, Deane R, Zlokovic BV (2007) Transport pathways for clearance of human Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide and apolipoproteins E and J in the mouse central nervous system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(5):909–918
Benarroch EE (2005) Neuron-astrocyte interactions: partnership for normal function and disease in the central nervous system. Mayo Clin Proc 80(10):1326–1338
Berthiaume EP, Medina C, Swanson JA (1995) Molecular size-fractionation during endocytosis in macrophages. J Cell Biol 129(4):989–998
Beurel E, Michalek SM, Jope RS (2010) Innate and adaptive immune responses regulated by glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3). Trends Immunol 31(1):24–31
Bilikiewicz A, Gaus W (2004) Colostrinin (a naturally occurring, proline-rich, polypeptide mixture) in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 6(1):17–26
Birks J, Grimley Evans J (2009) Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD003120
Blach-Olszewska Z, Leszek J (2007) Mechanisms of over-activated innate immune system regulation in autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 3(3):365–372
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69
Blum-Degen D, Muller T, Kuhn W, Gerlach M, Przuntek H, Riederer P (1995) Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s and de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 202(1–2):17–20
Bolanos JP, Almeida A, Stewart V, Peuchen S, Land JM, Clark JB, Heales SJ (1997) Nitric oxide-mediated mitochondrial damage in the brain: mechanisms and implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 68(6):2227–2240
Breitner JC, Haneuse SJ, Walker R, Dublin S, Crane PK, Gray SL, Larson EB (2009) Risk of dementia and AD with prior exposure to NSAIDs in an elderly community-based cohort. Neurology 72(22):1899–1905
Brenn A, Grube M, Peters M, Fischer A, Jedlitschky G, Kroemer HK, Warzok RW, Vogelgesang S (2011) Beta-amyloid downregulates MDR1-P-glycoprotein (Abcb1) expression at the blood-brain barrier in mice. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:690121
Brewer GJ (1997) Effects of acidosis on the distribution of processing of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol Chem Neuropathol 31(2):171–186
Brown GC, Bal-Price A (2003) Inflammatory neurodegeneration mediated by nitric oxide, glutamate, and mitochondria. Mol Neurobiol 27(3):325–355
Bruno MA, Mufson EJ, Wuu J, Cuello AC (2009) Increased matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity in mild cognitive impairment. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68(12):1309–1318
Calabrese V, Bates TE, Stella AM (2000) NO synthase and NO-dependent signal pathways in brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders: the role of oxidant/antioxidant balance. Neurochem Res 25(9–10):1315–1341
Calabrese V, Sultana R, Scapagnini G, Guagliano E, Sapienza M, Bella R, Kanski J, Pennisi G, Mancuso C, Stella AM, Butterfield DA (2006) Nitrosative stress, cellular stress response, and thiol homeostasis in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(11–12):1975–1986
Calabrese V, Mancuso C, Calvani M, Rizzarelli E, Butterfield DA, Stella AM (2007) Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(10):766–775
Carlsson CM (2010) Type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 20(3):711–722
Chalbot S, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Fladby T, Andreasen N, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K (2011) Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier permeability in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 25(3):505–515
Chen Y, Vartiainen NE, Ying W, Chan PH, Koistinaho J, Swanson RA (2001) Astrocytes protect neurons from nitric oxide toxicity by a glutathione-dependent mechanism. J Neurochem 77(6):1601–1610
Cho JY, Um HS, Kang EB, Cho IH, Kim CH, Cho JS, Hwang DY (2010) The combination of exercise training and alpha-lipoic acid treatment has therapeutic effects on the pathogenic phenotypes of Alzheimer’s disease in NSE/APPsw-transgenic mice. Int J Mol Med 25(3):337–346
Combs CK, Johnson DE, Karlo JC, Cannady SB, Landreth GE (2000) Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease: inhibition of beta-amyloid-stimulated proinflammatory responses and neurotoxicity by PPARgamma agonists. J Neurosci 20(2):558–567
Combs CK, Karlo JC, Kao SC, Landreth GE (2001) beta-Amyloid stimulation of microglia and monocytes results in TNFalpha-dependent expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 21(4):1179–1188
Contestabile A, Fila T, Bartesaghi R, Contestabile A, Ciani E (2006) Choline acetyltransferase activity at different ages in brain of Ts65Dn mice, an animal model for Down’s syndrome and related neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 97(2):515–526
Craft JM, Watterson DM, Van Eldik LJ (2006) Human amyloid beta-induced neuroinflammation is an early event in neurodegeneration. Glia 53(5):484–490
Cullheim S, Thams S (2007) The microglial networks of the brain and their role in neuronal network plasticity after lesion. Brain Res Rev 55(1):89–96
Danysz W, Parsons CG (1998) Glycine and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors: physiological significance and possible therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Rev 50(4):597–664
Davies TA, Billingslea AM, Long HJ, Tibbles H, Wells JM, Eisenhauer PB, Smith SJ, Cribbs DH, Fine RE, Simons ER (1998) Brain endothelial cell enzymes cleave platelet-retained amyloid precursor protein. J Lab Clin Med 132(4):341–350
Deane R, Du Yan S, Submamaryan RK, LaRue B, Jovanovic S, Hogg E, Welch D, Manness L, Lin C, Yu J, Zhu H, Ghiso J, Frangione B, Stern A, Schmidt AM, Armstrong DL, Arnold B, Liliensiek B, Nawroth P, Hofman F, Kindy M, Stern D, Zlokovic B (2003) RAGE mediates amyloid-beta peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med 9(7):907–913
Deane R, Wu Z, Zlokovic BV (2004) RAGE (yin) versus LRP (yang) balance regulates alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide clearance through transport across the blood-brain barrier. Stroke 35(11 Suppl 1):2628–2631
Desai BS, Schneider JA, Li JL, Carvey PM, Hendey B (2009) Evidence of angiogenic vessels in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 116(5):587–597
Dong XX, Wang Y, Qin ZH (2009) Molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity and their relevance to pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30(4):379–387
Drzezga A, Lautenschlager N, Siebner H, Riemenschneider M, Willoch F, Minoshima S, Schwaiger M, Kurz A (2003) Cerebral metabolic changes accompanying conversion of mild cognitive impairment into Alzheimer’s disease: a PET follow-up study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30(8):1104–1113
Edison P, Archer HA, Gerhard A, Hinz R, Pavese N, Turkheimer FE, Hammers A, Tai YF, Fox N, Kennedy A, Rossor M, Brooks DJ (2008) Microglia, amyloid, and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease: an [11C](R)PK11195-PET and [11C]PIB-PET study. Neurobiol Dis 32(3):412–419
Eikelenboom P, van Gool WA (2004) Neuroinflammatory perspectives on the two faces of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 111(3):281–294
El-Fawal HA, O’Callaghan JP (2008) Autoantibodies to neurotypic and gliotypic proteins as biomarkers of neurotoxicity: assessment of trimethyltin (TMT). Neurotoxicology 29(1):109–115
Ellis RJ, Olichney JM, Thal LJ, Mirra SS, Morris JC, Beekly D, Heyman A (1996) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: the CERAD experience, Part XV. Neurology 46(6):1592–1596
Engel T, Hernandez F, Avila J, Lucas JJ (2006) Full reversal of Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotype in a mouse model with conditional overexpression of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Neurosci 26(19):5083–5090
Faraci FM (2003) Hyperhomocysteinemia: a million ways to lose control. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23(3):371–373
Fiebich BL, Schleicher S, Spleiss O, Czygan M, Hull M (2001) Mechanisms of prostaglandin E2-induced interleukin-6 release in astrocytes: possible involvement of EP4-like receptors, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase C. J Neurochem 79(5):950–958
Fioravanzo L, Venturini M, Liddo RD, Marchi F, Grandi C, Parnigotto PP, Folin M (2010) Involvement of rat hippocampal astrocytes in beta-amyloid-induced angiogenesis and neuroinflammation. Curr Alzheimer Res 7(7):591–601
Freemantle E, Vandal M, Tremblay-Mercier J, Tremblay S, Blachere JC, Begin ME, Brenna JT, Windust A, Cunnane SC (2006) Omega-3 fatty acids, energy substrates, and brain function during aging. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 75(3):213–220
Fuller S, Steele M, Munch G (2010) Activated astroglia during chronic inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease—do they neglect their neurosupportive roles? Mutat Res 690(1–2):40–49
Furchgott RF (1999) Endothelium-derived relaxing factor: discovery, early studies, and identification as nitric oxide. Biosci Rep 19(4):235–251
Galimberti D, Scarpini E (2011) Disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 4(4):203–216
Gallucci M, Zanardo A, De Valentin L, Vianello A (2004) Homocysteine in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl 9:195–200
Galluzzi KE, Appelt DM, Balin BJ (2010) Modern care for patients with Alzheimer disease: rationale for early intervention. J Am Osteopath Assoc 110(9 Suppl 8):S37–S42
Garwood CJ, Pooler AM, Atherton J, Hanger DP, Noble W (2011) Astrocytes are important mediators of Abeta-induced neurotoxicity and tau phosphorylation in primary culture. Cell Death Dis 2:e167
Gearing M, Mirra SS, Hedreen JC, Sumi SM, Hansen LA, Heyman A (1995) The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part X. Neuropathology confirmation of the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 45(3 Pt 1):461–466
Ghosal K, Stathopoulos A, Pimplikar SW (2010) APP intracellular domain impairs adult neurogenesis in transgenic mice by inducing neuroinflammation. PLoS One 5(7):e11866
Grammas P, Samany PG, Thirumangalakudi L (2006) Thrombin and inflammatory proteins are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease microvessels: implications for disease pathogenesis. J Alzheimers Dis 9(1):51–58
Granzotto A, Zatta P (2011) Resveratrol acts not through anti-aggregative pathways but mainly via its scavenging properties against Abeta and Abeta-metal complexes toxicity. PLoS One 6(6):e21565
Griffin WS, Stanley LC, Ling C, White L, MacLeod V, Perrot LJ, White CL 3rd, Araoz C (1989) Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(19):7611–7615
Guglielmotto M, Aragno M, Tamagno E, Vercellinatto I, Visentin S, Medana C, Catalano MG, Smith MA, Perry G, Danni O, Boccuzzi G, Tabaton M (2010) AGEs/RAGE complex upregulates BACE1 via NF-kappaB pathway activation. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.026
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Moore KJ, Golenbock DT (2008) The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol 9(8):857–865
Hashioka S, Klegeris A, Schwab C, McGeer PL (2009) Interferon-gamma-dependent cytotoxic activation of human astrocytes and astrocytoma cells. Neurobiol Aging 30(12):1924–1935
Hayden KM, Zandi PP, Khachaturian AS, Szekely CA, Fotuhi M, Norton MC, Tschanz JT, Pieper CF, Corcoran C, Lyketsos CG, Breitner JC, Welsh-Bohmer KA (2007) Does NSAID use modify cognitive trajectories in the elderly? The Cache County study. Neurology 69(3):275–282
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK (2007) Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 184(1–2):69–91
Hensley K, Maidt ML, Yu Z, Sang H, Markesbery WR, Floyd RA (1998) Electrochemical analysis of protein nitrotyrosine and dityrosine in the Alzheimer brain indicates region-specific accumulation. J Neurosci 18(20):8126–8132
Hermann C, Stern RG, Losonzcy MF, Jaff S, Davidson M (1991) Diagnostic and pharmacological approaches in Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Aging 1(2):144–162
Hernandez F, Borrell J, Guaza C, Avila J, Lucas JJ (2002) Spatial learning deficit in transgenic mice that conditionally over-express GSK-3beta in the brain but do not form tau filaments. J Neurochem 83(6):1529–1533
Hollenberg NK (2006) Organ systems dependent on nitric oxide and the potential for nitric oxide-targeted therapies in related diseases. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 8(12 Suppl 4):63–73
Hoozemans JJ, Rozemuller JM, van Haastert ES, Veerhuis R, Eikelenboom P (2008) Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in the different stages of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Curr Pharm Des 14(14):1419–1427
Huell M, Strauss S, Volk B, Berger M, Bauer J (1995) Interleukin-6 is present in early stages of plaque formation and is restricted to the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol 89(6):544–551
Hwang J, Hwang H, Lee HW, Suk K (2010) Microglia signaling as a target of donepezil. Neuropharmacology 58(7):1122–1129
Iadecola C (2004) Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(5):347–360
Iadecola C, Zhang F, Niwa K, Eckman C, Turner SK, Fischer E, Younkin S, Borchelt DR, Hsiao KK, Carlson GA (1999) SOD1 rescues cerebral endothelial dysfunction in mice overexpressing amyloid precursor protein. Nat Neurosci 2(2):157–161
Ince P, Xuereb J, MacKenzie J, Rossi M, Lowe J, Morris HJ, Matthews F, Brayne C, Esiri MM (2000) Neuropathology of a community sample of elderly demented and nondemented people. Brain Pathol 10:591–593. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00310.x
Iqbal K, Alonso Adel C, Chen S, Chohan MO, El-Akkad E, Gong CX, Khatoon S, Li B, Liu F, Rahman A, Tanimukai H, Grundke-Iqbal I (2005) Tau pathology in Alzheimer disease and other tauopathies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1739(2–3):198–210
Isaac MG, Quinn R, Tabet N (2008) Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3):CD002854
Jana A, Pahan K (2010) Fibrillar amyloid-beta-activated human astroglia kill primary human neurons via neutral sphingomyelinase: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 30(38):12676–12689
Ji Y, Permanne B, Sigurdsson EM, Holtzman DM, Wisniewski T (2001) Amyloid beta40/42 clearance across the blood-brain barrier following intra-ventricular injections in wild-type, apoE knock-out and human apoE3 or E4 expressing transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 3(1):23–30
Kalaria RN, Grahovac I (1990) Serum amyloid P immunoreactivity in hippocampal tangles, plaques and vessels: implications for leakage across the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 516(2):349–353
Kar S, Slowikowski SP, Westaway D, Mount HT (2004) Interactions between beta-amyloid and central cholinergic neurons: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29(6):427–441
Kawahara M, Ohtsuka I, Yokoyama S, Kato-Negishi M, Sadakane Y (2011) Membrane incorporation, channel formation, and disruption of calcium homeostasis by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid protein. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:304583
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M, Verkhratsky A (2011) Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev 91(2):461–553
Kihara T, Shimohama S (2004) Alzheimer’s disease and acetylcholine receptors. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 64(1):99–105
Klapstein GJ, Colmers WF (1997) Neuropeptide Y suppresses epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Neurophysiol 78(3):1651–1661
Klapstein GJ, Levine MS (2005) Age-dependent biphasic changes in ischemic sensitivity in the striatum of Huntington’s disease R6/2 transgenic mice. J Neurophysiol 93(2):758–765
Klempin F, Kempermann G (2007) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and aging. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257(5):271–280
Koenigsknecht-Talboo J, Landreth GE (2005) Microglial phagocytosis induced by fibrillar beta-amyloid and IgGs are differentially regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. J Neurosci 25(36):8240–8249
Kovac A, Zilkova M, Deli MA, Zilka N, Novak M (2009) Human truncated tau is using a different mechanism from amyloid-beta to damage the blood-brain barrier. J Alzheimers Dis 18(4):897–906
Krause DL, Muller N (2010) Neuroinflammation, microglia and implications for anti-inflammatory treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2010:732806. doi:10.4061/2010/732806
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19(8):312–318
Krishnan S, Cairns R, Howard R (2009) Cannabinoids for the treatment of dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2):CD007204
Kuiper MA, Teerlink T, Visser JJ, Bergmans PL, Scheltens P, Wolters EC (2000) l-glutamate, l-arginine and l-citrulline levels in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy, and Alzheimer’s disease patients. J Neural Transm 107(2):183–189
Landreth GE, Reed-Geaghan EG (2009) Toll-like receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 336:137–153
Lee RK, Knapp S, Wurtman RJ (1999) Prostaglandin E2 stimulates amyloid precursor protein gene expression: inhibition by immunosuppressants. J Neurosci 19(3):940–947
Lee H, Kim HJ, Kim JM, Chang N (2004) Effects of dietary folic acid supplementation on cerebrovascular endothelial dysfunction in rats with induced hyperhomocysteinemia. Brain Res 996(2):139–147
Lee KS, Chung JH, Choi TK, Suh SY, Oh BH, Hong CH (2009) Peripheral cytokines and chemokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 28(4):281–287
Leszek J, Inglot AD, Janusz M, Lisowski J, Krukowska K, Georgiades JA (1999) Colostrinin: a proline-rich polypeptide (PRP) complex isolated from ovine colostrum for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 47(6):377–385
Levine MS, Klapstein GJ, Koppel A, Gruen E, Cepeda C, Vargas ME, Jokel ES, Carpenter EM, Zanjani H, Hurst RS, Efstratiadis A, Zeitlin S, Chesselet MF (1999) Enhanced sensitivity to N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor activation in transgenic and knockin mouse models of Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci Res 58(4):515–532
Li J, Schmidt AM (1997) Characterization and functional analysis of the promoter of RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation end products. J Biol Chem 272(26):16498–16506
Li S, Mallory M, Alford M, Tanaka S, Masliah E (1997) Glutamate transporter alterations in Alzheimer disease are possibly associated with abnormal APP expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56(8):901–911
Li J, Wu HM, Zhou RL, Liu GJ, Dong BR (2008) Huperzine A for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2):CD005592
Lindesay J, Bullock R, Daniels H, Emre M, Forstl H, Frolich L, Gabryelewicz T, Martinez-Lage P, Monsch AU, Tsolaki M, van Laar T (2010) Turning principles into practice in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Clin Pract 64(9):1198–1209
Lipton SA, Kim WK, Choi YB, Kumar S, D’Emilia DM, Rayudu PV, Arnelle DR, Stamler JS (1997) Neurotoxicity associated with dual actions of homocysteine at the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(11):5923–5928
Liu Y, Walter S, Stagi M, Cherny D, Letiembre M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Heine H, Penke B, Neumann H, Fassbender K (2005) LPS receptor (CD14): a receptor for phagocytosis of Alzheimer’s amyloid peptide. Brain 128(Pt 8):1778–1789
Lucas JJ, Hernandez F, Gomez-Ramos P, Moran MA, Hen R, Avila J (2001) Decreased nuclear beta-catenin, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration in GSK-3beta conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J 20(1–2):27–39
Lue LF, Brachova L, Civin WH, Rogers J (1996) Inflammation, A beta deposition, and neurofibrillary tangle formation as correlates of Alzheimer’s disease neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55(10):1083–1088
Luo J, Grammas P (2010) Endothelin-1 is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease brain microvessels and is neuroprotective. J Alzheimers Dis 21(3):887–896
Maccioni RB, Rojo LE, Fernandez JA, Kuljis RO (2009) The role of neuroimmunomodulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1153:240–246
Mackic JB, Weiss MH, Miao W, Kirkman E, Ghiso J, Calero M, Bading J, Frangione B, Zlokovic BV (1998) Cerebrovascular accumulation and increased blood-brain barrier permeability to circulating Alzheimer’s amyloid beta peptide in aged squirrel monkey with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J Neurochem 70(1):210–215
Majumdar A, Cruz D, Asamoah N, Buxbaum A, Sohar I, Lobel P, Maxfield FR (2007) Activation of microglia acidifies lysosomes and leads to degradation of Alzheimer amyloid fibrils. Mol Biol Cell 18(4):1490–1496
Malouf R, Grimley Evans J (2008) Folic acid with or without vitamin B12 for the prevention and treatment of healthy elderly and demented people. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4):CD004514
Martin BK, Szekely C, Brandt J, Piantadosi S, Breitner JC, Craft S, Evans D, Green R, Mullan M (2008) Cognitive function over time in the Alzheimer’s Disease Anti-inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT): results of a randomized, controlled trial of naproxen and celecoxib. Arch Neurol 65(7):896–905
Matsuoka Y, Picciano M, Malester B, LaFrancois J, Zehr C, Daeschner JM, Olschowka JA, Fonseca MI, O’Banion MK, Tenner AJ, Lemere CA, Duff K (2001) Inflammatory responses to amyloidosis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 158(4):1345–1354
Mayeux R, Tang MX, Jacobs DM, Manly J, Bell K, Merchant C, Small SA, Stern Y, Wisniewski HM, Mehta PD (1999) Plasma amyloid beta-peptide 1–42 and incipient Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 46(3):412–416
Mayeux R, Honig LS, Tang MX, Manly J, Stern Y, Schupf N, Mehta PD (2003) Plasma A[beta]40 and A[beta]42 and Alzheimer’s disease: relation to age, mortality, and risk. Neurology 61(9):1185–1190
McAdam BF, Catella-Lawson F, Mardini IA, Kapoor S, Lawson JA, FitzGerald GA (1999) Systemic biosynthesis of prostacyclin by cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: the human pharmacology of a selective inhibitor of COX-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(1):272–277
McGeer EG, McGeer PL (2003) Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27(5):741–749
McShane R, Areosa Sastre A, Minakaran N (2006) Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2):CD003154
Mielke R, Kessler J, Szelies B, Herholz K, Wienhard K, Heiss WD (1998) Normal and pathological aging—findings of positron-emission-tomography. J Neural Transm 105(8–9):821–837
Mines MA, Beurel E, Jope RS (2011) Regulation of cell survival mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease by glycogen synthase kinase-3. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:861072. doi:10.4061/2011/861072
Minoretti P, Gazzaruso C, Vito CD, Emanuele E, Bianchi M, Coen E, Reino M, Geroldi D (2006) Effect of the functional toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly polymorphism on susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 391(3):147–149
Mondragon-Rodriguez S, Basurto-Islas G, Lee HG, Perry G, Zhu X, Castellani RJ, Smith MA (2010) Causes versus effects: the increasing complexities of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Expert Rev Neurother 10(5):683–691
Montine TJ, Sidell KR, Crews BC, Markesbery WR, Marnett LJ, Roberts LJ 2nd, Morrow JD (1999) Elevated CSF prostaglandin E2 levels in patients with probable AD. Neurology 53(7):1495–1498
Moore AH, O’Banion MK (2002) Neuroinflammation and anti-inflammatory therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54(12):1627–1656
Morley JE, Farr SA, Banks WA, Johnson SN, Yamada KA, Xu L (2010) A physiological role for amyloid-beta protein: enhancement of learning and memory. J Alzheimers Dis 19(2):441–449
Moser KV, Reindl M, Blasig I, Humpel C (2004) Brain capillary endothelial cells proliferate in response to NGF, express NGF receptors and secrete NGF after inflammation. Brain Res 1017(1–2):53–60
Mundy DI (1994) Identification of the multicatalytic enzyme as a possible gamma-secretase for the amyloid precursor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 204(1):333–341
Nagele RG, D’Andrea MR, Lee H, Venkataraman V, Wang HY (2003) Astrocytes accumulate A beta 42 and give rise to astrocytic amyloid plaques in Alzheimer disease brains. Brain Res 971(2):197–209
Nathan C, Calingasan N, Nezezon J, Ding A, Lucia MS, La Perle K, Fuortes M, Lin M, Ehrt S, Kwon NS, Chen J, Vodovotz Y, Kipiani K, Beal MF (2005) Protection from Alzheimer’s-like disease in the mouse by genetic ablation of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Exp Med 202(9):1163–1169
Nitsch RM, Slack BE, Wurtman RJ, Growdon JH (1992) Release of Alzheimer amyloid precursor derivatives stimulated by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Science 258(5080):304–307
O’Banion MK, Miller JC, Chang JW, Kaplan MD, Coleman PD (1996) Interleukin-1 beta induces prostaglandin G/H synthase-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) in primary murine astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem 66(6):2532–2540
Okamoto M, Wang X, Baba M (2005) HIV-1-infected macrophages induce astrogliosis by SDF-1alpha and matrix metalloproteinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336(4):1214–1220
Orrego F, Villanueva S (1993) The chemical nature of the main central excitatory transmitter: a critical appraisal based upon release studies and synaptic vesicle localization. Neuroscience 56(3):539–555
Paresce DM, Chung H, Maxfield FR (1997) Slow degradation of aggregates of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-protein by microglial cells. J Biol Chem 272(46):29390–29397
Paris D, Townsend KP, Humphrey J, Obregon DF, Yokota K, Mullan M (2002a) Statins inhibit A beta-neurotoxicity in vitro and A beta-induced vasoconstriction and inflammation in rat aortae. Atherosclerosis 161(2):293–299
Paris D, Townsend KP, Obregon DF, Humphrey J, Mullan M (2002b) Pro-inflammatory effect of freshly solubilized beta-amyloid peptides in the brain. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 70(1–2):1–12
Park SA, Shaked GM, Bredesen DE, Koo EH (2009) Mechanism of cytotoxicity mediated by the C31 fragment of the amyloid precursor protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388(2):450–455
Perry VH, Newman TA, Cunningham C (2003) The impact of systemic infection on the progression of neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(2):103–112
Persson M, Brantefjord M, Hansson E, Ronnback L (2005) Lipopolysaccharide increases microglial GLT-1 expression and glutamate uptake capacity in vitro by a mechanism dependent on TNF-alpha. Glia 51(2):111–120
Phiel CJ, Wilson CA, Lee VM, Klein PS (2003) GSK-3alpha regulates production of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides. Nature 423(6938):435–439
Plant LD, Boyle JP, Smith IF, Peers C, Pearson HA (2003) The production of amyloid beta peptide is a critical requirement for the viability of central neurons. J Neurosci 23(13):5531–5535
Pooler AM, Arjona AA, Lee RK, Wurtman RJ (2004) Prostaglandin E2 regulates amyloid precursor protein expression via the EP2 receptor in cultured rat microglia. Neurosci Lett 362(2):127–130
Puzzo D, Privitera L, Fa M, Staniszewski A, Hashimoto G, Aziz F, Sakurai M, Ribe EM, Troy CM, Mercken M, Jung SS, Palmeri A, Arancio O (2011) Endogenous amyloid-beta is necessary for hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory. Ann Neurol 69(5):819–830
Qaseem A, Snow V, Cross JT Jr, Forciea MA, Hopkins R Jr, Shekelle P, Adelman A, Mehr D, Schellhase K, Campos-Outcalt D, Santaguida P, Owens DK (2008) Current pharmacologic treatment of dementia: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Ann Intern Med 148(5):370–378
Reed-Geaghan EG, Savage JC, Hise AG, Landreth GE (2009) CD14 and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are required for fibrillar A{beta}-stimulated microglial activation. J Neurosci 29(38):11982–11992
Reisberg B, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Mobius HJ (2003) Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 348(14):1333–1341
Remarque EJ, Bollen EL, Weverling-Rijnsburger AW, Laterveer JC, Blauw GJ, Westendorp RG (2001) Patients with Alzheimer’s disease display a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Exp Gerontol 36(1):171–176
Ringman JM, Frautschy SA, Cole GM, Masterman DL, Cummings JL (2005) A potential role of the curry spice curcumin in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2(2):131–136
Rodriguez JJ, Olabarria M, Chvatal A, Verkhratsky A (2009) Astroglia in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ 16(3):378–385
Rogers J, Shen Y (2000) A perspective on inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 924:132–135
Roher AE, Lowenson JD, Clarke S, Woods AS, Cotter RJ, Gowing E, Ball MJ (1993) beta-Amyloid-(1–42) is a major component of cerebrovascular amyloid deposits: implications for the pathology of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(22):10836–10840
Sabbagh M, Cummings J (2011) Progressive cholinergic decline in Alzheimer’s disease: consideration for treatment with donepezil 23 mg in patients with moderate to severe symptomatology. BMC Neurol 11:21
Sadowski M, Pankiewicz J, Scholtzova H, Li YS, Quartermain D, Duff K, Wisniewski T (2004) Links between the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Neurochem Res 29(6):1257–1266
Sastre M, Walter J, Gentleman SM (2008) Interactions between APP secretases and inflammatory mediators. J Neuroinflammation 5:25
Schmitz ML, Mattioli I, Buss H, Kracht M (2004) NF-kappaB: a multifaceted transcription factor regulated at several levels. Chembiochem 5(10):1348–1358
Schneider LS (2000) A critical review of cholinesterase inhibitors as a treatment modality in Alzheimer’s disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2(2):111–128
Schubert P, Morino T, Miyazaki H, Ogata T, Nakamura Y, Marchini C, Ferroni S (2000) Cascading glia reactions: a common pathomechanism and its differentiated control by cyclic nucleotide signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 903:24–33
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81(2):741–766
Seshadri S (2006) Elevated plasma homocysteine levels: risk factor or risk marker for the development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease? J Alzheimers Dis 9(4):393–398
Shibata M, Yamada S, Kumar SR, Calero M, Bading J, Frangione B, Holtzman DM, Miller CA, Strickland DK, Ghiso J, Zlokovic BV (2000) Clearance of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta(1–40) peptide from brain by LDL receptor-related protein-1 at the blood-brain barrier. J Clin Invest 106(12):1489–1499
Shih AY, Erb H, Sun X, Toda S, Kalivas PW, Murphy TH (2006) Cystine/glutamate exchange modulates glutathione supply for neuroprotection from oxidative stress and cell proliferation. J Neurosci 26(41):10514–10523
Shors TJ, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M, Rydel T, Gould E (2001) Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 410(6826):372–376
Simard AR, Rivest S (2004) Bone marrow stem cells have the ability to populate the entire central nervous system into fully differentiated parenchymal microglia. FASEB J 18(9):998–1000
Simonian NA, Coyle JT (1996) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:83–106
Simpson JE, Ince PG, Haynes LJ, Theaker R, Gelsthorpe C, Baxter L, Forster G, Lace GL, Shaw PJ, Matthews FE, Savva GM, Brayne C, Wharton SB (2010) Population variation in oxidative stress and astrocyte DNA damage in relation to Alzheimer-type pathology in the ageing brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36(1):25–40
Skovronsky DM, Lee VM, Pratico D (2001) Amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta peptide in human platelets. Role of cyclooxygenase and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 276(20):17036–17043
Small GW, Ercoli LM, Silverman DH, Huang SC, Komo S, Bookheimer SY, Lavretsky H, Miller K, Siddarth P, Rasgon NL, Mazziotta JC, Saxena S, Wu HM, Mega MS, Cummings JL, Saunders AM, Pericak-Vance MA, Roses AD, Barrio JR, Phelps ME (2000) Cerebral metabolic and cognitive decline in persons at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(11):6037–6042
Smith WL, Garavito RM, DeWitt DL (1996) Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases (cyclooxygenases)-1 and -2. J Biol Chem 271(52):33157–33160
Snowdon DA, Greiner LH, Mortimer JA, Riley KP, Greiner PA, Markesbery WR (1997) Brain infarction and the clinical expression of Alzheimer disease. The Nun Study. JAMA 277(10):813–817
Snyder JS, Hong NS, McDonald RJ, Wojtowicz JM (2005) A role for adult neurogenesis in spatial long-term memory. Neuroscience 130(4):843–852
Tahara K, Kim HD, Jin JJ, Maxwell JA, Li L, Fukuchi K (2006) Role of toll-like receptor signalling in Abeta uptake and clearance. Brain 129(Pt 11):3006–3019
Takahashi RH, Milner TA, Li F, Nam EE, Edgar MA, Yamaguchi H, Beal MF, Xu H, Greengard P, Gouras GK (2002) Intraneuronal Alzheimer abeta42 accumulates in multivesicular bodies and is associated with synaptic pathology. Am J Pathol 161(5):1869–1879
Takashima A, Noguchi K, Sato K, Hoshino T, Imahori K (1993) Tau protein kinase I is essential for amyloid beta-protein-induced neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(16):7789–7793
Takatori Y (2006) Mechanisms of neuroprotective effects of therapeutic acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Yakugaku Zasshi 126(8):607–616
Tan J, Town T, Paris D, Mori T, Suo Z, Crawford F, Mattson MP, Flavell RA, Mullan M (1999) Microglial activation resulting from CD40-CD40L interaction after beta-amyloid stimulation. Science 286(5448):2352–2355
Tang BL (2009) Neuronal protein trafficking associated with Alzheimer disease: from APP and BACE1 to glutamate receptors. Cell Adh Migr 3(1):118–128
Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Xu X, Cheng A, Mughal MR, Jo DG, Lathia JD, Siler DA, Chigurupati S, Ouyang X, Magnus T, Camandola S, Mattson MP (2007) Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(34):13798–13803
Tang SC, Lathia JD, Selvaraj PK, Jo DG, Mughal MR, Cheng A, Siler DA, Markesbery WR, Arumugam TV, Mattson MP (2008) Toll-like receptor-4 mediates neuronal apoptosis induced by amyloid beta-peptide and the membrane lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Exp Neurol 213(1):114–121
Tanzi RE, Moir RD, Wagner SL (2004) Clearance of Alzheimer’s Abeta peptide: the many roads to perdition. Neuron 43(5):605–608
Tariot PN, Farlow MR, Grossberg GT, Graham SM, McDonald S, Gergel I (2004) Memantine treatment in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease already receiving donepezil: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291(3):317–324
Thirumangalakudi L, Samany PG, Owoso A, Wiskar B, Grammas P (2006) Angiogenic proteins are expressed by brain blood vessels in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 10(1):111–118
Triantafilou M, Morath S, Mackie A, Hartung T, Triantafilou K (2004) Lateral diffusion of Toll-like receptors reveals that they are transiently confined within lipid rafts on the plasma membrane. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 17):4007–4014
Troen AM (2005) The central nervous system in animal models of hyperhomocysteinemia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29(7):1140–1151
Udan ML, Ajit D, Crouse NR, Nichols MR (2008) Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 mediate Abeta(1–42) activation of the innate immune response in a human monocytic cell line. J Neurochem 104(2):524–533
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415(6875):1030–1034
Vehmas AK, Kawas CH, Stewart WF, Troncoso JC (2003) Immune reactive cells in senile plaques and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):321–331
Vicenzini E, Ricciardi MC, Altieri M, Puccinelli F, Bonaffini N, Di Piero V, Lenzi GL (2007) Cerebrovascular reactivity in degenerative and vascular dementia: a transcranial Doppler study. Eur Neurol 58(2):84–89
Wakasa S, Shiiya N, Tachibana T, Ooka T, Matsui Y (2009) A semiquantitative analysis of reactive astrogliosis demonstrates its correlation with the number of intact motor neurons after transient spinal cord ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 137(4):983–990
Walter S, Letiembre M, Liu Y, Heine H, Penke B, Hao W, Bode B, Manietta N, Walter J, Schulz-Schuffer W, Fassbender K (2007) Role of the toll-like receptor 4 in neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Physiol Biochem 20(6):947–956
Wang DD, Bordey A (2008) The astrocyte odyssey. Prog Neurobiol 86(4):342–367
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, Al-Abed Y, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2003) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 421(6921):384–388
Wang JM, Singh C, Liu L, Irwin RW, Chen S, Chung EJ, Thompson RF, Brinton RD (2010) Allopregnanolone reverses neurogenic and cognitive deficits in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(14):6498–6503
Warner DS, Sheng H, Batinic-Haberle I (2004) Oxidants, antioxidants and the ischemic brain. J Exp Biol 207(Pt 18):3221–3231
Watkins PB, Zimmerman HJ, Knapp MJ, Gracon SI, Lewis KW (1994) Hepatotoxic effects of tacrine administration in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA 271(13):992–998
Weir DG, Molloy AM (2000) Microvascular disease and dementia in the elderly: are they related to hyperhomocysteinemia? Am J Clin Nutr 71(4):859–860
Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Struble RG, Clark AW, Coyle JT, Delon MR (1982) Alzheimer’s disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science 215(4537):1237–1239
Willard LB, Hauss-Wegrzyniak B, Danysz W, Wenk GL (2000) The cytotoxicity of chronic neuroinflammation upon basal forebrain cholinergic neurons of rats can be attenuated by glutamatergic antagonism or cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition. Exp Brain Res 134(1):58–65
Wirths O, Multhaup G, Bayer TA (2004) A modified beta-amyloid hypothesis: intraneuronal accumulation of the beta-amyloid peptide—the first step of a fatal cascade. J Neurochem 91(3):513–520
Wolfson C, Perrault A, Moride Y, Esdaile JM, Abenhaim L, Momoli F (2002) A case-control analysis of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and Alzheimer’s disease: are they protective? Neuroepidemiology 21(2):81–86
Wu HM, Tzeng NS, Qian L, Wei SJ, Hu X, Chen SH, Rawls SM, Flood P, Hong JS, Lu RB (2009) Novel neuroprotective mechanisms of memantine: increase in neurotrophic factor release from astroglia and anti-inflammation by preventing microglial activation. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(10):2344–2357
Xiao XQ, Wang R, Tang XC (2000) Huperzine A and tacrine attenuate beta-amyloid peptide-induced oxidative injury. J Neurosci Res 61(5):564–569
Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1996) RAGE and amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 382(6593):685–691
Yan SF, Yan SD, Ramasamy R, Schmidt AM (2009) Tempering the wrath of RAGE: an emerging therapeutic strategy against diabetic complications, neurodegeneration, and inflammation. Ann Med 41(6):408–422
Yang F, Lim GP, Begum AN, Ubeda OJ, Simmons MR, Ambegaokar SS, Chen PP, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2005) Curcumin inhibits formation of amyloid beta oligomers and fibrils, binds plaques, and reduces amyloid in vivo. J Biol Chem 280(7):5892–5901
Yermakova AV, O’Banion MK (2001) Downregulation of neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 expression in end stage Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22(6):823–836
Yokoyama A, Yang L, Itoh S, Mori K, Tanaka J (2004) Microglia, a potential source of neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Glia 45(1):96–104
Yoshiyama Y, Kojima A, Ishikawa C, Arai K (2010) Anti-inflammatory action of donepezil ameliorates tau pathology, synaptic loss, and neurodegeneration in a tauopathy mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis 22(1):295–306
Zhang D, Hu X, Qian L, Wilson B, Lee C, Flood P, Langenbach R, Hong JS (2009) Prostaglandin E2 released from activated microglia enhances astrocyte proliferation in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(1):64–70
Zlokovic BV, Yamada S, Holtzman D, Ghiso J, Frangione B (2000) Clearance of amyloid beta-peptide from brain: transport or metabolism? Nat Med 6(7):718–719
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broussard, G.J., Mytar, J., Li, Rc. et al. The role of inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacol 20, 109–126 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-012-0130-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-012-0130-z
Keywords
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Inflammation
- Neuron
- Neuronal
- Astrocyte
- Microglia
- Cardiovascular
- Microvessels
- Vascular
- Endothelial
- Cytokine
- Chemokine
- Immune
- Neurodegenerative
- Aβ
- Amyloid
- β-amyloid
- Pathogenesis
- Pathology
- Reactive oxygen species
- Reactive nitrogen species
- Interleukin
- Blood–brain barrier
- Cyclooxygenase
- Inflammatory mediators
- Activated endothelium