Abstract
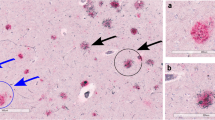
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) immunoreactivity has previously been shown in plaques in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and elevated IL-6 concentrations have been measured biochemically in brains of AD patients. In this study, we investigated the appearance of IL-6 immunoreactivity in AD plaques according to the stage of plaque formation. Using the Bielschowsky silver-staining method, we were able to differentiate between four types of plaques described earlier: diffuse, primitive, classic and compact. While diffuse plaques represent the early stage of plaque formation, primitive and classic plaques are thought to represent later stages of plaque development. We investigated serial sections of paraffin-embedded cortices of ten clinically diagnosed and histopathologically confirmed AD patients and ten patients with no clinical history of dementia. We found plaques in the brains of both nondemented and demented persons using the silver staining method or immunohistochemistry with antibodies against the amyloid precursor protein. In the group of clinically nondemented persons, diffuse plaques were the predominant plaque type, whereas primitive plaques formed the larger portion of lesions in the group of AD brains. IL-6 could not be detected in plaques of patients without dementia. Many IL-6-positive plaques were found in six of the AD brains and to a smaller extent in the other four AD cases. In the six cases with a large number of IL-6-positive plaques, IL-6 was found in a significantly higher ratio of diffuse plaques than expected from a random distribution of IL-6 in all plaque types. We conclude from these findings that IL-6 immunoreactivity correlates with clinical dementia and that in AD patients, an IL-6-related immunological event may contribute to plaque formation. IL-6 might be involved both in the transformation from diffuse to primitive plaques in AD as well as in the development of dementia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham CR, Selkoe DJ, Potter H (1988) Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell 52:487–501
Aisen PS, Davis KL (1994) Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease: implications for therapy. Am J Psychiatry 151:1105–1113
Altstiel L, Sperper K (1991) Cytokines in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15:481–495
Araujo DM, Cotman CW (1992) β-Amyloid stimulates glial cells in vitro to produce growth factors that accumulate in senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 569:141–145
Bancher C, Braak H, Fischer P, Jellinger KA (1993) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer lesions and intellectual status in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease patients. Neurosci Lett 162:179–182
Bauer J (1989) Interleukin-6 and its receptor during homeostasis, inflammation and tumor growth. Klin Wochenschr 67:697–706
Bauer J, Herrmann F (1991) Interleukin-6 in clinical medicine. Ann Hematol 62:203–213
Bauer J, Strauss S, Schreiter-Gasser U, Ganter U, Schlegel P, Witt I, Volk B, Berger M (1991) Interleukin-6 and α2-macroglobulin indicate and acute phase state in Alzheimer's disease cortices. FEBS Lett 285:111–114
Bauer J, Ganter U, Abel J, Strauss S, Jonas U, Weiss R, Gebicke-Haerter P, Volk B, Berger M (1993) Effects of interleukin 1 and interleukin 6 on metallothionin and amyloid precursor protein expression in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neuroimmunol 45:163–173
Baumann H, Gauldie J (1994) The acute phase response. Immunol Today 15:74–80
Berg L, McKeel DWJ, Miller JP, Baty J, Morris JC (1993) Neuropathological indexes of Alzheimer's disease in demented and nondemented persons aged 80 years and older. Arch Neurol 50:349–358
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Bugiani O, Giaccone G, Verga L, Pollo B, Ghetti B, Frangione B, Tagliavini F (1990) Alzheimer patients and Down-patients: abnormal presynaptic terminals are related to cerebral preamyloid deposits. Neurosci Lett 119:56–59
Campbell IL, Abraham CR, Masliah E, Kemper P, Inglis JD, Oldstone MBA, Mucke L (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10061–10065
Cras P, Kawai M, Lowery D, Gonzalez DeWhitt P, Greenberg B, Perry G (1991) Senile plaque neurites in Alzheimer disease accumulate amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7552–7556
Crystal HA, Dickson DW, Sliwinski MJ, Lipton RB, Grober E, Marks-Nelson H, Antis P (1993) Pathological markers associated with normal aging and dementia in the elderly. Ann Neurol 34:1682–1687
DeKosky ST, Scheff SW (1990) Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer's disease. correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol 27:457–464
Delaere P, Duyckaerts C, He Y, Piette F, Hauw JJ (1991) Subtypes and differential laminar distributions of βA4 deposits in Alzheimer's disease: relationship with the intellectual status of 26 cases. Acta Neuropathol 81:328–335
Ershler WB (1993) Interleukin-6: a cytokine for gerontologists. J Am Geriatr Soc 41:176–181
Friedland RP, May C, Dahlberg J (1990) The viral hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 47:177–178
Gadient RA, Otten U (1994) Expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) mRNAs in rat brain during postnatal development. Brain Res 637:10–14
Gallo P, Frei K, Rordorf C, Lazdins J, Tavolta B, Fontana A (1989) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the central nervous system: an evaluation of cytokines in the cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 23:109–116
Gottschall PE, Tatsuno I, Arimura A (1994) Regulation of interleukin 6 (IL-6) secretion in primary cultured rat astrocytes: synergism of interleukin 1 (IL-1) and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP). Brain Res 637:197–203
Greenamyre JT, Young AB (1989) Excitatory amino acids in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 10:593–602
Haga S, Ikeda K, Sato M, Ishii T (1993) Synthetic Alzheimer amyloid βA4 peptides enhance production of complement c3 component by cultured microglial cells. Brain Res 601:88–94
Hager K, Machein U, Krieger L, Seefried G, Bauer J (1994) Plasma concentrations of interleukin-6 and selected plasma proteins in healthy persons of different ages. Neurobiol Aging 15:771–772
Halliday G, Flowers D, Baum L (1994) Analysis of staining methods for different cortical plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 87:174–188
Helfgott DC, Tatter SB, Santhanam U, Clarick RH, Bhardwaj N, May L, Seghal BP (1989) Multiple forms of IFN-β2/IL-6 in serum and body fluids during acute bacterial infection. J Immunol 142:948–953
Ikeda S, Glenner GG (1989) Morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases. Lab Invest 60:113–122
Ikeda S, Yanagisawa N, Allsop D, Glenner GG (1990) Early senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease demonstrated by histochemistry, immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy. Hum Pathol 21:1221–1226
Jellinger K, Bancher C, Fischer P, Lassmann H (1992) Quantitative histopathologic validation of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Eur J Gerontol 3:146–156
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42:1097–1104
Laurenzi MA, Siden A, Persson MA, Norkrans G, Hageberg L, Chiodi F (1990) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 activity in HIV infection and inflammatory and non-inflammatory diseases of the nervous system. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 57:233–241
Mackenzie IRA (1994) Senile plaques do not progressively accumulate with normal aging. Acta Neuropathol 87:520–525
Masliah E, Terry RD, Mallory M, Alford M, Hansen LA (1990) Diffuse plaques do not accentuate synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 137:1293–1297
McGeer PL, Akiyama H, Itagaki S, McGeer EG (1989) Activation of the classical complement pathway in brain tissue of Alzheimer patients. Neurosci Lett 107:341–346
Mirra SS, Hart MN, Terry RD (1993) Making the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 117:132–144
Probst A, Brunnschweiler H, Lautenschlager C, Ulrich J (1987) A special type of senil plaque possibly an initial stage. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:133–141
Roberts GW, Gentleman SM, Lynch A, Murray L, Landon M, Graham DI (1994) β-Amyloid protein deposition in the brain after severe head injury: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:419–425
Rozemuller JM, Eikelenboom P, Stam FC, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (1989) A4 protein in Alzheimer's disease: primary and secondary cellular events in extracellular amyloid depositin. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:674–691
Rozemuller JM, Stam FC, Eikelenboom P (1990) Acute phase proteins are present in amorphous plaques in the cerebral but not in the cerebellar cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 119:75–78
Rozemuller JM, Abbink JJ, Kamp AM, Stam FC, Hack CE, Eikelenboom P (1991) Distribution pattern and functional state of a1-antichymotrypsin in plaques and vascular amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 82:200–207
Schöbitz B, de Kloet RE, Sutanto W, Holsboer R (1993) Cellular localisation of interleukin 6 mRNA and interleukin 6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 5:1426–1435
Sparks DL, Liu H, Scheff SW, Coyne CM, Hunsaker JC (1993) Temporal sequence of plaque formation in the cerebral cortex of non-demented individuals. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:135–142
Strauss S, Bauer J, Ganter U, Jonas U, Berger M, Vok B (1992) Detection of interleukin-6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin immunoreactivity in cortex and hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease patients. Lab Invest 66:223–230
Terry RD, Maliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, Hansen LA, Katzman R (1991) Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss in the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 30:572–580
Walker DG, McGeer PL (1993) Complement gene expression in neuroblastoma and astrocytoma cell lines of human origin. Neurosci Lett 157:99–102
Wisniewski HM, Terry RD (1973) Reexamination of the pathogenesis of the senile plaque. Prog Neuropathol 2:1–26
Wisniewski HM, Bancher C, Barcikowska M, Wen GY, Currie J (1989) Spectrum of morphological appearance of amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 78:337–347
Wisniewski HM, Wen GY, Kim KS (1989) Comparison of four staining methods on the detection of neuritic plaques. Acta Neuropathol 78:22–27
Wood JA, Wood PL, Ryan R, Graff-Radford NR, Pilapil C, Robitaille Y, Quirion R (1993) Cytokine indices in Alzheimer's temporal cortex: no changes in mature IL-1 beta or IL-1 RA but increases in the associated acute phase proteins IL-6, alphy-2-macroglobulin and C-reactive protein. Brain Res 629:245–252
Yamaguchi H, Haga C, Hirai S, Nakazato Y, Kosaka K (1990) Distinctive, rapid, and easy labeling of diffuse plaques in the Alzheimer brains by a new methenamine silver stain. Acta Neuropathol 79:569–572
Yamaguchi H, Nakazato Y, Shoji M, Takatama M, Hirai S (1991) Ultrastructure of diffuse plaques in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type: comparison with primitive plaques. Acta Neuropathol 82:13–20
Yamamoto T, Hirano A (1986) A comparative study by modified Bielschowsky, Bodian and thioflavin S stains on Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:3–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huell, M., Strauss, S., Volk, B. et al. Interleukin-6 is present in early stages of plaque formation and is restricted to the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. Acta Neuropathol 89, 544–551 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571510
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571510